1. Introduction:
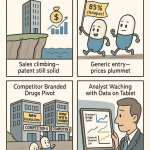
Generic drugs are indispensable for maintaining affordable and accessible healthcare systems globally. These medications, which are cost-effective alternatives to brand-name drugs, typically offer savings of 80-85%.1 Their crucial role lies in expanding medication access and reducing the financial burden on patients and healthcare systems alike.1 In the United States, generic drugs constitute a significant proportion of all prescriptions dispensed, with estimates reaching as high as 91% in 2022 2, and even 88.6% according to some data 3, demonstrating a widespread reliance on these lower-cost options. Despite this high volume of utilization, generic drugs account for a considerably smaller share of the total pharmaceutical expenditure, for instance, around 26% of total drug costs 4 or less than 20% of the overall spending according to other sources.3 This discrepancy underscores the substantial cost savings that generics provide to the healthcare system, even as brand-name and specialty drugs contribute more significantly to the overall spending figures. The high usage rates also suggest a strong acceptance of generic medications by both patients and prescribers, highlighting their importance in controlling healthcare costs while ensuring broad access to necessary treatments.
The pricing of generic drugs is a complex process influenced by a multitude of factors and involves various stakeholders. Considerations such as profitability, ethical obligations, the intensity of market competition, government regulations, and the intricacies of supply chain logistics all play a critical role in determining the final price of these medications.5 Generic drug companies employ a range of pricing strategies, including approaches based on cost, market conditions, and sales volume.8 Furthermore, government regulations and healthcare policies exert a substantial influence on how generic drugs are priced.8 Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs), key players in the pharmaceutical supply chain, also significantly impact pricing through their operational practices.1 The intricate interplay of these diverse elements and the involvement of numerous stakeholders create a complex ecosystem that governs the pricing of generic drugs. A thorough understanding of these dynamics is therefore essential for manufacturers, policymakers, payers, and patients to ensure a sustainable and affordable supply of these crucial medications.
This report aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the various strategies employed in pricing generic drugs. It will delve into the key factors that exert influence over these pricing strategies, offering a detailed examination of their impact. Additionally, the report will explore the effects of market dynamics, regulatory environments, and international comparisons on the prices of generic drugs. The ultimate objective is to develop a nuanced understanding of the complexities inherent in generic drug pricing, identify potential challenges that exist within the market, and suggest possible future directions for ensuring a stable and affordable supply of these essential medicines.
2. Foundational Pricing Strategies in the Generic Pharmaceutical Market:
Generic pharmaceutical companies utilize several foundational pricing strategies to determine the cost of their medications. These strategies often reflect the unique characteristics of the generic market, which is typically marked by high competition and a focus on cost efficiency.
Cost-Based Pricing: A primary method employed by generic manufacturers is cost-based pricing. This strategy involves calculating the total expenses associated with producing the medication, encompassing the costs of raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, and other production-related expenditures.8 Generic companies frequently adopt this approach to ensure that the selling price adequately covers their production costs and allows for a reasonable profit margin.8 Given the emphasis on efficiency and the absence of substantial research and development expenses typically associated with brand-name drugs, cost-based pricing offers a transparent and straightforward way for generic manufacturers to establish their prices. However, this method may not always fully account for the prevailing market competition or the perceived value of the medication, potentially leading to pricing that is not optimally aligned with market conditions.
Market-Based Pricing: Another significant strategy in the generic market is market-based pricing. This approach involves setting prices by carefully considering the prices of similar products that are already available to consumers.8 Companies utilizing this strategy will closely monitor what their competitors are charging for comparable generic medications and adjust their own pricing accordingly.8 Market-based pricing is particularly prevalent among small and medium-sized pharmaceutical companies operating in the generic space.8 To gain a competitive edge and capture a larger share of the market, generic companies often adopt aggressive competitive pricing tactics.31 This can involve either matching the prices offered by competitors or strategically undercutting them to attract price-sensitive customers.30 Given the intense competition that typically arises after the expiration of patents, market-based pricing becomes a critical factor in determining the success of a generic drug in the marketplace. Manufacturers must maintain a keen awareness of competitor pricing to effectively position their products and remain competitive.
Value-Based Pricing: While value-based pricing, which sets the price of a product based on its perceived effectiveness and the benefits it offers 6, is a common strategy for innovative pharmaceutical companies with novel drugs 8, its direct applicability to generic drugs is generally limited.1 This is primarily because generic medications are by definition copies of existing brand-name drugs and do not typically offer unique therapeutic benefits. However, certain adaptations of value-based pricing might find relevance in specific niches within the generic market. For instance, the “mortgage model,” a variation that allows purchasers to distribute the cost of expensive therapies over an extended period 30, could potentially be applied to complex generics or biosimilars that offer substantial advantages over older, less sophisticated generic versions. In such cases, while not a direct application of traditional value-based pricing, elements focusing on improved patient outcomes or cost savings for the healthcare system might influence pricing considerations for these more advanced generic products.
