The pharmaceutical industry has long operated under the paradigm that achieving blockbuster status for a drug necessitates substantial US market penetration. This conviction stems from the United States’ historically high drug prices, extensive insurance coverage, and massive patient population. However, as global healthcare markets evolve, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly questioning whether the path to billion-dollar sales must invariably run through America. This comprehensive analysis explores the changing dynamics of the global pharmaceutical landscape, examining whether drugs can achieve coveted blockbuster status without heavily relying on US sales, the strategies companies employ to diversify revenue streams, and the future outlook for global pharmaceutical success.
Understanding Blockbuster Drugs in the Global Pharmaceutical Market
Defining What Makes a Drug a “Blockbuster”
A “blockbuster drug” represents the pinnacle of commercial success in the pharmaceutical industry, defined explicitly as a medication generating annual sales of at least $1 billion for the company that sells it. These pharmaceutical powerhouses typically address common medical conditions affecting large patient populations, such as high cholesterol, diabetes, hypertension, asthma, or cancer5. Beyond their impressive revenue generation, blockbuster drugs often dominate their therapeutic categories, setting industry standards for treatment approaches and patient care.
The blockbuster designation encompasses several key characteristics that distinguish these medications in the marketplace. They typically enjoy robust patent protection, which prevents generic competition and allows manufacturers to maintain premium pricing structures. Additionally, these drugs frequently represent significant therapeutic advancements, offering improved efficacy, reduced side effects, or greater convenience compared to existing treatment options. This combination of innovation and exclusivity creates the perfect conditions for substantial and sustained market success6.
Historical Reliance on US Sales for Blockbuster Status
The road to blockbuster status has traditionally run through the United States, with American sales typically accounting for the lion’s share of global revenue for top-performing drugs. This phenomenon is clearly illustrated by Humira (adalimumab), which generated a staggering $20.7 billion in global revenue in 2021, with $17.3 billion-over 83% of the total-coming exclusively from US sales7. This lopsided revenue distribution underscores the historical importance of the US market in achieving and maintaining blockbuster status.
Several factors have contributed to the outsize importance of US pharmaceutical sales. The American healthcare system lacks the centralized price negotiations common in many other developed nations, allowing pharmaceutical companies to command premium prices. Additionally, the expansive private insurance market, coupled with government programs like Medicare and Medicaid, creates a large pool of patients with some form of prescription drug coverage. These structural characteristics have traditionally made the US market the primary target for pharmaceutical companies pursuing blockbuster aspirations.
The Traditional Blockbuster Model and Its Limitations
The traditional blockbuster model has focused on developing medications for common conditions affecting millions of patients, securing strong patent protection, and implementing aggressive marketing strategies primarily targeting US healthcare providers and consumers. This approach reached its zenith with drugs like Lipitor for cholesterol management, which dominated global sales charts for years before facing generic competition. The model’s success has been so profound that for years, the pharmaceutical industry’s research and development priorities have been largely shaped by the pursuit of potential blockbusters.
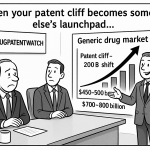
However, this US-centric blockbuster approach faces mounting challenges and inherent limitations. The model’s heavy reliance on a single market creates vulnerability to US-specific regulatory changes, pricing pressures, and healthcare reforms. Additionally, as patent expirations inevitably approach, the dramatic revenue drops that follow generic or biosimilar entry-particularly in the US market-can severely impact a company’s financial stability. Humira provides a telling example, with international revenues decreasing by 9.6% on a reported basis in 2021 due to biosimilar competition in markets outside the US7. These limitations have increasingly pushed pharmaceutical companies to explore alternative paths to blockbuster status that rely less heavily on US market dominance.
The Changing Landscape of the Global Pharmaceutical Market
Current State of Regional Pharmaceutical Markets
North America Pharmaceutical Market Outlook
North America continues to dominate the global pharmaceutical landscape, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% in the coming years1. The United States remains the centerpiece of this regional powerhouse, representing the largest single pharmaceutical market globally. This continued growth reflects both the region’s economic strength and its distinctive healthcare system characteristics.
The US market’s dominance stems from several factors beyond just its pricing structure. The country leads in pharmaceutical innovation, houses many of the world’s largest pharmaceutical companies, and maintains a regulatory framework that, while rigorous, offers well-established pathways to market approval. Additionally, the sheer volume of prescriptions in the US market-reaching approximately 6.7 billion medical prescriptions in 2022-creates enormous sales potential even for non-blockbuster medications2.
