In an industry where the stakes are measured in billions and the outcomes in human lives, how does a pharmaceutical giant like Pfizer consistently navigate turbulent waters, sustain innovation, and deliver shareholder value? The answer lies in a meticulously crafted strategy of “precision investment.” This report delves into Pfizer’s strategic approach to its portfolio, research and development (R&D), and capital allocation, demonstrating how a data-driven, highly targeted methodology can translate into enduring competitive advantage. For business professionals seeking to optimize their strategic foresight and leverage intellectual property for market leadership, Pfizer’s journey offers a compelling blueprint.
The Imperative of Precision in Modern Pharmaceutical Investment
The pharmaceutical sector, a crucible of scientific advancement and economic dynamism, operates under unique pressures. The pursuit of groundbreaking therapies demands colossal investments and carries inherent risks. In this environment, a generalized approach to investment is no longer sufficient; precision has become not just an advantage, but a fundamental requirement for sustained success.
Defining Precision in Pharma Investments: Beyond Broad Strokes
Precision in pharmaceutical investments extends far beyond merely targeting specific diseases or patient populations. It represents a holistic, data-informed strategy that permeates every facet of a biopharmaceutical company’s operations, from the earliest stages of R&D to market entry and capital deployment. At its core, it is about optimizing every dollar spent to maximize both therapeutic impact for patients and financial returns for shareholders.
This multifaceted approach encompasses several key components. Firstly, targeted R&D focuses on identifying and pursuing specific biological pathways, patient subgroups, and areas of high unmet medical need. This involves rigorous scientific validation and a deep understanding of disease mechanisms. Secondly, strategic mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are executed not as opportunistic plays, but as precise maneuvers to fill critical pipeline gaps, acquire complementary technologies, or bolster existing core therapeutic areas. Thirdly, data-driven decision-making is paramount, leveraging advanced analytics, including artificial intelligence (AI), to de-risk investments, identify high-potential opportunities, and forecast market dynamics with greater accuracy. Finally, dynamic portfolio management ensures continuous evaluation and adjustment of the pipeline based on evolving scientific understanding, shifting market landscapes, and competitive intelligence. This constant recalibration ensures resources are consistently directed towards the most promising avenues.
The pharmaceutical industry is inherently high-risk, characterized by an arduous and expensive drug development process. Research indicates that R&D failure rates can exceed 90% in clinical trials, with the average cost to bring a single asset to market reaching approximately $2.23 billion in 2024.1 Given these staggering figures, broad, untargeted investments are simply unsustainable. Without a precise approach, companies risk squandering vast resources on ventures with low probabilities of success, jeopardizing their long-term viability. Therefore, precision in investment is not merely a competitive differentiator; it represents a fundamental strategic evolution, akin to a surgeon making a precise incision to save a life. It is a necessary adaptation for long-term survival and profitability in the face of immense financial and scientific challenges, ensuring that every investment dollar is deployed with maximum intent and potential impact.
The Shifting Sands of the Pharmaceutical Landscape: Why Precision is Paramount
Several powerful external forces are compelling pharmaceutical companies to adopt a more precise investment methodology. One of the most significant is the looming “patent cliff.” The industry faces potential revenue losses exceeding $300 billion by 2030 due to patent expirations, including several mega-blockbuster drugs such as Merck’s Keytruda.3 This impending loss of exclusivity creates an urgent and undeniable imperative to replenish pipelines with new, innovative products that can offset these revenue declines. Without a precise strategy for identifying and developing or acquiring these new assets, companies risk substantial financial contraction.
Compounding this challenge are increasing regulatory headwinds. Governments worldwide are intensifying efforts to reduce drug prices, exemplified by the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the Most-Favored-Nation (MFN) executive order.5 Albert Bourla, Pfizer’s Chairman and CEO, characterized the MFN order as a “radical change” that introduces dual risks: downward pressure on U.S. prices and uncertainty in trade negotiations aimed at raising international prices. Such interventions directly impact pharmaceutical margins and influence R&D investment decisions, necessitating a more targeted and efficient allocation of resources.
The competitive landscape is also intensifying. The market is witnessing an proliferation of new medicines, a growing number of competitors, and a faster pace of change in treatment standards. In this dynamic environment, speed to market and organizational agility are paramount. Furthermore, while R&D productivity has shown signs of improvement, the underlying costs and complexity of research continue to rise, demanding ever more efficient processes to bring therapies from discovery to patient.