Volume-Based Pricing: Another foundational strategy employed in the pharmaceutical industry, including by some generic manufacturers, is volume-based pricing.6 This approach operates on the principle that the price per unit of a product decreases as the volume of products sold increases.8 This strategy is often favored by large pharmaceutical companies that have the infrastructure and capacity to achieve high sales volumes.8 In the context of generic drugs, manufacturers with established distribution networks and the ability to produce medications on a large scale can leverage volume-based pricing to achieve economies of scale. By lowering the per-unit cost through high production volumes, these companies can offer competitive prices while still maintaining profitability. Furthermore, financial risk-based contracts and health outcomes contracts can sometimes incorporate volume considerations, where pricing adjustments are tied to the quantity of medication used or the number of patients treated.6
| Pricing Strategy | Description | Typical Users | Advantages | Limitations |
| Cost-Based Pricing | Price set based on production expenses (raw materials, labor, overhead) | Generic pharmaceutical companies | Transparent, ensures cost recovery and profit margin | May not fully account for market competition or perceived value |
| Market-Based Pricing | Price set by considering competitor pricing for similar products | Small and medium-sized pharmaceutical companies | Highly competitive, allows for strategic positioning within the market | Requires constant monitoring of competitor prices |
| Value-Based Pricing | Price linked to perceived effectiveness and benefits of the product | Innovative pharmaceutical companies | Captures the value of unique benefits | Limited applicability to standard generics, more relevant for complex generics or biosimilars with advantages |
| Volume-Based Pricing | Price per unit decreases with increasing sales volume | Large pharmaceutical companies | Achieves economies of scale, allows for competitive pricing at high volumes | Requires significant production capacity and established distribution networks |
3. Regulatory and Market-Driven Pricing Mechanisms:
Beyond the foundational pricing strategies employed by individual companies, the pricing of generic drugs is significantly shaped by various regulatory and market-driven mechanisms. These mechanisms often aim to balance affordability, promote competition, and ensure the sustainability of the generic drug market.
Reference Pricing: A common regulatory tool used in many countries to manage the cost of generic drugs is reference pricing.5 This system establishes a specific reimbursement level, known as the reference price, for a group of medicines that are considered interchangeable, typically based on having the same active ingredient and dosage form.5 If a particular medicine within that group is priced above the established reference price, the patient is usually required to pay the difference.5 This mechanism creates a strong incentive for both originator drug manufacturers and generic companies to price their products at or below the reference price to maintain market share.5 In 2004, a significant majority of countries, around 74%, had implemented a reference pricing system 5, and overall, 82% of countries impose some form of pricing regulation.5 Reference pricing can effectively encourage price competition among generic manufacturers, potentially leading to lower prices for consumers.36 For example, setting the reference price at the level of the cheapest available medicine in the group has been credited with contributing to the low generic drug prices observed in Denmark.36 However, policymakers must exercise caution when setting reference price levels, as prices that are too low may discourage manufacturers from entering the market or could potentially lead to supply issues.5 Furthermore, reference pricing systems may face challenges such as the reallocation of demand towards originator medicines that fall outside the reference price grouping, potentially undermining the intended cost-saving effects.36
Tiered Pricing: Another regulatory mechanism gaining traction in the generic drug market is tiered pricing.37 This model establishes multiple price tiers, setting a maximum allowable price for generic medicines based on the number of competitors that are currently marketing the drug.37 The primary goal of tiered pricing is to strike a balance between encouraging the entry of generic drugs into the market and ensuring that prices decrease as competition intensifies.37 For instance, in markets with limited competition, the tiered pricing model may allow for a higher maximum price, thereby making market entry more attractive to potential manufacturers.37 Conversely, as the number of generic competitors increases, the maximum allowable price is reduced, leading to cost savings for healthcare systems and patients.37 Canada, for example, implemented a tiered pricing model for generic medicines in April 2014.37 This model effectively mimics the dynamics of price competition while also providing a degree of market sustainability for generic manufacturers.37 However, the successful implementation of tiered pricing requires a robust infrastructure to accurately monitor the number of competitors in the market and to adjust prices accordingly.37
Negotiable Pricing and Maximum Price Setting: In addition to reference and tiered pricing, some countries utilize direct negotiation between payers and manufacturers to determine the prices of generic medicines.5 This approach allows for prices to be tailored to specific market conditions and the negotiating power of the involved parties. Furthermore, setting maximum prices for generic drugs is another mechanism employed by governments to directly control costs.5 While the negotiation of generic drug prices is not universally practiced, with countries like Lithuania and Poland being notable examples of its implementation 40, maximum price setting provides a more direct form of price regulation. Negotiable pricing offers flexibility but can be resource-intensive, while maximum price setting provides a clear price ceiling but might risk discouraging supply if the set price is too low to ensure profitability for manufacturers.
Impact of Government Regulations and Healthcare Policies: Government regulations and broader healthcare policies play a fundamental role in shaping the pricing landscape for generic drugs.5 A significant majority of nations, around 82%, have some form of regulation in place to influence drug prices.5 These policies can encompass various aspects, including the regulation of mark-ups within the distribution chain, the provision of tariff and tax exemptions, and initiatives aimed at promoting the utilization of generic medicines.41 Some countries have implemented specific regulations that restrict the size of price mark-ups on certain types of drugs to ensure their affordability for patients.41 The overall regulatory environment in which a drug is introduced to the market has a substantial impact on its price.8 For instance, markets with stringent price controls, such as those within the European Union, necessitate careful pricing strategies to avoid overpricing products.8 In contrast, the United States generally adopts a more free-market approach to generic drug pricing, although landmark legislation like the Hatch-Waxman Act has profoundly influenced the structure and dynamics of the generic market.5 More recently, the Inflation Reduction Act in the U.S. includes provisions designed to lower prescription drug costs for beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare.44 Across various jurisdictions, healthcare policies often aim to encourage the use of generic drugs through measures such as streamlined regulatory approval processes, the provision of market-based incentives, and the implementation of public awareness and education campaigns.12 These diverse regulatory and policy interventions underscore the critical role of government in shaping the pricing of generic drugs, striving to achieve a balance between affordability for patients, fostering a competitive market environment, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the supply chain.
4. Key Determinants Influencing Generic Drug Pricing:
The pricing of generic drugs is not solely determined by the strategies employed by manufacturers or the regulatory frameworks in place. Several key factors exert significant influence on the final price that consumers and payers encounter.