European Pharmaceutical Market Dynamics
Europe represents another mature and sophisticated pharmaceutical market with distinct characteristics that differ significantly from the North American landscape. The European pharmaceutical market reached $285.35 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $496.74 billion by 2033, reflecting a steady CAGR of 5.7%3. This substantial market, while growing more modestly than North America, offers pharmaceutical companies a large, diverse, and increasingly unified regulatory environment.
The European market’s strength lies in its comprehensive healthcare systems, strong academic research institutions, advanced biotechnology capabilities, and favorable reimbursement policies. Countries like Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and Switzerland serve as both important markets and hosts to several global pharmaceutical giants. The region benefits from the European Medicines Agency (EMA), which facilitates streamlined drug approvals across member nations, creating a more cohesive market despite national differences in pricing and reimbursement3.
Asian Pharmaceutical Markets: Focus on China and Japan
Asian pharmaceutical markets, particularly China and Japan, represent increasingly vital components of global pharmaceutical strategy. Japan’s pharmaceutical market reached $82.27 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to $101.90 billion by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 2.57%4. Though growing more slowly than other regions, Japan’s market remains the third-largest globally and features a highly developed healthcare system with near-universal coverage.
China, meanwhile, has emerged as one of the fastest-growing pharmaceutical markets worldwide. Its rapid economic development, massive population, increasing healthcare coverage, and growing chronic disease burden make it an essential consideration for any pharmaceutical company with global ambitions. Notably, even after Lipitor lost patent protection in the US, it continued generating significant revenue from overseas markets, particularly China, demonstrating the growing importance of Asian markets in extending a drug’s commercial success beyond its US patent life5.
Factors Influencing Pharmaceutical Market Growth Outside the US
Aging Populations and Rising Chronic Disease Burden
One of the most significant drivers of pharmaceutical market growth globally is the rapid aging of populations, particularly in developed economies. In Europe, more than 20% of the EU population is now aged 65 and over, a proportion that continues to rise3. This demographic shift correlates directly with increased incidences of chronic conditions requiring ongoing pharmaceutical intervention, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.
The relationship between aging populations and pharmaceutical demand is particularly evident in treatments targeting age-related conditions. For example, the use of anticoagulants and biologics has become increasingly widespread in Western Europe’s elderly population, spurring innovation and generating substantial revenue streams for manufacturers3. This trend extends to Japan, which has the world’s oldest population, creating sustained demand for medications treating chronic and age-related conditions despite the country’s overall slower market growth rate.
Healthcare Infrastructure Development in Emerging Markets
The development and maturation of healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets represents another crucial factor driving pharmaceutical growth outside the US. As middle-income countries expand their healthcare systems, increase insurance coverage, and develop more sophisticated supply chains, access to both essential and specialty medications improves dramatically. This infrastructure development creates new markets for pharmaceutical products that previously may have been available only in the most advanced economies.
Countries across Asia, Latin America, and parts of Africa have made significant investments in healthcare infrastructure, medical education, and pharmaceutical distribution networks. These improvements allow for more complex medications to reach patients in regions that historically might have had limited access to advanced therapies. For pharmaceutical companies, these developing markets represent opportunities to build brand recognition and loyalty early in a market’s evolution, potentially establishing strong positions that can deliver sustained revenue growth for decades.
Policy and Regulatory Changes Affecting Global Drug Sales
Policy and regulatory environments across global markets continue to evolve in ways that significantly impact pharmaceutical sales potential. Many countries have implemented policies to increase access to medications, particularly for serious conditions, while simultaneously working to contain overall healthcare costs. These dual objectives create both opportunities and challenges for pharmaceutical companies seeking blockbuster status through global sales.
In Europe, the unified regulatory approach through the EMA facilitates more efficient market entry across multiple countries, though individual nations maintain control over pricing and reimbursement decisions. Japan has worked to accelerate approval processes for innovative medications while implementing price revision mechanisms to control costs. Meanwhile, China has dramatically reformed its drug approval process, reducing backlogs and aligning more closely with international standards, while also expanding its national reimbursement drug list to include more innovative therapies. These regulatory evolutions create pathways for drugs to achieve substantial sales across multiple international markets, even without dominant US market share.
Case Studies: Successful Drugs with Significant Non-US Revenue
Blockbuster Drugs with Strong Global Performance
Several notable medications have demonstrated the potential to achieve remarkable global sales without overwhelming reliance on the US market. While comprehensive data on regional sales breakdowns is limited in the search results, the patterns of certain blockbuster drugs offer instructive examples. Medications with truly global appeal often address conditions with worldwide prevalence, have clear efficacy advantages over alternatives, and employ strategic approaches to market access across diverse healthcare systems.