Adding another layer of complexity, the political and regulatory environment can significantly influence strategic choices. For instance, the “Trump factor,” as noted in industry analyses, could potentially foster a more M&A-friendly environment due to anticipated new appointments at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). This is not merely a political observation; it represents a significant regulatory shift that directly impacts investment strategy. A more favorable M&A environment, coupled with the pressing reality of the patent cliff, accelerates the need for precision in identifying the right acquisition targets. If regulatory hurdles for large deals are perceived to lessen, companies can more aggressively pursue strategic acquisitions to precisely fill pipeline gaps, rather than relying solely on the slower and inherently riskier path of internal R&D. This establishes a direct causal link between political shifts and corporate investment strategies, highlighting how external policy changes can become powerful catalysts for internal strategic reorientation towards greater precision.
Pfizer’s Strategic Compass: Navigating Growth and Innovation
Pfizer’s trajectory in recent years illustrates a deliberate and strategic evolution, moving from a broadly diversified healthcare conglomerate to a sharply focused biopharmaceutical leader. This transformation underscores a commitment to precision in its operational and investment strategies.
A Legacy of Innovation Meets Future-Forward Vision
Pfizer has undergone significant structural changes, including the spin-off of its Upjohn unit and the merger of its Consumer Healthcare segment, to streamline its operations and sharpen its focus on innovative drugs and vaccines. This strategic divestiture allowed the company to concentrate its resources on areas with the highest potential for scientific breakthrough and market impact.
Albert Bourla, Pfizer’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, articulated this forward-looking vision, stating that Pfizer is “sharpening [its] focus to improve the productivity of [its] R&D pipeline and advance the clear strategic priorities guiding [its] company in 2025”. This statement is more than just corporate rhetoric; it signifies a deliberate and precise re-anchoring of Pfizer’s growth strategy.
The company’s financial reporting for 2024 offers a compelling illustration of this strategic reorientation. While Pfizer reported strong full-year 2024 revenues of $63.6 billion, reflecting 7% year-over-year operational growth, a crucial detail emerges when examining the figures “excluding contributions from Paxlovid and Comirnaty”.9 These pandemic-era products, while generating substantial revenue, were extraordinary and not representative of sustainable, long-term core business growth. The fact that Pfizer consistently highlights a 12% operational revenue growth
excluding these products 9 is a clear strategic narrative. It signifies a proactive management of the transition away from these temporary revenue drivers. This emphasis demonstrates a precise commitment to building a robust underlying business that can thrive independently of pandemic-related demand, showcasing a deliberate re-anchoring of their growth strategy towards sustainable, core pharmaceutical innovation.
Strategic Pillars: Pfizer’s Core Therapeutic Areas
Pfizer strategically concentrates its efforts in six core therapeutic areas where it believes it is “best positioned to develop medicines for much needed therapy areas”.11 These areas include Anti-infectives, Inflammation & Immunology, Internal Medicine, Oncology, Rare Diseases, and Vaccines.11 This focused approach allows for deeper expertise, more targeted R&D, and a more efficient allocation of resources.
Oncology: The Crown Jewel of Future Growth
Pfizer Oncology is a cornerstone of the company’s future growth strategy. The division is dedicated to advancing cancer biology and translating scientific knowledge into high-impact medicines for patients.12 This commitment extends to actively seeking partnerships in core areas such as tumor cell biology, precision medicine, tumor-targeted therapeutics, and immuno-oncology.12
Pfizer’s oncology pipeline is particularly robust, poised to deliver critical readouts in 2025. Key candidates include Padcev (enfortumab vedotin), with Phase 3 data anticipated for muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC), a condition affecting over 60,000 U.S. patients annually.13 Success in this indication could significantly expand Padcev’s market potential. Another pivotal asset is Elrexfio (elranatamab), with a Phase 3 readout expected for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma in earlier treatment lines, potentially positioning it as a first-line therapy for a global patient population of approximately 200,000.13 Other late-stage oncology candidates include sasanlimab for BCG-naive high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and vepdegestrant for ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer.14
The industry is currently grappling with a significant patent cliff, which threatens substantial revenue streams.3 In this context, oncology, with its high unmet medical needs and potential for premium pricing due to complex, often personalized treatments, serves as a vital strategic counter-balance. By heavily investing in and acquiring oncology assets, as exemplified by the Seagen acquisition, Pfizer is precisely targeting a segment with robust long-term growth potential. This strategic focus can effectively offset future revenue losses from expiring patents on other drugs, demonstrating a proactive, defensive, and offensive precision play designed to secure the company’s financial future.