Competition: Perhaps the most significant factor influencing the price of generic drugs is the level of market competition.5 The entry of generic competitors into the market plays a vital role in driving down drug prices by increasing the availability of alternative options for patients and prescribers.7 As more generic producers gain regulatory approval and begin marketing their versions of a particular drug, the resulting competition typically leads to substantial price reductions.7 Studies have consistently shown that drug prices decline significantly as the number of generic competitors in the market increases.2 For example, prices have been observed to decrease by approximately 20% when there are about three generic competitors, and even more dramatically, by 70-80% when the number of competitors reaches ten or more.2 Landmark legislation like the Hatch-Waxman Act in the United States was instrumental in fostering a robust generic pharmaceutical market, leading to significantly lower drug costs through increased competition.5 Conversely, a lack of competition in the market can create opportunities for price increases, as seen in instances where only a limited number of generic manufacturers are present.5 Mergers and acquisitions within the generic drug industry can also have a notable impact on the level of competition, potentially either increasing market concentration or creating more efficient players that can offer lower prices.2 Therefore, policies and market dynamics that promote robust competition are crucial for ensuring the affordability of generic medications.
Manufacturing Costs and Supply Chain Logistics: The expenses associated with manufacturing generic drugs, as well as the intricacies of the supply chain, are also critical determinants of their pricing.8 These costs encompass the procurement of raw materials, labor expenses, and the operational costs of manufacturing facilities.8 Additionally, the costs related to research and development (albeit typically lower for generics), conducting clinical trials (if required), and obtaining regulatory approvals contribute to the overall cost structure.53 External factors such as tariffs imposed on imported pharmaceutical ingredients can also have a direct impact on the prices of generic drugs.41 While a modest tariff of 10% might not significantly affect the final cost, a more substantial tariff of 25% could potentially lead to higher prices for consumers.54 Furthermore, disruptions within the supply chain, including shortages of raw materials, logistical challenges, and production difficulties, can also exert upward pressure on generic drug prices.5 The concentration of purchasing power and distribution channels within the pharmaceutical industry can also create vulnerabilities in the supply chain, potentially exacerbating the impact of disruptions on pricing.58 Therefore, the efficiency and resilience of manufacturing processes and supply chain logistics are essential for maintaining stable and affordable prices for generic medications.
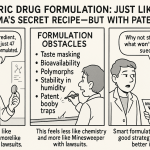
Research and Development (R&D) Costs: A key factor that distinguishes generic drugs and allows them to be priced significantly lower than their brand-name counterparts is the substantially lower investment required in research and development.7 Unlike brand-name drug manufacturers, generic companies do not bear the initial costs of discovering and developing the original drug molecule.7 This avoidance of extensive upfront R&D expenditure is a primary reason why generic medications can be offered at a fraction of the price of brand-name drugs.44 However, it is important to note that the development of generic drugs still involves certain costs, such as those associated with formulating the generic version, conducting bioequivalence studies, navigating the regulatory approval process, and establishing efficient manufacturing processes.53 Nevertheless, the absence of the significant R&D burden associated with novel drug discovery provides a fundamental economic advantage to generic manufacturers, enabling them to focus on cost-effective production and competitive pricing strategies.
Market Size and Accessibility: The overall size of the market for a particular generic drug and the ease with which it can be accessed by patients can also influence its pricing.8 In general, larger markets might be able to sustain slightly higher prices, although this often attracts more competition, which subsequently drives prices down. Additionally, the accessibility of a drug, such as whether it is available only through specialty pharmacies or requires specific handling, can add to the distribution costs and potentially affect the final price.8 Drugs that are more widely available through standard pharmacies typically face greater price competition compared to those with restricted distribution channels.
Ethical Considerations and the Balance Between Profitability and Public Health: Beyond the purely economic factors, ethical considerations and the need to balance profitability with the broader goals of public health play a crucial role in shaping generic drug pricing.5 There is an ongoing societal debate regarding the appropriate balance between allowing pharmaceutical companies to operate profitably and ensuring that essential medications remain affordable and accessible to all patients who need them.5 Pricing strategies for generic drugs must navigate this complex landscape, considering not only the financial sustainability of the manufacturers but also the potential impact of pricing decisions on patient access and overall healthcare affordability.5 Striking the right balance is essential to maintain a healthy and equitable pharmaceutical market that serves both the needs of the industry and the well-being of the public.
5. The Impact of Market Dynamics on Generic Drug Prices:
The prices of generic drugs are significantly affected by various market dynamics, including patent settlements, mergers and acquisitions, the role of pharmacy benefit managers, and the occurrence of drug shortages. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for comprehending the complexities of generic drug pricing.
Patent Settlements and Their Implications: Brand-name pharmaceutical companies sometimes employ strategies aimed at delaying the entry of more affordable generic versions of their drugs into the market.64 One such strategy involves “pay-for-delay” or reverse payment settlements, where the brand-name company provides financial incentives to potential generic competitors to postpone their market entry.64 The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has estimated that these types of anticompetitive agreements cost consumers and taxpayers billions of dollars annually in the form of higher drug prices.64 Another tactic involves the introduction of authorized generics (AGs), which are generic versions of a brand-name drug marketed under the brand company’s label or through an affiliate, often during the 180-day exclusivity period granted to the first generic filer.45 While AGs can offer some price reduction compared to the original brand, their introduction can significantly reduce the potential revenue for the first generic entrant.64 Furthermore, brand-name companies may utilize “patent thickets,” which involve filing numerous overlapping patents on a single drug, making it challenging and costly for generic manufacturers to navigate the patent landscape and bring their products to market.65 These various strategies can effectively delay the entry of generic competition, allowing brand-name companies to maintain higher prices for a longer period than would otherwise be possible.64 A notable example of this is the case of Cephalon’s sleep-disorder medication, Provigil, where a patent settlement significantly delayed the entry of generic versions.65 Such practices highlight the significant impact that patent settlements can have on impeding generic competition and sustaining elevated drug prices, ultimately affecting healthcare costs and patient access. Increased regulatory scrutiny and policy interventions are often deemed necessary to address these potentially anticompetitive behaviors.