Cancer therapies, in particular, have shown strong potential for balanced global revenue generation. Keytruda (pembrolizumab), which reported $25 billion in sales in 2023 to become the world’s top-selling drug, has built substantial market share across multiple continents8. While specific regional breakdowns aren’t provided in the search results, Keytruda’s growth trajectory shows how oncology drugs addressing critical unmet medical needs can achieve blockbuster status through truly global performance.
Regional Success Stories: Drugs that Dominate Outside the US
Some medications have achieved remarkable success in specific regional markets even while maintaining more modest positions in the United States. These regional powerhouses often address conditions with particular prevalence in certain populations or align especially well with specific healthcare system structures. By dominating key markets outside the US, these drugs can achieve substantial global sales that approach or exceed blockbuster thresholds.
For example, certain cardiovascular and diabetes medications have achieved dominant positions in Asian markets, where these conditions are increasingly prevalent. Similarly, treatments for specific infectious diseases may find their largest markets in regions where those conditions are endemic. While the search results don’t provide specific examples of drugs that have achieved blockbuster status primarily through non-US sales, the growing importance of markets like China, where Lipitor continues to generate significant revenue even after US patent expiration, points to the increasing feasibility of this approach5.
Lessons from Humira’s International Market Journey
Humira (adalimumab) offers perhaps the most instructive case study in both the traditional US-centric blockbuster model and the challenges of maintaining global revenue in the face of regional competition. In 2021, Humira generated $20.7 billion in global revenue, with $17.3 billion coming from US sales and only $3.4 billion from international markets7. This stark imbalance reflects both the higher US pricing and the impact of biosimilar competition already present in international markets.
When biosimilar versions of Humira entered European and other international markets, AbbVie experienced a 9.6% decrease in reported international revenues, highlighting the vulnerability of even the strongest blockbusters to competition outside protected US markets7. This experience underscores both the historical reliance on US sales and the potential value of developing more balanced global revenue streams resistant to region-specific competitive pressures. As biosimilar competition has finally entered the US market in 2023, Humira’s sales have begun to plummet, demonstrating the risks of over-reliance on a single market, even one as lucrative as the United States.
Strategies for Achieving Blockbuster Status Beyond US Markets
Market Entry and Expansion Approaches for International Success
Pharmaceutical companies pursuing global blockbuster status increasingly employ sophisticated market entry and expansion strategies tailored to the unique characteristics of individual regions. Rather than applying a standardized global approach, successful companies develop nuanced strategies that account for regional differences in disease prevalence, competitive landscapes, physician preferences, and patient expectations. This tailored approach allows drugs to gain traction in multiple markets simultaneously, building the diverse revenue base necessary for blockbuster status without overwhelming US dependence.
Successful international expansion often begins with careful market prioritization, focusing initial efforts on regions with the highest potential return on investment. Companies may strategically sequence market entries, using success in one region to facilitate entry into related markets. For example, gaining approval and adoption in major European markets may facilitate entry into smaller European nations or countries that reference EU approvals in their own regulatory decisions. Similarly, success in Japan often provides a foundation for broader Asian market entry, leveraging the country’s rigorous regulatory standards and sophisticated healthcare system.
Pricing and Reimbursement Strategies for Different Markets
Developing effective pricing and reimbursement strategies across diverse global markets represents one of the most challenging aspects of achieving international blockbuster status. While the US market generally permits premium pricing, particularly for innovative therapies, most other markets exercise significantly greater price control through various mechanisms. Successful global pharmaceutical companies have developed sophisticated approaches to navigate these variations while maintaining overall profitability.
Differential pricing strategies-setting different price points across markets based on factors such as economic development, healthcare system structure, and competitive environment-allow companies to maximize both access and revenue. In advanced economies with universal healthcare systems, companies often focus on demonstrating cost-effectiveness through health technology assessments to secure favorable reimbursement positions. In emerging markets, companies may offer patient assistance programs, tiered pricing models, or special distribution arrangements to balance affordability with commercial viability. These nuanced approaches enable drugs to generate substantial revenue across diverse markets despite significant pricing variations.
Adapting to Local Healthcare Systems and Patient Needs
Cultural Considerations in Drug Marketing and Adoption
Cultural factors significantly influence medication acceptance, adherence, and overall market success across global regions. Successful pharmaceutical companies recognize that attitudes toward health, disease, treatment, and medical authority vary substantially across cultures, necessitating tailored approaches to education, marketing, and patient support. Even the same medical condition may be perceived differently across cultural contexts, requiring sensitivity in how treatments are positioned and promoted.