Vaccines: Sustaining Impact Beyond the Pandemic Era
While the revenue contributions from Comirnaty, Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine, are naturally declining from their pandemic peaks, vaccines remain a core and strategically vital area for the company. Pfizer is actively advancing its respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, ABRYSVO®, which has received expanded recommendations and approvals across various age groups and international markets.15 This demonstrates a continued commitment to addressing significant public health needs with innovative vaccine solutions. The late-stage pipeline also includes promising candidates such as a
C. difficile vaccine and an mRNA-based flu/COVID combination vaccine, highlighting ongoing innovation in infectious disease prevention.14 Furthermore, Pfizer is at the forefront of maternal immunization, diligently working to discover and develop vaccines that can protect young infants globally through maternal vaccination.16
The unprecedented success of Comirnaty, an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine, provided Pfizer with invaluable experience and a validated technological platform. A key strategic approach is that Pfizer is not allowing the potential of this platform to be confined to COVID-19. By actively developing an mRNA-based flu/COVID combination vaccine 14 and exploring the application of mRNA technology in rare genetic diseases 12, Pfizer is precisely leveraging a proven technological capability to diversify its vaccine portfolio and explore entirely new therapeutic modalities. This represents a strategic re-deployment of a core innovation, extending the value and impact of its initial, pandemic-driven investment into new frontiers of medicine.
Internal Medicine & Metabolic Therapies: Addressing Global Health Burdens
Pfizer’s Internal Medicine focus addresses some of the most prevalent global health burdens, including cardiovascular (heart) and metabolic diseases like Type 2 diabetes, obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), as well as kidney diseases.12 The company aims to develop novel medicines that treat or prevent disease progression and significantly improve patients’ quality of life.
A significant area of pipeline activity is Pfizer’s obesity strategy, which is considered a “wildcard” with substantial market potential. The company is developing a Phase 2 GIPR antagonist, a drug designed to tackle metabolic dysfunction through personalized combinations, targeting not just weight loss but also cardiometabolic risks such as hypertension or diabetes.13 If successful, this could position Pfizer as a leader in a market estimated to be over $10 billion, competing with established players.13 While the development of its oral GLP-1R agonist, danuglipron, was discontinued in April 2025 14, Pfizer’s continued investment in the broader metabolic space with a different mechanism of action demonstrates a crucial aspect of precision:
strategic resilience. This is not about avoiding failure, but rather about learning from setbacks and adapting the investment strategy to pursue the overarching market opportunity with alternative, potentially more effective, therapeutic approaches. This illustrates a calculated, long-term commitment to a high-value therapeutic area, even after an initial stumble, reflecting a flexible and enduring precision in its investment philosophy.
Inflammation & Immunology and Rare Diseases: Unlocking Niche Opportunities
Beyond the large-scale markets of oncology and metabolic therapies, Pfizer maintains a focused commitment to Inflammation & Immunology (I&I) and Rare Diseases. In I&I, the company is dedicated to discovering and developing novel therapeutics for chronic immune diseases, striving to address the root causes at a molecular level rather than merely providing symptomatic relief.12 This includes efforts in rheumatology, gastroenterology/hepatology, and medical dermatology.12
Similarly, in Rare Diseases, Pfizer aims to be a leader, focusing on rare hematology, neurology, renal, cardiology, and metabolic conditions. This includes a strong interest in genetic-based approaches such as gene therapy and gene editing.12
While oncology and metabolic diseases represent expansive, high-profile markets, Pfizer’s continued and dedicated focus on Inflammation & Immunology and Rare Diseases 11 demonstrates a nuanced and sophisticated precision strategy. These therapeutic areas often involve smaller patient populations, but they frequently present significant unmet medical needs, which can translate into premium pricing and, consequently, higher internal rates of return (IRR) for novel mechanisms of action. This approach highlights a balanced portfolio strategy, where precision means identifying and strategically investing in both large-market opportunities and high-value niche segments. It reflects a comprehensive understanding that competitive advantage can be forged not only through scale but also through targeted innovation in specialized, underserved areas.
The Engine Room: Pfizer’s R&D Strategy and Pipeline Precision
At the heart of Pfizer’s precision investment model lies its sophisticated R&D engine, a powerhouse designed to translate cutting-edge science into impactful therapies. This engine is characterized by its embrace of advanced technologies, a strategically diverse pipeline, and a meticulous approach to portfolio optimization.