Mergers and Acquisitions in the Generic Drug Industry: The generic drug industry has witnessed significant consolidation in recent years through mergers and acquisitions (M&As), and these activities can have varied effects on drug prices.2 In some instances, mergers involving generic drug producers can lead to lower prices. This can occur when the merging firms achieve cost savings and increased efficiencies through the consolidation of operations, such as streamlining manufacturing processes, reducing overhead, and optimizing distribution networks.68 For example, a study found that mergers involving companies primarily producing generic drugs, such as Teva Pharmaceuticals or Activis Generics, resulted in an average price decrease of 5.8% for overlapping drugs.68 However, M&As can also lead to a reduction in the overall level of competition within the generic drug market, particularly when the merging companies were significant competitors prior to the transaction. This decrease in competition can, in turn, create opportunities for price increases, especially in markets that are already relatively concentrated.2 Research has indicated that drugs produced by merging firms can experience price increases in the range of 8-15% in the years following a merger.78 The increasing consolidation within the generic manufacturing sector has therefore raised concerns about its potential to limit price competition and potentially lead to higher costs for consumers.2 The ultimate impact of M&As on generic drug prices is complex and depends on the specific characteristics of the merger and the competitive dynamics of the affected market.
The Role of Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs): Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) play a significant role in the pharmaceutical supply chain, acting as intermediaries between health insurers and pharmacies.1 Their responsibilities include negotiating drug prices with manufacturers, developing and managing formularies (lists of covered drugs), and processing prescription claims.16 While PBMs are intended to help control drug costs, their business practices have come under increasing scrutiny for their potential to inflate the prices of generic drugs.1 Practices such as spread pricing, where PBMs charge health plans more for a drug than they reimburse pharmacies, and copay clawbacks, where patients’ copays exceed the actual cost of the drug, can lead to higher out-of-pocket expenses for consumers.1 The increasing consolidation within the PBM industry has also raised concerns about the market power wielded by the largest PBMs and their influence on drug pricing.15 The top three PBMs currently manage a substantial share of all prescription drug claims in the United States.17 Reports from the FTC have indicated that these major PBMs often mark up the prices of specialty generic drugs by significant margins, sometimes reaching hundreds or even thousands of percent, generating billions of dollars in revenue.15 For instance, markups as high as 3,600% have been observed for certain generic cancer drugs like Imatinib.25 Furthermore, PBMs may sometimes favor brand-name drugs over less expensive generic alternatives on their formularies due to the rebates they receive from manufacturers.1 These dynamics suggest that the role of PBMs in the pharmaceutical supply chain can have a considerable impact on the final prices paid for generic drugs, often leading to higher costs for patients and payers despite the availability of lower-cost options.
Drug Shortages and Their Effect on Pricing: The occurrence of drug shortages represents another significant market dynamic that can profoundly affect the pricing of generic drugs.49 Generic drugs often constitute a large proportion of the medications that experience shortages.61 When a generic drug becomes unavailable or is in short supply, it can lead to substantial price spikes, particularly for those generics that have limited competition in the market.5 Historical examples include significant price increases for common antibiotics like tetracycline 5 and doxycycline 50 during periods of shortage. The low profit margins associated with some generic drugs can contribute to the problem of shortages, as manufacturers may find it economically unviable to continue producing certain medications, leading them to exit the market.60 In fact, a significant percentage of drugs currently in shortage have a very low unit price, often less than $1.60 Manufacturing and quality control issues are frequently cited as primary causes of drug shortages.49 These shortages not only impact patient access to necessary medications and may necessitate the use of less effective or more risky alternatives, but they also contribute to increased healthcare costs as the prices of available alternatives or the drugs themselves rise due to limited supply and high demand.5
6. International Perspectives on Generic Drug Pricing:
Examining how generic drugs are priced in different countries provides valuable context and highlights the influence of varying healthcare systems and regulatory approaches.
Comparative Analysis of Generic Drug Prices: When comparing generic drug prices internationally, a notable observation is that the United States generally offers lower prices for unbranded generic drugs compared to many other developed countries within the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).89 For every dollar spent on unbranded generics in other OECD countries, consumers in the U.S. typically pay around 67 cents.89 This is likely attributable to the intense price competition among generic manufacturers in the U.S. market. However, it is crucial to note that when considering overall drug prices, including both branded and generic medications, the U.S. stands out as having significantly higher prices compared to other high-income nations, averaging about 2.78 times higher.89 Interestingly, the U.S. also has a higher rate of generic drug dispensing compared to many other countries.89 The strategies employed for pricing generic drugs vary considerably across European countries. Some nations adopt a relatively free-market approach, allowing market forces to largely determine prices, while others implement more stringent price control measures or utilize reference pricing systems.5 It has been observed that in some European countries where drug prices are tightly regulated and kept at very low levels, manufacturers may be discouraged from entering the market, potentially leading to a reduced availability of certain medications.5 These international comparisons underscore the fact that the pricing of generic drugs is heavily influenced by the specific healthcare system structure and the regulatory philosophies adopted by different countries.
Influence of International Reference Pricing and other global pricing models: Many countries around the world, particularly in Europe, utilize international reference pricing (IRP) as a mechanism to manage the cost of pharmaceuticals, including generic drugs.30 Under an IRP system, the price of a drug in a particular country is set based on its price in a selection of other countries.30 This approach aims to ensure that drug prices are generally in line with international levels and can be an effective tool for controlling costs.30 By benchmarking domestic prices against those in comparable nations, IRP can limit the pricing power of manufacturers and potentially lead to more consistent pricing across different markets.