In some Asian markets, for instance, integrating modern pharmaceuticals with traditional medicine concepts can enhance patient acceptance. In regions with strong family-centered healthcare decision-making, educational efforts may need to target both patients and their wider family support systems. Religious beliefs and cultural taboos may affect willingness to use certain treatment modalities or medications for specific conditions. By addressing these cultural dimensions thoughtfully, pharmaceutical companies can significantly improve adoption rates and patient adherence, building stronger market positions across diverse global regions.
Navigating Diverse Regulatory Environments
The global pharmaceutical marketplace presents a complex patchwork of regulatory requirements that companies must navigate to achieve multi-market success. While certain regulatory harmonization exists, particularly within regions like the European Union, significant differences persist in approval requirements, clinical trial expectations, manufacturing standards, and post-marketing obligations. Companies pursuing global blockbuster status develop regulatory strategies that efficiently address these variations while maintaining compliance across all markets.
Increasingly, pharmaceutical companies design global clinical development programs that simultaneously satisfy the requirements of multiple major regulatory agencies, including the FDA, EMA, and PMDA (Japan). This approach accelerates global market access by reducing the need for region-specific studies. Similarly, companies may strategically select manufacturing sites and supply chain configurations that satisfy the most stringent global requirements, facilitating simultaneous regulatory submissions across multiple markets. These synchronized approaches help drugs achieve the broad global presence necessary for blockbuster status without overwhelming US market dependence.
“The global medicines market has grown substantially, from approximately $1 trillion annually in 2013 to $1.5 trillion in 2022. This growth indicates that there are ample opportunities for drugs to achieve blockbuster status through international sales.”5
The Role of Innovation in Creating Global Blockbusters
Precision Medicine and Its Global Appeal
Precision medicine represents one of the most significant shifts in the pharmaceutical landscape, moving away from the traditional blockbuster model toward more targeted therapies. This approach focuses on developing medications for specific patient subpopulations based on genetic, biomarker, or other personal characteristics. While a single precision medicine product may target a smaller patient population than traditional blockbusters, these therapies often command premium prices globally due to their enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects in appropriate patients.
The pharmaceutical industry is increasingly exploring what might be called “distributed” or “incremental” blockbusters-collections of precision medicine products that collectively generate blockbuster-level revenue5. This approach allows companies to build global blockbuster franchises across multiple indications and patient populations rather than relying on a single broad-spectrum medication. By addressing specific patient needs with targeted solutions, these precision medicine portfolios can achieve strong adoption and reimbursement across global markets despite their higher prices, potentially reducing dependence on US sales for blockbuster status.
Addressing Unmet Medical Needs Across Different Regions
Developing medications that address significant unmet medical needs-particularly those with global distribution-represents another powerful strategy for achieving worldwide blockbuster status. Conditions that lack effective treatments, especially serious or life-threatening diseases, often receive accelerated regulatory reviews and more favorable reimbursement decisions across multiple markets simultaneously. This synchronized global access facilitates rapid revenue growth across diverse regions.
Oncology therapies like Keytruda exemplify this approach, addressing critical unmet needs in cancer treatment with innovative mechanisms that have transformed outcomes for patients worldwide. Keytruda’s rise to become the top-selling global medication in 2023, with $25 billion in sales, demonstrates how addressing fundamental unmet needs can drive exceptional performance across international markets8. Similar opportunities exist in areas like neurodegenerative diseases, certain infectious diseases, and autoimmune conditions, where effective treatments remain limited and the burden of disease spans continental boundaries.
Digital Therapeutics and Their International Potential
Digital therapeutics-software-based interventions that prevent, manage, or treat medical conditions-represent an emerging category with potentially distinctive international market dynamics. Unlike traditional pharmaceuticals, digital therapeutics may face different regulatory pathways, reimbursement mechanisms, and adoption barriers across global markets. However, they also offer unique advantages in international expansion, including reduced physical supply chain requirements, the ability to rapidly implement improvements, and potential for remote delivery to underserved populations.
While still emerging, digital therapeutics could eventually present novel pathways to global blockbuster status less dependent on traditional US pharmaceutical market dynamics. Their ability to scale across markets with lower marginal costs than physical products, combined with potential for real-world evidence generation at unprecedented scale, may create commercial opportunities that diverge significantly from traditional pharmaceutical market patterns. For companies pursuing blockbuster status without overwhelming US dependence, this emerging category warrants close attention.
Challenges and Barriers to Global Blockbuster Status
Regulatory Hurdles in Different Markets
Despite progress in regulatory harmonization, pharmaceutical companies pursuing global blockbuster status still face significant regulatory challenges across international markets. Each major regulatory region maintains distinct requirements regarding clinical trial design, safety monitoring, manufacturing standards, and post-approval commitments. These variations increase the complexity and cost of global drug development, potentially limiting the number of markets a company can practically enter.
