Expiring Drug Patents Cheat Sheet
We analyse the patents covering drugs in 134 countries and quickly give you the likely loss-of-exclusivity/generic entry date
Montenegro: These 5 Drugs Face Patent Expirations and Generic Entry From 2025 - 2026
The content of this page is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

Generic Entry Dates in Other Countries
Friedman, Yali, "Montenegro: These 5 Drugs Face Patent Expirations and Generic Entry From 2025 - 2026" DrugPatentWatch.com thinkBiotech, 2025 www.drugpatentwatch.com/p/expiring-drug-patents-generic-entry/.
Media collateral
These estimated drug patent expiration dates and generic entry opportunity dates are calculated from analysis of known patents covering drugs. Many factors can influence early or late generic entry. This information is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source. The methodology is described in this blog post.
When can XIFAXAN (rifaximin) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: rifaximin
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: February 27, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Montenegro Patent P34408
Patent Title: NOVI POLIMORFNI OBLICI RIFAKSIMINA, POSTUPAK NJIHOVE PROIZVODNJE I NJIHOVA UPOTREBA U MEDICINSKIM PREPARATIMA (NEW POLYMORPHOUS FORMS OF RIFAXIMIN, PROCESSES FOR THEIR PRODUCTION AND USE THEREOF IN THE MEDICINAL)
This drug has two hundred and nineteen patent family members in forty-one countries. There has been litigation on patents covering XIFAXAN
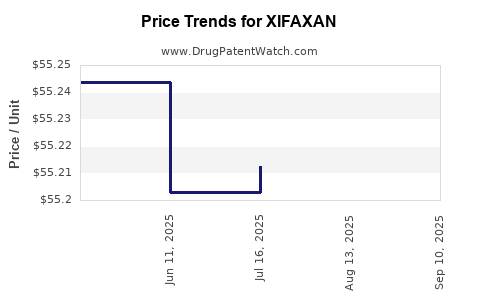
See drug price trends for XIFAXAN.
The generic ingredient in XIFAXAN is rifaximin. There are fourteen drug master file entries for this API. Three suppliers are listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the rifaximin profile page.
When can TRADJENTA (linagliptin) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: linagliptin
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: May 04, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Montenegro Patent 1,170
This drug has four hundred and eighty-six patent family members in forty-five countries. There has been litigation on patents covering TRADJENTA
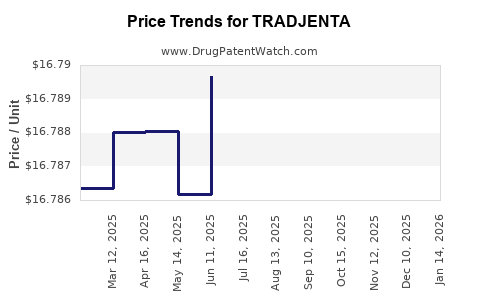
See drug price trends for TRADJENTA.
The generic ingredient in TRADJENTA is linagliptin. There are nineteen drug master file entries for this API. Three suppliers are listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the linagliptin profile page.
When can TRADJENTA (linagliptin) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: linagliptin
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: May 04, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Montenegro Patent 1,941

This drug has four hundred and eighty-six patent family members in forty-five countries. There has been litigation on patents covering TRADJENTA
See drug price trends for TRADJENTA.
The generic ingredient in TRADJENTA is linagliptin. There are nineteen drug master file entries for this API. Three suppliers are listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the linagliptin profile page.
When can RASUVO (methotrexate) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: methotrexate
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: July 21, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Montenegro Patent 1,940
This drug has twenty-nine patent family members in twenty-one countries. There has been litigation on patents covering RASUVO
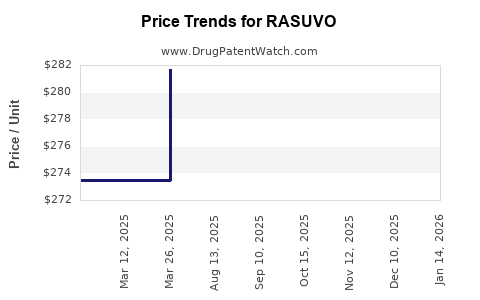
See drug price trends for RASUVO.
The generic ingredient in RASUVO is methotrexate. There are twenty drug master file entries for this API. Four suppliers are listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the methotrexate profile page.
When can OLYSIO (simeprevir sodium) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: simeprevir sodium
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: July 28, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Montenegro Patent 1,231
Patent Title: Makrociklički inhibitori virusa hepatitisa C (MACROCYCLIC INHIBITORS OF HEPATITIS C VIRUS)
OLYSIO is a drug marketed by Janssen Prods. There are nine patents protecting this drug.
This drug has one hundred and forty patent family members in forty-three countries.
See drug price trends for OLYSIO.
The generic ingredient in OLYSIO is simeprevir sodium. There is one drug master file entry for this API. Additional details are available on the simeprevir sodium profile page.
When can OLYSIO (simeprevir sodium) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: simeprevir sodium
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: July 28, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Montenegro Patent 2,415
Patent Title: Intermedijari za pripremu makrocikličkih inhibitora virusa hepatitisa C (Intermediates for the preparation of Macrocyclic inhibitors of hepatitis c virus)
OLYSIO is a drug marketed by Janssen Prods. There are nine patents protecting this drug.
This drug has one hundred and forty patent family members in forty-three countries.
See drug price trends for OLYSIO.
The generic ingredient in OLYSIO is simeprevir sodium. There is one drug master file entry for this API. Additional details are available on the simeprevir sodium profile page.
When can LYRICA CR (pregabalin) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: pregabalin
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: October 23, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Montenegro Patent 482
Patent Title: ČVRSTE FARMACEUTSKE KOMPOZICIJE KOJE SADRŽE PREGABALIN SREDSTVO ZA FORMIRANJE MATRIKSA I SREDSTVO ZA BUBRENJE (SOLID ORAL PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS FOR ONCE DAILY DOSING CONTAINING PREGABALIN, A MATRIX FORMING AGENT AND A SWELLING AGENT)

This drug has thirty-seven patent family members in thirty-three countries.
See drug price trends for LYRICA CR.
The generic ingredient in LYRICA CR is pregabalin. There are forty-one drug master file entries for this API. Fifty-four suppliers are listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the pregabalin profile page.
Montenegro Branded and Generic Drug Markets: Assessment, Regulatory Opportunities, and Challenges
More… ↓
DrugPatentWatch cited by CNN, NEJM, Nature Journals, and more …

Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