7. Challenges and Future Directions in Generic Drug Pricing:
The generic drug market, while crucial for healthcare affordability, faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its long-term sustainability and effectiveness.
Ensuring the sustainability of the generic drug market amidst price erosion: The intense price competition that characterizes the generic drug market, while beneficial for driving down costs in the short term, can also lead to a significant erosion of profit margins for generic manufacturers.60 This sustained downward pressure on prices can create a challenging economic environment for manufacturers, potentially leading some to exit the market altogether. Such market exits can, in turn, result in a reduced number of suppliers for certain essential medications, increasing the risk of drug shortages and subsequent price spikes when supply becomes limited.5 The concept of a “commoditization loop” has been used to describe this phenomenon, where the relentless focus on price reduction transforms essential medicines into low-margin commodities, making the supply chain increasingly vulnerable to disruptions.95 Therefore, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the generic drug market requires careful consideration of pricing pressures and the potential for unintended consequences like market instability and shortages.
Balancing affordability and incentivizing continued production and quality: A key challenge in the generic drug market is finding the right balance between the societal goal of affordable medications and the need to provide sufficient economic incentives for manufacturers to continue producing these drugs at high quality standards.5 When prices are driven down to levels that are unsustainably low, it can discourage manufacturers from entering the market or even lead existing manufacturers to discontinue production of certain drugs that are no longer profitable.5 This can have serious implications for the availability of essential medicines and the overall stability of the supply chain. Policies aimed at promoting affordability must therefore also consider the economic realities faced by generic drug manufacturers to ensure a reliable and high-quality supply of these crucial medications for the long term.
The need for greater transparency in pricing mechanisms: The lack of transparency in the pricing of generic drugs throughout the supply chain is a significant challenge that can contribute to inflated costs and hinder efforts to ensure affordability.1 Complex pricing mechanisms, confidential agreements between various stakeholders, and opaque supply chain dynamics can obscure the true costs of generic medications and potentially allow for excessive markups. In particular, the pricing practices of Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) have come under scrutiny for their lack of transparency and their potential to inflate generic drug prices.1 Greater transparency in pricing at all levels of the supply chain would provide valuable information to policymakers, payers, and patients, enabling them to better understand the factors that contribute to the final cost of generic drugs and to identify potential areas for improvement and cost savings.
Exploring innovative pricing models to address market challenges: To address the evolving challenges within the generic drug market, there is a growing need to explore and potentially adopt innovative pricing models that move beyond traditional cost-plus or market-based approaches. For example, tiered pricing models, which adjust the maximum allowable price based on the number of competitors, have shown promise in balancing market entry incentives with price reductions.37 Other potential models include price de-linkage from the originator medicine and automatic indexation to account for inflation.37 While traditional value-based pricing might have limited applicability to standard generics, modified versions or its principles could be relevant for more complex generics or biosimilars.6 Furthermore, the potential of dynamic pricing models, which adjust prices in response to real-time market conditions, is also being explored as a way to improve efficiency and responsiveness within the generic drug market.30 Investigating and potentially implementing such innovative pricing strategies could be crucial for ensuring a sustainable, affordable, and accessible supply of generic drugs in the future.
8. Recommendations:
To foster a competitive and affordable generic drug market while ensuring its long-term sustainability, several strategic considerations and policy recommendations can be made.
Strategic considerations for generic drug manufacturers in formulating pricing strategies: Generic drug manufacturers should prioritize a thorough analysis of their production costs and strive for efficiency in their manufacturing processes to maintain profitability in a competitive market. Continuous monitoring of competitor pricing is essential to inform the adoption of effective competitive pricing strategies. For manufacturers with the capacity for large-scale production, exploring volume-based pricing models can be advantageous. In the case of complex generics or biosimilars that offer unique benefits or improved outcomes, manufacturers should consider the potential for incorporating elements of value-based pricing into their strategies. Staying abreast of regulatory changes and adapting pricing strategies accordingly is also crucial for navigating the evolving market landscape. Finally, investing in the development of resilient and diversified supply chains can help mitigate the risk of drug shortages and price volatility, ensuring a more stable market position.
Policy recommendations for governments and regulatory bodies to foster a competitive and affordable generic drug market: Governments and regulatory bodies should actively promote competition within the generic drug market by streamlining the approval processes for generic drugs and addressing any existing barriers to market entry. Increased scrutiny and regulation of patent settlement practices are necessary to prevent anti-competitive delays in the introduction of generic medications. Enhancing transparency and oversight of the practices of Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) is critical to address potential markups and ensure fair pricing for generic drugs. Policymakers should also consider the implementation or refinement of pricing models such as reference pricing and tiered pricing to effectively manage costs and incentivize competition among manufacturers. To ensure the long-term sustainability of the generic drug market, policies should be developed that balance affordability with incentives for manufacturers, potentially through the establishment of minimum pricing levels or the provision of incentives for the production of essential medicines. Finally, proactive measures are needed to address the persistent issue of drug shortages, including policies that encourage a reliable supply and prevent opportunistic price gouging during periods of scarcity.
Considerations for healthcare providers and payers in optimizing generic drug utilization and cost management: Healthcare providers should consistently encourage the prescribing and dispensing of generic drugs whenever they are clinically appropriate and available. Payers should implement formularies that prioritize the inclusion of cost-effective generic options to maximize savings. Negotiating transparent and favorable contracts with PBMs that ensure fair pricing for generic medications is also essential. Furthermore, educating patients about the benefits, safety, and cost savings associated with generic medications can promote greater utilization and contribute to overall cost management within the healthcare system.
By implementing these considerations and recommendations, stakeholders can work towards a more competitive, affordable, and sustainable generic drug market that effectively serves the needs of patients and the healthcare system as a whole.
