Last updated: October 15, 2025
Introduction
Gilead Sciences Inc. stands as a formidable player within the global pharmaceutical industry, distinguished by its focus on innovative therapies for infectious diseases, oncology, and liver health. As of 2023, the company’s strategic positioning, product portfolio, and R&D trajectory continue to influence prevailing trends in the biotechnology sector. This analysis explores Gilead's market standing, core strengths, competitive challenges, and strategic opportunities, providing vital insights for stakeholders navigating a dynamic and competitive landscape.
Gilead’s Market Position
Leadership in Infectious Diseases
Gilead’s reputation originates from pioneering antiviral therapies, notably within HIV/AIDS and hepatitis C (HCV). Its flagship products, such as Truvada and Harvoni, have set industry standards, establishing Gilead as a leader in these segments. As of 2022, Gilead commanded approximately 35-40% of the global HCV treatment market, highlighting its dominance on several key markets, including the U.S., Europe, and Asia-Pacific [1].
Expansion into Oncology and COVID-19
In recent years, Gilead has diversified beyond infectious diseases, increasingly investing in oncology and anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Its acquisition of Immunomedics in 2020, alongside strategic collaborations with biotech innovators, positioned Gilead as a rising contender in cancer immunotherapy, exemplified by Trodelvy, approved for triple-negative breast cancer. Additionally, Gilead’s pivotal role in COVID-19 therapeutic development, notably Remdesivir, bolstered its portfolio and visibility during the pandemic, although the COVID-19 vaccine market remains highly competitive and saturated.
Global Footprint and Revenue Dynamics
Gilead's revenues, primarily derived from HIV (~45%), HCV (~20%), and other antiviral markets (~10-15%), are aligned with its target sectors. Despite intense competition from firms like Merck, AbbVie, and Cipla, Gilead’s robust pipeline and established market presence sustain its competitive position. Regionally, North America remains its primary revenue source, with expanding footprints in Europe and emerging markets such as Asia and Latin America.
Core Strengths of Gilead
1. Pioneering Antiviral Portfolio
Gilead’s foundational strength lies in its extensive antiviral drug portfolio. With high barriers to entry and significant patent protections, its HCV and HIV treatments have achieved high market penetration. Their combination therapies, such as Epclusa, exemplify multi-drug regimens that optimize patient adherence and clinical outcomes, reinforcing Gilead’s leadership.
2. R&D Innovation and Strategic Acquisitions
Gilead invests approximately 20% of its revenue into R&D annually, underlining its commitment to innovation. Notable acquisitions, such as Immunomedics, reinforce its oncology ambitions, while collaborations with biotech firms accelerate its pipeline in immunotherapy, cell therapy, and next-generation anti-infective agents. This strategic approach fosters a continuous influx of novel therapies aligned with evolving disease paradigms.
3. Strong Regulatory and Commercial Infrastructure
Gilead benefits from a well-established global network for clinical development, regulatory navigation, and commercialization. Its early access programs and strategic partnerships facilitate rapid market penetration, particularly in multiple jurisdictions with diverse healthcare systems.
4. Commitment to Pandemic Response
The development and deployment of Remdesivir as a COVID-19 treatment exemplify Gilead’s agility and capacity to respond swiftly to global health crises. This asset enhanced its visibility and provided a foundation for future antiviral innovations.
Strategic Challenges
1. Patent Expirations and Generic Competition
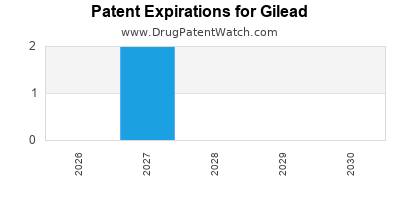
Gilead faces imminent patent expirations for flagship HCV therapies, notably Harvoni and Sovaldi, which could lead to significant revenue erosion via generic competition, especially in price-sensitive emerging markets.