Embracing Cutting-Edge Science: Precision Medicine, Gene Therapy, and mRNA
Pfizer’s R&D strategy is fundamentally guided by a philosophy of precision medicine. This approach is “not only a focus of our R&D strategy, but a philosophy that guides everything we do”.16 It involves a deep understanding of the biological basis of disease, leveraging new technology platforms to develop highly targeted therapies.
A significant area of focus is gene therapy, where Pfizer is pioneering breakthroughs for rare genetic diseases, particularly for conditions where current standards of care fall short.16 This commitment reflects an investment in potentially curative treatments that address profound unmet needs. Similarly, the company is actively expanding its
mRNA scientific innovation, moving beyond its initial success with COVID-19 vaccines. This technology is now being explored for infectious diseases like influenza and shingles, and critically, its application is being extended to rare genetic diseases, demonstrating a versatile and forward-looking approach to drug discovery.12
Central to this advanced scientific endeavor is the increasing role of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI is rapidly becoming a critical emerging technology in precision oncology and drug development more broadly. It is utilized to analyze massive datasets, identify pertinent patterns, and predict the potential efficacy and safety profiles of investigational molecules.18 Pfizer is leveraging AI to better design clinical trials and to synthesize complex multi-omic information, gaining a more complete understanding of challenging diseases.18 Beyond R&D, AI also significantly enhances decision-making in pharmaceutical portfolio management, leading to improved efficiency and substantial reductions in R&D costs.19
The explicit mention of AI’s pervasive role in precision oncology and drug development 18 signifies more than just technological adoption; it represents a profound shift in how R&D investments are guided. AI’s capacity to “discern complex, non-linear relationships within datasets” and to “identify potential risks early in the drug development lifecycle” 19 directly enables a higher degree of
precision in R&D investment. It empowers Pfizer to make more informed, data-driven decisions about which drug candidates to advance, how to design clinical trials for optimal outcomes, and where to strategically allocate its considerable resources. This effectively de-risks the inherently uncertain R&D process, allowing for a more targeted and efficient pursuit of breakthrough therapies. Thus, AI serves as the unseen technological backbone, providing the crucial intelligence that underpins Pfizer’s commitment to investment precision.
Pipeline Powerhouse: Key Candidates and Anticipated Milestones (2024-2025)
Pfizer’s product pipeline is a testament to its robust R&D capabilities and strategic focus. As of April 29, 2025, the company’s pipeline comprises a total of 108 candidates across various development phases: 47 in Phase 1, 28 in Phase 2, 30 in Phase 3, and 3 in the Registration phase.17 This distribution indicates a healthy balance of early-stage exploration and late-stage assets nearing market readiness.
The year 2025 is anticipated to be a period of significant pipeline catalysts for Pfizer. The company expects 13 Phase 3 program starts, up to nine late-stage readouts, and four regulatory decisions.13 These milestones include several potential mega-blockbuster treatments in critical therapeutic areas such as oncology, vaccines, and obesity, underscoring the near-term potential for substantial revenue generation.20
Key examples from the late-stage pipeline include:
- Oncology: Padcev, being evaluated for muscle-invasive bladder cancer; Elrexfio, for earlier-line multiple myeloma; sasanlimab, for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer; and vepdegestrant, for ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer.13
- Vaccines: A C. difficile vaccine and an mRNA-based flu/COVID combination vaccine are in late-stage development.14
- Internal Medicine: A Phase 2 GIPR antagonist is being explored for metabolic dysfunction.13
This comprehensive pipeline, with its diverse array of candidates across various therapeutic areas and development phases, demonstrates a deliberate strategy to mitigate concentration risk. By not over-relying on any single therapeutic area or a handful of potential blockbuster drugs, Pfizer ensures that its growth drivers are diversified. This approach helps to spread risk, minimizing the impact of individual pipeline setbacks, such as the discontinuation of danuglipron, or unforeseen market shifts. The high number of late-stage candidates and anticipated catalysts further reinforces this strategic approach, ensuring multiple potential avenues for future revenue growth and reinforcing the company’s commitment to a balanced and resilient portfolio.