Works cited
- The generic drug pricing game: What you need to know. – Rightway, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.rightwayhealthcare.com/blog/the-generic-drug-pricing-game
- Drug Competition Series – Analysis of New Generic Markets Effect of Market Entry on Generic Drug Prices, accessed May 8, 2025, https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/510e964dc7b7f00763a7f8a1dbc5ae7b/aspe-ib-generic-drugs-competition.pdf
- Federal Regulation of Prescription Drugs in the United States – The Actuary Magazine, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.theactuarymagazine.org/federal-regulation-of-prescription-drugs-in-the-united-states/
- The Generic Drug Supply Chain | Association for Accessible Medicines, accessed May 8, 2025, https://accessiblemeds.org/resources/blog/generic-drug-supply-chain/
- Strategies for Pricing Generic Drugs – DrugPatentWatch – Transform …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/strategies-for-pricing-generic-drugs/
- Six drug pricing models have emerged to improve product access and affordability – PwC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industries/health-industries/library/6-drug-pricing-models.html
- The Economics of Generic Drug Pricing Strategies: A Comprehensive Analysis, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/the-economics-of-generic-drug-pricing-strategies-a-comprehensive-analysis/
- Pharma Pricing Strategies – Supra.tools, accessed May 8, 2025, https://supra.tools/pharma-pricing-strategies
- Fact Sheet: President Donald J. Trump Announces Actions to Lower Prescription Drug Prices – The White House, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.whitehouse.gov/fact-sheets/2025/04/fact-sheet-president-donald-j-trump-announces-actions-to-lower-prescription-drug-prices/
- Lowering Drug Prices by Once Again Putting Americans First – The White House, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/2025/04/lowering-drug-prices-by-once-again-putting-americans-first/
- Regulation of Prescription Drug Pricing | AMCP.org, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.amcp.org/legislative-regulatory-position/regulation-prescription-drug-pricing
- The Effect of Drug Pricing Policies on Healthcare Equity and Affordability, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.jbclinpharm.org/articles/the-effect-of-drug-pricing-policies-on-healthcare-equity-and-affordability-13081.html
- The Impact of 2024 Health Policies on Generic Drug Access – East Street Pharmacy, accessed May 8, 2025, https://eaststreetpharmacy.com/the-impact-of-2024-health-policies-on-generic-drug-access.html
- What is MAC pricing – and how are generic drugs related? – Truveris, accessed May 8, 2025, https://truveris.com/mac-pricing/
- A closer look at how health care consolidation drives up patient costs, creates barriers to care | PhRMA, accessed May 8, 2025, https://phrma.org/blog/a-closer-look-at-how-health-care-consolidation-drives-up-patient-costs-creates-barriers-to-care
- What Pharmacy Benefit Managers Do, and How They Contribute to Drug Spending, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/explainer/2025/mar/what-pharmacy-benefit-managers-do-how-they-contribute-drug-spending
- Pharmacy benefit managers raised prices by over 1000% on specialty drugs, accessed May 8, 2025, https://healthjournalism.org/blog/2025/02/pharmacy-benefit-managers-raised-prices-by-over-1000-on-specialty-drugs/
- FTC Releases Second Interim Staff Report on Prescription Drug …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/press-releases/2025/01/ftc-releases-second-interim-staff-report-prescription-drug-middlemen
- FTC Issues PBM Report Signaling Consolidation Is Impacting Pharmaceutical Prices, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.mccarter.com/insights/ftc-issues-pbm-report-signaling-consolidation-is-impacting-pharmaceutical-prices/
- LUGPA Policy Overview – Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform in 2024, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.lugpa.org/pharmacy-benefit-manager-reform-in-2024
- FTC Report Shows Pharmacy Benefit Managers Profit from Specialty Generic Drug Markups and Reimbursements – Duane Morris, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.duanemorris.com/alerts/ftc_report_shows_pharmacy_benefit_managers_profit_specialty_generic_drug_markups_0125.html
- FTC finds PBMs make billions in profit from marking up cancer, other critical generic drugs, accessed May 8, 2025, https://phrma.org/blog/ftc-finds-pbms-make-billions-in-profit-from-marking-up-cancer-other-critical-generic-drugs
- FTC Releases Second Report on PBMs Meddling in Generic Drug Markets, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.centerforbiosimilars.com/view/ftc-releases-second-report-on-pbms-meddling-in-generic-drug-markets
- PBMs Significantly Marked Up Specialty Generic Drugs, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugtopics.com/view/pbms-significantly-marked-up-specialty-generic-drugs
- Study suggests PBMs are gaming pharmacy system to overcharge for drugs | PharmaVoice, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharmavoice.com/news/pbm-study-overcharge-drug-price-generic/702431/
- PBM 101: PBM Pricing Models – Innovative Rx Strategies, accessed May 8, 2025, https://innovativerxstrategies.com/pbm-pricing-models/
- How PBMs Are Driving Up Prescription Drug Costs – The New York Times – nacds.org, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.nacds.org/pdfs/PBMarticle-6-21-24.pdf
- Following the Money: Untangling U.S. Prescription Drug Financing, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.americanprogress.org/article/following-the-money-untangling-u-s-prescription-drug-financing/
- Specialty Generic Drugs:A Growing Profit Center for Vertically Integrated Pharmacy Benefit Managers – Federal Trade Commission, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/PBM-6b-Second-Interim-Staff-Report.pdf
- Decoding Drug Pricing Models: A Strategic Guide to Market Domination – DrugPatentWatch, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/decoding-drug-pricing-models-a-strategic-guide-to-market-domination/
- Pharma companies need to explore various pricing strategies for …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharmabiz.com/NewsDetails.aspx?aid=168717&sid=1
- Value-based pricing – the concept – Generics and Biosimilars Initiative, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.gabionline.net/generics/research/Value-based-pricing-the-concept?msclkid=3e2327c5cf9411ec8f2f92a182343157