Even when a medication receives approval across multiple regions, variations in approved indications, dosing recommendations, contraindications, and required monitoring can complicate global marketing efforts and confuse international prescribing patterns. For some specialized medications, particularly those requiring sophisticated administration or monitoring, regulatory requirements for healthcare provider training or certification may further complicate international expansion. Companies pursuing global blockbuster status must navigate these regulatory complexities while maintaining consistent core messaging about their products’ benefits and appropriate use.
Pricing Pressures and Market Access Challenges
Pricing and market access represent perhaps the most significant barriers to achieving global blockbuster status without heavy US market reliance. Most countries outside the United States employ various mechanisms to control pharmaceutical prices, including reference pricing, health technology assessments, mandatory discounts, price caps, and volume-based agreements. These measures typically result in substantially lower prices than those commanded in the US market, requiring much higher volume to achieve comparable revenue.
The pricing differential across markets creates both practical and political challenges for pharmaceutical companies. Setting prices too high in controlled markets may result in restricted reimbursement or limited patient access, reducing volume potential. Conversely, global reference pricing-where countries reference prices in other nations when setting their own-means that low prices in some markets can potentially impact achievable prices elsewhere. Navigating these interconnected pricing pressures while maintaining overall profitability requires sophisticated global strategy that few companies have fully mastered.
Competition from Biosimilars and Generics
The growing impact of biosimilar and generic competition across global markets significantly affects blockbuster sustainability, as illustrated by Humira’s experience with international biosimilar entry. When biosimilar versions of adalimumab entered European and other international markets, AbbVie experienced a 9.6% decrease in reported international Humira revenues despite continued US market exclusivity7. This bifurcated competitive landscape-with intense competition in some markets while maintaining exclusivity in others-creates complex strategic challenges for companies managing global brands.
The timing of patent expirations and competitive entry often varies across international markets due to differences in patent filing dates, regulatory data protection periods, and litigation outcomes. This asynchronous competition requires pharmaceutical companies to develop market-specific strategies that account for different competitive environments across their global footprint. For drugs seeking blockbuster status through balanced global revenue rather than US dominance, developing robust strategies to maintain value despite regional competitive entry becomes particularly important.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Considerations
Establishing and maintaining the global supply chain infrastructure necessary to support worldwide blockbuster status presents significant operational challenges. Manufacturing facilities must meet the quality standards of multiple regulatory authorities while production volumes must align with demand across diverse markets. International distribution networks must accommodate varying storage requirements, import regulations, and local distribution practices while maintaining product integrity throughout the supply chain.
These supply chain complexities increase with the sophistication of the medication involved. Biologics, cell therapies, and other advanced treatment modalities often require specialized handling, controlled temperature shipping, and limited shelf life, further complicating global distribution. For companies pursuing blockbuster status across diverse international markets rather than through US concentration, building supply chain capacity and resilience across multiple regions becomes a strategic imperative rather than merely an operational consideration.
Future Outlook: The Evolving Definition of Pharmaceutical Success
The Rise of “Distributed” Blockbusters
The pharmaceutical industry appears to be evolving toward what might be called “distributed” or “incremental” blockbusters-portfolios of related products that collectively generate blockbuster-level revenue even if no single medication reaches the billion-dollar threshold independently5. This approach aligns with the precision medicine paradigm, where medications increasingly target specific patient subpopulations based on genetic profiles, biomarkers, or other distinguishing characteristics rather than broad disease categories.
This distributed blockbuster model potentially reduces dependence on any single market, including the United States, as different portfolio components may find their strongest markets in different regions based on genetic factors, disease epidemiology, or healthcare system characteristics. For example, a cancer therapy targeting a mutation more common in Asian populations might generate its highest sales in that region, while a companion product addressing a mutation more prevalent in European populations might perform best there. Collectively, these targeted therapies could achieve blockbuster status through truly global performance rather than US concentration.
Emerging Markets as Primary Revenue Drivers
The relative importance of emerging markets in global pharmaceutical revenue continues to grow, with implications for future blockbuster development strategies. While the United States remains the single largest pharmaceutical market, the collective importance of major emerging markets-particularly China, Brazil, India, Russia, and others-is increasing rapidly. As these countries develop more sophisticated healthcare systems, expand insurance coverage, and increase healthcare spending, they represent increasingly viable primary markets rather than merely secondary opportunities.