Here is a snapshot of Pfizer’s product pipeline:
Table 2: Pfizer’s Product Pipeline Snapshot by Development Phase and Area of Focus (as of April 29, 2025)
| Development Phase | Total Candidates | Examples (Area of Focus & Product) | |||
| Phase 1 | 47 | Vaccines: ABRYSVO (pediatric RSV) 17 | Inflammation & Immunology: CTB+AVP (cUTI), Dekavil (Rheumatoid Arthritis) 17 | Oncology: felmetatug vedotin (Advanced Solid Tumors) 17 | Internal Medicine: PF-06954522 (Chronic Weight Management) 17 |
| Phase 2 | 28 | (Specific examples not detailed in provided material, but general areas include Inflammation & Immunology, Oncology, Internal Medicine, Vaccines) | |||
| Phase 3 | 30 | Oncology: Padcev (BCG-Unresponsive NMIBC), vepdegestrant (ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer), sigvotatug vedotin (metastatic non-small cell lung cancer) 14 | Vaccines: C. difficile vaccine, mRNA-based flu/COVID combination vaccine 14 | ||
| Registration | 3 | (Specific examples not detailed in provided material, but are in final stages for regulatory approval) | |||
| Total Pipeline | 108 |
The Art of Portfolio Optimization: Balancing Risk and Reward in R&D
Pfizer’s R&D investment strategy is a finely tuned exercise in portfolio optimization, meticulously balancing the inherent risks of drug development with the pursuit of high-reward opportunities. In 2024, Pfizer invested a substantial $10.8 billion in internal R&D projects 9, with projected R&D expenses for 2025 ranging between $10.7 billion and $11.7 billion.9 These significant investments underscore the company’s commitment to innovation.
Encouragingly, R&D productivity is on the rise, with an improvement in Phase III success rates observed in 2024. This has contributed to a stabilization of overall program cycle times, with the total duration from Phase I start to regulatory approval averaging 9.3 years in 2024, a slight decrease from the peak of 10.1 years in 2022.21 This indicates a more efficient progression of drug candidates through the development pipeline.
Strategic allocation of these R&D resources is a key priority. Under new R&D leadership, Chris Boshoff, Chief Scientific Officer, and Andrew Baum, Chief Strategy and Innovation Officer, are jointly leading a committee specifically tasked with ensuring that R&D investments are focused on the most impactful opportunities.20 This structured approach aims to maximize the return on every R&D dollar. Furthermore, a critical component of this strategy involves leveraging internal efficiencies: anticipated cost savings of approximately $500 million by the end of 2026 from R&D reorganization are explicitly slated to be reinvested directly into the pipeline.22
The financial data clearly illustrates Pfizer’s aggressive cost-cutting initiatives across its operations, including a target of $4.5 billion in net cost savings by the end of 2025 from its ongoing cost realignment program, and an additional $1.5 billion from manufacturing optimization by 2027.9 The critical aspect here is that these savings are not merely aimed at bolstering the bottom line; the R&D savings, in particular, are explicitly designated for reinvestment into the pipeline.22 This establishes a virtuous cycle: disciplined cost management frees up capital, which is then
precisely re-allocated to high-potential R&D initiatives. This strategic loop is meticulously designed to enhance R&D productivity and ultimately improve investment returns. The cost-cutting, therefore, serves as a direct enabler of precision investment, allowing Pfizer to continuously fuel its innovation engine with optimized resources.
Financial Discipline and Capital Allocation: The Bedrock of Precision
Sound financial management and a strategic approach to capital allocation are not merely supporting functions at Pfizer; they are fundamental pillars that enable and reinforce the company’s commitment to precision in its investments.
Strategic Cost Realignment: Enhancing Operational Efficiency
In response to evolving market dynamics and the need for sustainable growth, Pfizer has embarked on a comprehensive cost realignment program. The company is on track to deliver overall net cost savings of approximately $4.5 billion by the end of 2025 from this ongoing initiative.9 This target represents an increase from an initial $4 billion, signaling an intensified commitment to operational efficiency.9
Beyond the immediate cost realignment, Pfizer anticipates an additional $1.5 billion in net cost savings from its Manufacturing Optimization Program by the end of 2027, with initial savings expected in the latter part of 2025.9 Further productivity gains, estimated at approximately $1.2 billion in Selling, Information & Administrative (SI&A) expenses by 2027, are expected to be achieved through enhanced digital enablement and process simplification, notably leveraging automation and AI.20
These aggressive cost-saving targets and programs (cost realignment, manufacturing optimization, digital enablement) 9 are a direct and calculated response to the anticipated decline in pandemic-era revenues and increasing industry-wide pressures. This is not simply reactive belt-tightening; it is a proactive strategy aimed at “return[ing] to pre-pandemic operating margins in the coming years”.10 This demonstrates a profound level of financial precision, meticulously focused on maintaining profitability and securing the necessary capital to fund future growth, even as significant revenue sources shift. It is a strategic move to ensure the company’s financial foundation remains robust, enabling future precise investments in innovation.