- Value-Based Pricing of US Prescription Drugs. Estimated Savings Using Reports From the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review – ICER, accessed May 8, 2025, https://icer.org/news-insights/journal-articles/value-based-pricing-of-us-prescription-drugs-estimated-savings-using-reports-from-the-institute-for-clinical-and-economic-review/
- Value-Based Pricing of US Prescription Drugs: Estimated Savings Using Reports From the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9856524/
- Case Study: Pharmaceutical Pricing and Innovation – July 18, 2018 – USC Schaeffer Center, accessed May 8, 2025, https://schaeffer.usc.edu/research/case-study-pharmaceutical-pricing-and-innovation/
- Pricing strategies in generic medicines – Generics and Biosimilars Initiative, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.gabionline.net/generics/research/Pricing-strategies-in-generic-medicines
- New pricing models for generic medicines to ensure long-term sustainable competition in Europe – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10593415/
- New pricing models for generic medicines to ensure long-term sustainable competition in Europe – PubMed, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37876734/
- New pricing models for generic medicines to ensure long-term sustainable competition in Europe – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2023.1200641/full
- New pricing models for generic medicines to ensure long-term healthy competitiveness in Europe, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.medicinesforeurope.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/New-pricing-models-for-generic-medicines.pdf
- Factors Impacting Pharmaceutical Prices and Affordability: Narrative Review – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7838942/
- Price-Fixing Case Reveals Vulnerability of Generic Drug Policies | RAND, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.rand.org/pubs/commentary/2019/07/price-fixing-case-reveals-vulnerability-of-generic.html
- Getting a Handle on Generic-Drug Prices – U.S. Pharmacist, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/getting-a-handle-on-genericdrug-prices
- How Pharmaceutical Companies Price Their Drugs – Investopedia, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/020316/how-pharmaceutical-companies-price-their-drugs.asp
- New Evidence Linking Greater Generic Competition and Lower Generic Drug Prices – FDA, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.fda.gov/media/133509/download
- Price Declines after Branded Medicines Lose Exclusivity in the US – IQVIA, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.iqvia.com/-/media/iqvia/pdfs/institute-reports/price-declines-after-branded-medicines-lose-exclusivity-in-the-us.pdf
- Competition in Generic Drug Markets | NBER, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.nber.org/digest/nov17/competition-generic-drug-markets
- Containing Generic-Drug Costs – U.S. Pharmacist, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/containing-genericdrug-costs
- Policy Position: Generic Drug Price Spikes – Healthcare Supply Chain Association, accessed May 8, 2025, https://supplychainassociation.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/HSCA_Policy_Position_-_Gener.pdf
- Do price spikes on some generic drugs indicate problems in the market? – USC Today, accessed May 8, 2025, https://today.usc.edu/do-price-spikes-on-some-generic-drugs-indicate-problems-in-the-market/
- Do Price Spikes on Some Generic Drugs Indicate Problems in the Generics Market?, accessed May 8, 2025, https://healthpolicy.usc.edu/article/do-price-spikes-on-some-generic-drugs-indicate-problems-in-the-generics-market/
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Opportunities and Challenges in Generic Drug Development – DrugPatentWatch – Transform Data into Market Domination, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/mergers-and-acquisitions-opportunities-and-challenges-in-generic-drug-development/
- Breaking Down the Cost of Generic Drug Production: Understanding the Factors Influencing Affordability – DrugPatentWatch, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/breaking-down-the-cost-of-generic-drug-production-understanding-the-factors-influencing-affordability/
- Impact of Tariffs on the Generic Drug Market – Pharmaceutical Commerce, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharmaceuticalcommerce.com/view/impact-of-tariffs-on-the-generic-drug-market
- Will Tariffs Affect Branded Drug Prices? – Pharmaceutical Commerce, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharmaceuticalcommerce.com/view/will-tariffs-affect-branded-drug-prices-
- How Supply Chain Issues Lead to Drug Price Surges and Quality Concerns, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharmaceuticalcommerce.com/view/supply-chain-issues-drug-price-surges-quality-concerns
- Trump Tariffs Could Raise Generic Drug Prices, Worsen Shortages, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharmacypracticenews.com/Online-First/Article/04-25/Tariffs-Pharmaceutical-Impacts/76825
- Optimizing the Generic Drug Supply Chain: Strategies for Success – DrugPatentWatch, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/optimizing-the-generic-drug-supply-chain-strategies-for-success/
- Drug Prices and Shortages Jeopardize Patient Access to Quality Hospital Care | AHA News, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.aha.org/news/blog/2024-05-22-drug-prices-and-shortages-jeopardize-patient-access-quality-hospital-care
- What’s Behind Drug Shortages and What to do About It – Third Way, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.thirdway.org/report/whats-behind-drug-shortages-and-what-to-do-about-it
- Preventing and Mitigating Generic Drug Shortages: Policy Options Under Federal Health Programs, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.finance.senate.gov/imo/media/doc/white_paper_preventing_drug_shortages.pdf
- Industrial Policy To Reduce Prescription Generic Drug Shortages, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.americanprogress.org/article/industrial-policy-to-reduce-prescription-generic-drug-shortages/
- Cheaper is not always better: Drug shortages in the United States and a value-based solution to alleviate them, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11217858/
- Strategies that delay or prevent the timely availability of affordable generic drugs in the United States, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4915805/