For specific therapeutic categories, emerging markets may eventually surpass traditional markets in revenue potential due to larger patient populations, growing disease burden, or particular epidemiological patterns. Medications addressing conditions with high prevalence in emerging markets-such as certain infectious diseases, specific cancers with regional prevalence patterns, or conditions related to environmental factors-may find their largest markets outside traditional pharmaceutical strongholds. This evolving market balance creates potential pathways to blockbuster status centered on emerging market strength rather than US dominance.
How Technology is Reshaping Drug Development and Marketing
Technological advances continue to transform both pharmaceutical development and marketing, with significant implications for global market access and potential blockbuster pathways. Artificial intelligence and machine learning accelerate drug discovery and development, potentially reducing costs and increasing the number of viable drug candidates advancing to clinical trials. Real-world evidence generation capabilities allow companies to demonstrate value across diverse healthcare systems more effectively, supporting market access and reimbursement globally.
Digital marketing technologies enable more targeted and efficient communication with healthcare providers and patients across international markets, reducing the resource intensity traditionally associated with global marketing campaigns. Telemedicine and digital health platforms create new channels for patient identification, diagnosis, and treatment initiation, potentially accelerating adoption curves for new medications globally. These technological capabilities collectively reduce some of the historical advantages of US market concentration, creating more viable pathways to global blockbuster status through balanced international performance.
Key Takeaways
The global pharmaceutical landscape is evolving in ways that increasingly enable drugs to achieve blockbuster status without overwhelming reliance on US sales. While the United States remains the single largest and most lucrative pharmaceutical market, several key factors are reshaping the pathways to billion-dollar drug status:
- Growing Global Market Size: The worldwide pharmaceutical market continues to expand significantly, with Europe projected to reach $496.74 billion by 2033 and Japan expected to reach $101.90 billion in the same timeframe34. This growth creates larger opportunities outside the US market.
- Changing Competitive Dynamics: The experience of blockbusters like Humira demonstrates the vulnerability of US-centric revenue models, with international biosimilar competition driving a 9.6% decrease in ex-US revenues even while US exclusivity continued7. This suggests value in developing more balanced global revenue streams.
- Precision Medicine Evolution: The shift toward more targeted therapies creates opportunities for “distributed blockbusters”-portfolios of related medications that collectively generate blockbuster-level revenue across multiple patient populations and geographic regions5.
- Emerging Market Importance: Rapidly developing healthcare systems in countries like China create significant new revenue opportunities, as demonstrated by Lipitor’s continued strong performance in China even after US patent expiration5.
- Technology Enablement: Advances in digital technologies reduce some of the historical barriers to efficient global commercialization, making balanced international performance more achievable than in previous eras.
While achieving blockbuster status without significant US sales remains challenging, the evolving global pharmaceutical landscape presents increasingly viable pathways to billion-dollar drug status through strong international performance. Companies that develop sophisticated global strategies addressing the unique characteristics of diverse markets will be best positioned to create truly global blockbusters less dependent on any single country’s pharmaceutical market.
FAQs About Global Pharmaceutical Blockbusters
What defines a blockbuster drug in the pharmaceutical industry?
A blockbuster drug is officially defined as a medication that generates at least $1 billion in annual sales revenue for the company that sells it. These drugs typically address common medical conditions affecting large patient populations, enjoy patent protection from competition, represent significant therapeutic advancements, and achieve widespread recognition among healthcare providers and patients. Historical examples include Lipitor for cholesterol management, Humira for various autoimmune conditions, and more recently, Keytruda for cancer treatment.
Which pharmaceutical markets outside the US offer the greatest potential for blockbuster sales?
The European and Chinese markets currently represent the greatest non-US potential for pharmaceutical blockbusters. Europe’s pharmaceutical market is projected to reach $496.74 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.7%, with particularly strong opportunities in Germany, France, and the UK. China’s rapidly expanding healthcare system, growing middle class, and massive population make it increasingly vital for global pharmaceutical strategy. Other important markets include Japan ($82.27 billion in 2024), Brazil, and increasingly, India, which offers enormous scale despite lower per-capita spending.
How does biosimilar competition affect global blockbuster sustainability?
Biosimilar competition significantly impacts blockbuster sustainability, often affecting international markets before the US due to differing patent expiration timelines and regulatory pathways. Humira experienced this directly, with international revenues decreasing 9.6% in 2021 due to biosimilar competition outside the US while US exclusivity continued. This asynchronous competition creates complex global lifecycle management challenges, requiring market-specific strategies that account for different competitive environments across regions. Effectively navigating biosimilar competition requires sophisticated approaches to maintaining brand value and patient access despite increasing alternatives.
What strategies do pharmaceutical companies use to achieve global blockbuster status?