For a clearer perspective on Pfizer’s financial performance and future outlook, the following table summarizes key figures:
Table 1: Pfizer’s Key Financial Performance & 2025 Guidance (2024-2025)
| Financial Metric | Full-Year 2024 | Q4 2024 | Q1 2025 | Full-Year 2025 Guidance |
| Revenues (Total) | $63.6 Billion 9 | $17.8 Billion 9 | $13.7 Billion 22 | $61.0 – $64.0 Billion 9 |
| Revenues (Excl. Paxlovid & Comirnaty) | Grew 12% Operationally 9 | Grew 11% Operationally 9 | (Operational decrease due to Paxlovid decline, partially offset by Vyndaqel, Comirnaty) 22 | N/A |
| Reported Diluted EPS | $1.41 9 | $0.07 9 | $0.52 22 | N/A |
| Adjusted Diluted EPS | $3.11 9 | $0.63 9 | $0.92 22 | $2.80 – $3.00 9 |
| R&D Expenses | $10.8 Billion 9 | $3.035 Billion | $2.203 Billion 22 | $10.7 – $11.7 Billion 9 |
| Total Net Cost Savings Target (by End of 2025) | On track for $4.5 Billion 9 | |||
| Manufacturing Optimization Program Savings Target (by End of 2027) | On track for $1.5 Billion 9 | |||
| Additional SI&A Savings Target (by End of 2027) | On track for $1.2 Billion 22 | |||
| R&D Re-organization Savings Target (by End of 2026) | On track for $500 Million (reinvested in pipeline) 22 |
M&A as a Precision Tool: The Transformative Seagen Acquisition
Mergers and acquisitions play a pivotal role in Pfizer’s precision investment strategy, particularly in a dynamic industry where pipeline replenishment is critical. While M&A activity in the life sciences sector experienced a dip in 2024, it is widely anticipated to rebound strongly in 2025, driven by the urgent need for companies to augment their pipelines and an improving economic outlook.23 Biopharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer, possess significant deal capacity, estimated to exceed $1.5 trillion in 2025, providing ample “dry powder” for strategic transactions.
A prime example of M&A as a precision tool is Pfizer’s acquisition of cancer therapy maker Seagen for $45.7 billion in 2023.23 This monumental deal significantly contributed to the overall M&A volume in the life sciences sector that year.23 The strategic rationale behind the Seagen acquisition was not merely about adding revenue, although legacy Seagen did contribute $3.4 billion in revenue in 2024.9 More importantly, it was a meticulously calculated move to bolster Pfizer’s oncology pipeline and expertise, aligning perfectly with its overarching focus on precision medicine in cancer.12
The pharmaceutical industry is facing an imminent and substantial patent cliff, with over $200 billion of biopharma industry revenue expected to lose exclusivity by 2030.3 Pfizer’s acquisition of Seagen, a leading cancer therapy maker, for $45.7 billion 23 is a direct, large-scale illustration of M&A being deployed as a
precision tool to proactively address this looming revenue gap. Rather than solely relying on the slower and often less predictable path of internal R&D to fill the void, Pfizer made a decisive, forward-looking move to acquire a company whose portfolio and expertise—particularly in oncology and precision medicine—precisely align with its long-term growth strategy. This demonstrates M&A as a strategic, foresight-driven investment, meticulously chosen to secure future revenue streams and competitive positioning, rather than merely opportunistic buying.
Capital Deployment: Fueling Innovation and Shareholder Value
Pfizer’s capital allocation strategy is a carefully balanced approach designed to fuel innovation, maintain financial strength, and deliver consistent shareholder value. The company’s priorities for capital deployment are clear: growing and maintaining its dividend, prudently de-levering its balance sheet, and strategically reinvesting for future growth.20
A significant portion of capital is directed towards R&D, underscoring the company’s commitment to its pipeline. In 2024, Pfizer invested $10.8 billion in internal research and development projects, complemented by approximately $300 million invested in business development transactions.9 This trend continued into Q1 2025, with $2.2 billion invested in internal R&D projects and about $90 million in business development transactions.22 These investments are critical for advancing the pipeline and securing future revenue streams.