- The Role of Patents and Regulatory Exclusivities in Drug Pricing …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.congress.gov/crs-product/R46679
- Pay for Delay | Federal Trade Commission, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/topics/competition-enforcement/pay-delay
- The Connection Between Patents and High Drug Prices – Politico, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.politico.com/sponsored/2024/12/the-connection-between-patents-and-high-drug-prices/
- When pharma mergers lead to lower drug prices | Tippie College of Business, accessed May 8, 2025, https://tippie.uiowa.edu/news/2025/01/when-pharma-mergers-lead-lower-drug-prices
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&As) in Pharmaceutical Markets: Associations with Market Concentration, Prices, Drug Quantity Sold, and Shortages – Scholars @ Bentley, accessed May 8, 2025, https://scholars.bentley.edu/cisi_pubs/9/
- M&A in Pharma: Balancing Growth and Risk – Pharmaceutical Commerce, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharmaceuticalcommerce.com/view/m-a-in-pharma-balancing-growth-and-risk
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&As) in Pharmaceutical Markets – Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, accessed May 8, 2025, https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/ec5de77c72cff3abf802b5e9c6cc8ae4/aspe-pharma-ma-report.pdf
- Mergers, Product Prices, and Innovation: Evidence from the Pharmaceutical Industry, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.hec.edu/sites/default/files/documents/Bonaime_Wang_202204.pdf
- High & Rising Drug Prices: Myth vs. Fact | AHA, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.aha.org/2017-12-11-high-rising-drug-prices-myth-vs-fact
- The Effect of Acquisitions on Pharmaceutical Drug Prices – Yale Department of Economics, accessed May 8, 2025, https://economics.yale.edu/sites/default/files/2023-01/Alexis%20Henkel_Senior%20Essay.pdf
- Marching Toward Monopoly – Mergers and Acquisitions in the Pharmaceutical Industry – National Nurses United, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.nationalnursesunited.org/sites/default/files/nnu/files/pdf/research/MarchingTowardMonopoly-PharmaMA10-17-16.pdf
- Generic prescription drug price increases: which products will be affected by proposed anti-gouging legislation? – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6247773/
- UI study shows drug prices fall after some big pharma mergers – Radio Iowa, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.radioiowa.com/2025/01/20/ui-study-shows-drug-prices-fall-after-some-big-pharma-mergers/
- Effects of Horizontal Mergers on Prices of Generic Drugs – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388357104_Effects_of_Horizontal_Mergers_on_Prices_of_Generic_Drugs
- GENERIC DRUGS IN THE UNITED STATES: POLICIES TO ADDRESS PRICING AND COMPETITION, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6355356/
- Generic Drug Prices Are Declining, But Many Consumers Aren’t Benefiting – ProPublica, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.propublica.org/article/generic-drug-prices-are-declining-but-many-consumers-arent-benefiting
- The True Culprits Behind Rising Generic Drug Costs | The Daily Dose | CDPHP Blog, accessed May 8, 2025, https://blog.cdphp.com/corporate-news/the-true-culprits-behind-rising-generic-drug-costs/
- U.S. Consumers Overpay for Generic Drugs – May 31, 2022 – USC Schaeffer, accessed May 8, 2025, https://schaeffer.usc.edu/research/u-s-consumers-overpay-for-generic-drugs/
- ASPE Report to Congress: Impact of Drug Shortages on Consumer …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK603205/
- The Cost of Drug Shortages – OHE, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.ohe.org/publications/the-cost-of-drug-shortages/
- Blog: Bill Addressing Drug Shortages Provides Long Overdue Relief from Penalties Hurting Generic Drug Market | Association for Accessible Medicines, accessed May 8, 2025, https://accessiblemeds.org/resources/press-releases/blog-bill-addressing-drug-shortages-provides-long-overdue-relief-penalties/
- Nonprofit Drug Companies Aim to Curb High Prices and Shortages | U.S. GAO, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.gao.gov/blog/nonprofit-drug-companies-aim-curb-high-prices-and-shortages
- US drug prices and shortages set to rise despite Trump’s latest executive order – ING Think, accessed May 8, 2025, https://think.ing.com/articles/us-drug-prices-shortages-increase-despite-executive-orders-trump/
- Drug shortages drive up prices for consumers. Here’s how they can be avoided, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.fiercehealthcare.com/payers/how-drug-shortages-drive-prices-consumers-and-how-they-can-be-avoided-report
- aspe.hhs.gov, accessed May 8, 2025, https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/d5541b529a379d1f908ed2f9c00a9255/aspe-cover-idr-pricing-availability.pdf
- Comparing Generic Drug Markets in Europe and the United States: Prices, Volumes, and Spending – DrugPatentWatch, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/comparing-generic-drug-markets-europe-united-states-prices-volumes-spending/
- International Prescription Drug Price Comparisons: Estimates Using 2022 Data – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11147645/
- Politifact FL: U.S. pays double for prescriptions compared to other countries – WUSF, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.wusf.org/health-news-florida/2024-03-29/politifact-fl-us-pays-double-prescriptions-other-countries
- International Prescription Drug Price Comparisons: Estimates Using 2022 Data | RAND, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA788-3.html
- Prescription Drug Prices in the U.S. Are 2.78 Times Those in Other Countries – RAND, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.rand.org/news/press/2024/02/01.html
- US Generic Pharmaceutical Industry Economic Instability – API Innovation Center, accessed May 8, 2025, https://apicenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/US-Generic-Pharmaceutical-Industry-Economic-Instability.pdf
- Contributor: The Role of Dynamic Pricing in Health Technology Assessment for MDD, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.ajmc.com/view/contributor-the-role-of-dynamic-pricing-in-health-technology-assessment-for-mdd
- A Framework for the Fair Pricing of Medicines – PMC – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10810971/
- Dynamic Pricing: What Pharma Needs? – Pharmaceutical Commerce, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharmaceuticalcommerce.com/view/dynamic-pricing-what-pharma-needs-