2. Pricing Pressures and Market Access
Increasing scrutiny over drug pricing, especially for high-cost antivirals, constrains revenue growth. Governments and payers are demanding value-based pricing, which challenges Gilead’s historically premium pricing models. This was exemplified during the scaling-back of hepatitis C programs due to cost containment efforts.
3. Competitive Innovation Threats
While Gilead’s antiviral therapies remain market leaders, competitors such as AbbVie, Merck, and newer biotech entrants are rapidly advancing, with emerging therapies targeting drug-resistant HIV strains and next-generation hepatitis solutions. Oncology is characterized by intense innovation, with firms like Roche and AstraZeneca launching competing therapies.
4. Pipeline Risks and Clinical Development Challenges
Despite substantial R&D investments, clinical trial failures or delays can hinder Gilead’s pipeline momentum. Balancing investment risks with potential breakthroughs remains an ongoing strategic challenge.
Strategic Insights and Future Outlook
Diversification through Oncology and Cell Therapy
Gilead’s oncology pipeline, particularly through its acquisition of Immunomedics and collaborations in cellular therapies, signifies a pivotal pivot beyond traditional antiviral markets. Continued investment in immune-oncology, combination therapies, and personalized medicine could transform Gilead into a broader biopharmaceutical powerhouse.
Leveraging Digital and Precision Medicine
Integrating digital health solutions, biomarker development, and genomics can enhance Gilead's drug development efficiency and patient stratification, aligning with industry trends toward precision medicine.
Navigating Patent Cliffs
Proactive lifecycle management, including patent extensions, new formulation approvals, and combination regimens, will be essential to mitigate revenue declines from patent expiries.
Expanding in Emerging Markets
Growing healthcare infrastructure and disease burden in emerging markets offer substantial opportunities. Tailoring pricing strategies and forging local partnerships can accelerate Gilead’s market access.
Focus on Sustainable Innovation
Investing in next-generation antivirals that tackle resistant strains, alongside oncology and inflammatory diseases, positions Gilead to sustain competitive advantages amid industry consolidation.
Key Takeaways
-
Gilead holds a dominant position in antiviral therapeutics, notably for HIV and HCV, reinforced by high-quality R&D, strategic acquisitions, and global manufacturing capabilities.
-
Its diversification into oncology and cell therapy, notably via Immunomedics, signals a strategic shift toward broader disease areas with high growth potential.
-
Patent expirations pose significant revenue risks; proactive lifecycle management and pipeline innovation are critical to counteract impending generic competition.
-
Pricing pressures, healthcare reforms, and intense competition necessitate strategic agility and value-based approaches to sustain profitability.
-
Expanding into emerging markets and integrating digital health can unlock new growth avenues, ensuring Gilead’s resilience against industry shifts.
FAQs
1. How does Gilead maintain its leadership in the HIV and HCV markets amid increasing competition?
Gilead sustains its leadership through continuous innovation, high-efficacy combination therapies, and strategic patent extensions. Its early market entry, robust R&D, and patient-centric approaches solidify its position despite competitive pressures.
2. What are the primary growth drivers for Gilead beyond infectious diseases?
The company is actively scaling its oncology and cell therapy portfolio through acquisitions like Immunomedics and collaborations in immuno-oncology, aiming to capitalize on personalized medicine and expanded therapeutic areas.
3. How significant is Gilead’s COVID-19 antiviral Remdesivir in its overall revenue?
While instrumentally relevant during the pandemic, Remdesivir's contribution to Gilead’s annual revenue remains modest relative to core antiviral segments, but it enhances the company's strategic reputation and pipeline prospects.
4. What strategies can Gilead adopt to mitigate revenue declines caused by patent cliffs?
Implementing lifecycle management, developing next-generation formulations, expanding into new indications, and diversifying its portfolio can cushion the impact of patent expiries.
5. How is Gilead leveraging digital health and personalized medicine?
Gilead invests in biomarker research, digital monitoring platforms, and data analytics to enhance clinical trial efficiency, optimize patient outcomes, and tailor treatments, aligning with trends toward precision healthcare.
References
[1] Global Market Insights. (2022). HCV market share and competitive landscape report.