Simultaneously, Pfizer prioritizes returning capital directly to its shareholders. In 2024, the company distributed $9.5 billion in cash dividends, equating to $1.68 per share of common stock.9 This commitment continued in Q1 2025, with $2.4 billion returned through cash dividends, or $0.43 per share.22
Furthermore, Pfizer is actively managing its balance sheet. The company expects to sufficiently de-lever its balance sheet by the end of 2025, aiming to return to a more balanced capital allocation strategy. This will provide greater flexibility to deploy capital towards potential value-creating business development transactions and, potentially, to return additional capital to shareholders through share repurchases.10
Pfizer’s capital allocation strategy is not about maximizing a single metric; it is a meticulously balanced approach. The simultaneous commitment to maintaining and growing dividends, actively de-leveraging the balance sheet, and making significant reinvestments in R&D 9 exemplifies financial precision. This approach optimizes the use of capital across multiple stakeholders and strategic needs, ensuring both short-term shareholder returns and robust long-term growth through continuous innovation. This multi-faceted and harmonized approach to capital deployment is a hallmark of precise financial management, demonstrating a sophisticated understanding of how to sustain value creation over time.
The Unseen Advantage: Leveraging Patent Data for Investment Precision
In the pharmaceutical industry, intellectual property, particularly drug patents, represents an unseen yet profoundly powerful advantage. For investors and business strategists, understanding and leveraging patent data is paramount for making informed decisions, mitigating risks, and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Intellectual Property: The Lifeblood of Pharmaceutical Value
Pharmaceutical patents are far more than mere legal documents; they are the economic bedrock of the industry. These patents typically grant inventors exclusive rights to manufacture and market a drug for 20 years from the filing date in most jurisdictions.1 This period of market exclusivity is absolutely critical for companies to recoup the colossal R&D investments, which often span 5-15 years and can amount to billions of dollars per drug.1 Without this exclusivity, generic manufacturers could swiftly enter the market, significantly undercutting prices and eroding the innovator’s market share, thereby undermining the economic incentive for costly drug discovery. Research indicates that drugs protected by strong patents generate an astounding 80-90% of their lifetime revenue during these exclusivity periods.
The impact of patent expiry is equally dramatic. Following generic entry, average revenues for the original branded drug can plummet by 80-90%. This stark reality underscores the immense financial consequences of patent loss and highlights why effective patent management is central to a pharmaceutical company’s valuation and competitive standing.
From a strategic perspective, patents significantly enhance a company’s competitive position by legally preventing rivals from developing and marketing similar products. This allows the patent holder to dominate the market for the duration of the patent term, securing significant market share and revenue.24 Furthermore, a robust patent portfolio is a powerful magnet for investors. It provides assurance that a company’s innovations are protected and that there is a clear pathway to market exclusivity and profitability, making the company a more attractive investment opportunity. Patents can even be used as collateral in financing arrangements, providing a tangible asset against which companies can borrow.24
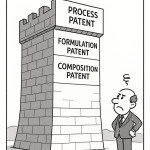
Modern patent strategies extend beyond the initial compound patent. Companies increasingly employ secondary patents to protect drug delivery mechanisms, specific dosage regimens, and combination therapies, effectively extending the commercial viability of a product beyond the primary patent’s expiration. Patent term adjustments and extensions, often granted for delays in regulatory reviews by agencies like the FDA, also play a crucial role in maximizing the effective patent life.1
Patents serve as both a shield and a sword in competitive strategy. They act as a “shield” by legally protecting the immense R&D investments and ensuring market exclusivity, which allows for premium pricing during the protected period.1 Simultaneously, patents function as a “sword” by deterring competitors from entering the market with similar products, thereby securing and maintaining market dominance for the patent holder.24 For investors, understanding this dual nature is crucial. It means that analyzing a company’s patent portfolio is not merely about assessing legal risks; it is fundamentally about evaluating its core competitive advantage and its future revenue potential. This comprehensive perspective on intellectual property is a key component of investment precision, allowing for a more accurate valuation of pharmaceutical assets.
DrugPatentWatch: Illuminating the Path to Informed Decisions
In an industry where intellectual property is paramount, specialized tools are essential for navigating the complex patent landscape. DrugPatentWatch stands out as a leading global biopharmaceutical business intelligence platform, providing deep analytics on pharmaceutical drugs, their patents across over 130 countries, clinical trials, litigation, and generic entry opportunities.1 This comprehensive database is invaluable for business professionals seeking to turn patent data into competitive advantage.
