Expiring Drug Patents Cheat Sheet
We analyse the patents covering drugs in 134 countries and quickly give you the likely loss-of-exclusivity/generic entry date
Nicaragua: These 4 Drugs Face Patent Expirations and Generic Entry From 2025 - 2026
The content of this page is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

Generic Entry Dates in Other Countries
Friedman, Yali, "Nicaragua: These 4 Drugs Face Patent Expirations and Generic Entry From 2025 - 2026" DrugPatentWatch.com thinkBiotech, 2025 www.drugpatentwatch.com/p/expiring-drug-patents-generic-entry/.
Media collateral
These estimated drug patent expiration dates and generic entry opportunity dates are calculated from analysis of known patents covering drugs. Many factors can influence early or late generic entry. This information is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source. The methodology is described in this blog post.
When can LASTACAFT (alcaftadine) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: alcaftadine
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: March 31, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Nicaragua Patent 200,800,261
Patent Title: TRATAMIENTOS DE ALERGIA OCULAR
This drug has forty-six patent family members in thirty countries. There has been litigation on patents covering LASTACAFT
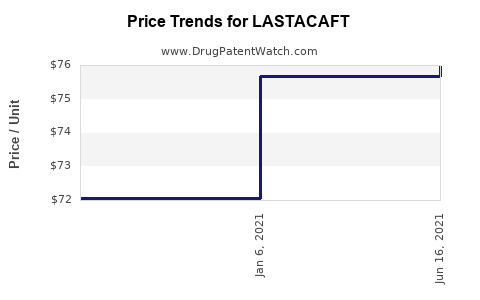
See drug price trends for LASTACAFT.
The generic ingredient in LASTACAFT is alcaftadine. There are six drug master file entries for this API. Four suppliers are listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the alcaftadine profile page.
When can INVOKAMET (canagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: canagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: December 04, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Nicaragua Patent 200,900,113
Patent Title: FORMA CRISTALINA DEL HEMIHIDRATO DE 1-(Beta-D-GLUCOPIRANOSIL)-4-METIL-3-[5-(4-FLUOROFENIL)-2-TIENILMETIL] BENCENO.
This drug has two hundred and seventy-one patent family members in forty-eight countries. There has been litigation on patents covering INVOKAMET
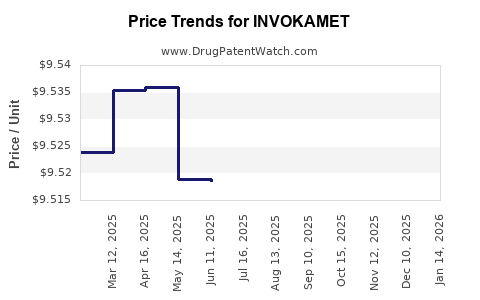
See drug price trends for INVOKAMET.
The generic ingredient in INVOKAMET is canagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride. There are twenty-one drug master file entries for this API. One supplier is listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the canagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride profile page.
When can INVOKAMET XR (canagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: canagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: December 04, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Nicaragua Patent 200,900,113
Patent Title: FORMA CRISTALINA DEL HEMIHIDRATO DE 1-(Beta-D-GLUCOPIRANOSIL)-4-METIL-3-[5-(4-FLUOROFENIL)-2-TIENILMETIL] BENCENO.
This drug has two hundred and twenty patent family members in forty-five countries. There has been litigation on patents covering INVOKAMET XR
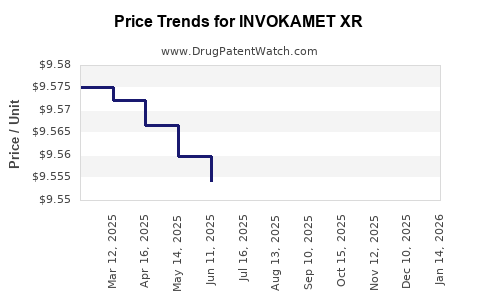
See drug price trends for INVOKAMET XR.
The generic ingredient in INVOKAMET XR is canagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride. There are twenty-one drug master file entries for this API. One supplier is listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the canagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride profile page.
When can INVOKANA (canagliflozin) generic drug versions launch?
Generic name: canagliflozin
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Key Patent Expiration / Generic Entry Date: December 04, 2026
Generic Entry Controlled by: Nicaragua Patent 200,900,113
Patent Title: FORMA CRISTALINA DEL HEMIHIDRATO DE 1-(Beta-D-GLUCOPIRANOSIL)-4-METIL-3-[5-(4-FLUOROFENIL)-2-TIENILMETIL] BENCENO.
This drug has two hundred and twenty patent family members in forty-five countries. There has been litigation on patents covering INVOKANA
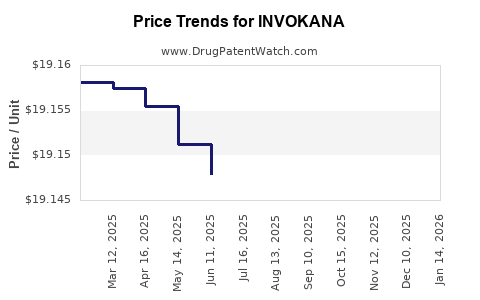
See drug price trends for INVOKANA.
The generic ingredient in INVOKANA is canagliflozin. There are twenty-one drug master file entries for this API. Three suppliers are listed for this generic product. Additional details are available on the canagliflozin profile page.
Nicaragua Branded and Generic Drug Markets: Assessment, Regulatory Opportunities, and Challenges
More… ↓
DrugPatentWatch cited by CNN, NEJM, Nature Journals, and more …

Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