Successful global pharmaceutical companies employ multifaceted strategies to achieve worldwide blockbuster status, including: (1) designing global clinical development programs that simultaneously satisfy multiple regulatory agencies’ requirements; (2) implementing differential pricing strategies tailored to each market’s economic conditions and healthcare system structure; (3) developing culturally appropriate educational and marketing approaches for diverse provider and patient populations; (4) building flexible supply chains capable of serving multiple international markets efficiently; and (5) increasingly, focusing on precision medicine approaches that can achieve collective blockbuster status across multiple targeted therapies and patient populations.
Is the traditional blockbuster model still viable in today’s pharmaceutical marketplace?
The traditional blockbuster model-developing broad-spectrum medications for common conditions and generating the majority of revenue from US sales-faces mounting challenges but remains viable for certain therapeutic categories. Oncology, in particular, continues to produce traditional blockbusters, as demonstrated by Keytruda’s rise to become the world’s top-selling drug in 2023 with $25 billion in sales. However, the industry is increasingly evolving toward modified blockbuster models, including “distributed blockbusters” comprising multiple precision medicines, more globally balanced revenue profiles less dependent on US sales, and digital therapeutic approaches that may eventually create entirely new blockbuster paradigms.
Citations:
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/299702/world-pharmaceutical-market-growth-by-region-forecast/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/734171/pharmacies-ranked-by-rx-market-share-in-us/
- https://www.novaoneadvisor.com/report/europe-pharmaceutical-market
- https://www.imarcgroup.com/japan-pharmaceutical-market
- https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/can-drugs-be-blockbusters-without-relying-on-us-sales/
- https://synapse.patsnap.com/blog/what-is-a-blockbuster-drug
- https://www.healio.com/news/gastroenterology/20230106/humira-exclusivity-expires-in-2023-will-biosimilar-boom-benefit-patients-or-industry
- https://www.fiercepharma.com/pharma/whos-no-1-25b-sales-mercks-keytruda-appears-set-be-top-selling-drug-2023
- https://www.axios.com/2019/10/30/lipitor-pfizer-drug-patent-sales-2019
- https://efpia.eu/media/2rxdkn43/the-pharmaceutical-industry-in-figures-2024.pdf
- https://www.iqvia.com/blogs/2023/11/aiming-higher-a-blockbuster-ambition-fit-for-our-times
- https://www.kiplinger.com/article/investing/t052-c000-s001-biggest-blockbuster-drugs-of-all-time.html
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/pharmaceutical-market-report
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3153529/
- https://www.iqvia.com/insights/the-iqvia-institute/reports-and-publications/reports/the-global-use-of-medicines-2024-outlook-to-2028
- https://media.nature.com/original/magazine-assets/d41573-022-00213-z/23814366
- https://www.novaoneadvisor.com/report/pharmaceutical-market
- https://www.fiercepharma.com/financials/does-1b-really-make-a-blockbuster-anymore
- https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg18224515-800-blockbuster-challenge/
- https://www.biospace.com/china-pharmaceutical-market-estimated-to-reach-a-cagr-of-7-50-during-2024-2032-impelled-by-the-rising-geriatric-population
- https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/impact-of-covid-19-on-pharmaceuticals-market-102685
- https://www.magnetaba.com/blog/u-s-pharmaceutical-statistics
- https://www.precedenceresearch.com/europe-pharmaceutical-cdmo-market
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/horizon/outlook/pharmaceutical-market/japan
- https://www.ciprocess.com/pharmaceuticals-market-in-China-and-NMPA-regulations.htm
- https://www.biospace.com/press-releases/pharmaceutical-market-size-to-surpass-usd-2-82-trillion-by-2033
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/us-pharmaceuticals-market-report
- https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/market-insight/europe-pharmaceutical-drugs-market-3541
- https://www.astuteanalytica.com/industry-report/japan-pharmaceutical-manufacturing-market
- https://www.gtlaw.com/en/insights/2024/11/china-on-the-move-new-level-of-opening-up-in-health-care-sector
- https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/02/07/3022874/0/en/Pharmaceutical-Market-Size-Expected-to-Reach-USD-3-033-21-Bn-by-2034.html
- https://atelfo.github.io/2023/02/26/pharmaceutical-blockbusters-the-past-present-and-future.html
- https://www.living.tech/articles/worlds-bestselling-drugs-addicted-broken-us-healthcare
- https://www.globalxetfs.com/articles/another-year-of-blockbuster-drug-and-treatment-approvals-possible-in-2023/
- https://academic.oup.com/book/40666/chapter/348351392
- https://www.zs.com/insights/dont-abandon-the-blockbuster-drug-model-just-yet
- https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/p/drug-sales/drugname/LIPITOR
- https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/analyst-comment/abbvies-immunology-humira-losses/
- https://assets.roche.com/f/176343/x/40d59063c5/hy23e.pdf
- https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/news/keytruda-remains-merck-cos-biggest-2023-success-story-as-patent-expiry-looms/
- https://xtalks.com/top-15-cardiovascular-disease-drugs-in-2023-by-2022-sales-data-3717/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/318206/revenue-of-humira/
- https://www.biochempeg.com/article/389.html
- https://www.pearceip.law/2025/02/04/merck-msds-worldwide-keytruda-sales-grow-18-to-us29-5-billion-in-2024/
- https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/atorvastatin-api-market-7885
- https://www.biospace.com/business/abbvies-humira-continues-to-lose-market-share-as-biosimilars-gain-ground-report
- https://www.globaldata.com/data-insights/healthcare/the-global-drug-sales-of-herceptin-1127376/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1269401/revenues-of-keytruda/
- https://xtalks.com/top-40-best-selling-cancer-drugs-in-2023-by-2022-data-3702/
- https://s21.q4cdn.com/488056881/files/doc_financials/2023/q4/Q4-2023-Merck-Earnings-Deck-FINAL.pdf
- https://www.biochempeg.com/article/427.html
- https://assets.roche.com/f/174029/x/2fb3fece51/roche-global-annual-report-2023.pdf
- https://www.daiichisankyo.com/files/investors/library/quarterly_result/2023/FY2023_Q4_Reference_Data_E.pdf
- https://www.biospace.com/press-releases/ad-hoc-announcement-pursuant-to-art-53-lr-roche-reports-strong-2024-results-with-7-sales-growth-fourth-quarter-marks-third-straight-quarter-of-9-growth
- https://www.fiercepharma.com/pharma/top-20-pharma-companies-2023-revenue
- https://www.merck.com/news/merck-announces-fourth-quarter-and-full-year-2023-financial-results/
- https://firstwordpharma.com/story/5906091
- https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/78003/000007800320000014/pfe-exhibit13x12312019.htm
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/254341/pfizers-worldwide-viagra-revenues-since-2003/
- https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/277371265a705c356c968977e87446ae/international-price-comparisons.pdf
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10203693/
- https://www.fiercepharma.com/special-report/top-20-drugs-by-2020-sales
- https://www.ahdbonline.com/web-exclusives/a-retrospective-trend-analysis-of-utilization-spending-and-prices-for-generic-statins-in-the-us-medicaid-population-1991-2022
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2019-09-24/china-drugmakers-slump-as-price-cuts-loom-in-next-buying-round-k0xeuq5u
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atorvastatin
- https://www.drugs.com/article/atorvastatin.html
- https://journalofethics.ama-assn.org/article/me-there-no-substitute-authenticity-uniqueness-and-lessons-lipitor/2010-10
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1089322/top-drugs-by-lifetime-sales-globally/
- https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-statin-market/77560/
- https://newsroom.viatris.com/2024-02-28-Viatris-Reports-Fourth-Quarter-and-Full-Year-2023-Financial-Results-and-Provides-2024-Financial-Guidance
- https://www.amgen.com/newsroom/press-releases/2024/02/amgen-reports-fourth-quarter-and-full-year-2023-financial-results
- https://roche.com/fb23e.pdf
- https://roche.com/appendix-tables-fy-2024.pdf
- https://assets.roche.com/f/176343/x/a9eae6e6b9/appendix-tables-hy-2024.pdf
- https://www.delveinsight.com/blog/roches-her2-positive-breast-cancer-therapies
- https://assets.roche.com/f/176343/x/5a5b5d48d1/240201_ir_fy23_en.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2213538324000675
- https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/china-atorvastatin-market-report-2021-2025—sales-value-will-continue-to-grow-301354959.html
- https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20150806005563/en/Research-and-Markets-Investigation-Report-on-Chinas-Atorvastatin-Market-2010-2019-Featuring-Ebang-Pharmaceutical-Pfizer-Topfond-Beijing-Jialin-Pharmaceutical
- https://www.statista.com/outlook/hmo/pharmaceuticals/lipid-lowering-agents/china
- https://s21.q4cdn.com/317678438/files/doc_financials/2018/ar/Pfizer-2019-Financial-Report.pdf
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/lipitor-short-account-its-life-cycle-wallace-macindoe-phd-mba
- https://s28.q4cdn.com/781576035/files/doc_financials/2019/q4/Q4-2019-PFE-Earnings-Release.pdf