The platform offers several critical functionalities that directly empower investors and strategists:
Anticipating Market Shifts: Patent Expirations and Generic Entry
One of the most vital functionalities of DrugPatentWatch is its ability to help users predict branded drug patent expiration dates and identify potential generic suppliers.25 This is indispensable for forecasting future budget requirements and proactively identifying generic sources to manage supply chains effectively.25 For investors, anticipating patent cliffs is paramount. This functionality enables precise forecasting of potential revenue erosion for existing branded drugs and identifies the exact windows for generic market entry. Such foresight allows for timely adjustments to investment portfolios, mitigating the financial impact of exclusivity loss.
De-risking Investments: Litigation Insights and Regulatory Landscapes
Drug patent litigation is a common and often high-stakes aspect of the pharmaceutical industry, capable of significantly impacting a drug’s market exclusivity and profitability. DrugPatentWatch provides detailed data on patent litigation, including Paragraph IV challenges (filed by generic companies seeking to market a drug before the innovator’s patent expires), and comprehensive regulatory status information.1 This intelligence helps investors assess the past successes of patent challengers and gain insights into the research and development paths of competitors.25 Access to such detailed litigation history and regulatory insights allows investors to precisely assess the intellectual property-related risks associated with a particular asset or company, thereby significantly de-risking their investment decisions.
Identifying Opportunities: Unlocking Undervalued Assets
Beyond risk mitigation, DrugPatentWatch serves as a powerful tool for identifying new investment opportunities. It helps pinpoint market entry opportunities for specialty pharmaceuticals and generics, informing strategic portfolio management decisions.25 The platform can also assist in discovering future therapeutic indications for existing drugs through sophisticated biopharmaceutical forecasting, revealing untapped potential.25 By providing comprehensive data on patent landscapes, market dynamics, and pipeline developments, DrugPatentWatch assists investors in identifying undervalued assets or emerging opportunities that might be overlooked by those relying on less granular information. This is precisely where “alpha generation” through superior patent intelligence comes into play, allowing astute investors to uncover hidden value.
Historically, deep and nuanced patent analysis was often the exclusive domain of large firms with extensive legal departments and specialized analytical teams. However, platforms like DrugPatentWatch, by providing a “fully integrated database” and enabling “dynamic browsing” of critical information 25, effectively democratize access to this sophisticated intelligence. This means that even smaller investment firms or individual business professionals can now leverage granular patent data to gain a significant competitive edge. What was once a specialized, opaque area of expertise has been transformed into an accessible tool for “precision investment.” This democratization of patent intelligence levels the playing field for informed decision-making, allowing a broader range of market participants to make more precise and strategic investment choices.
Table 3: Strategic Value of Patent Data in Pharmaceutical Investment Decisions
| Aspect of Patent Data | Actionable Insight for Investors (enabled by DrugPatentWatch) | Impact on Precision Investment |
| Patent Lifecycle Phases (Pre-Approval, Market Exclusivity, Post-Generic) | Anticipate generic entry; forecast revenue erosion for branded drugs; identify windows for new market entrants. | De-risks portfolio by predicting revenue shifts; optimizes entry/exit points for investments. |
| Family Size (Number of related patents across jurisdictions) | Assess robustness of IP protection; gauge global market reach. | Enhances valuation accuracy; identifies companies with strong, defensible market positions. |
| Forward Citations (Number of times a patent is cited by subsequent patents) | Indicates foundational innovation and broad applicability of technology. | Signals higher potential value and long-term relevance of patented assets. |
| Claim Breadth (Scope of independent claims, e.g., covering multiple therapeutic uses) | Reveals versatility and potential for expanded indications; identifies “blockbuster” potential. | Supports higher valuation premiums; identifies alpha generation opportunities. |
| Litigation Trends (History of patent challenges and outcomes) 1 | Assess IP-related risks; understand competitive dynamics and challenger success rates. | Mitigates investment risk by quantifying legal vulnerabilities; informs due diligence. |
| Regulatory Exclusivities (e.g., Patent Term Extensions (PTEs), data exclusivity) | Identify additional periods of market exclusivity beyond patent term. | Extends revenue predictability; enhances long-term valuation of assets. |
Industry Dynamics and Pfizer’s Future Trajectory
Pfizer’s strategic maneuvers, particularly its emphasis on precision investment, are not isolated decisions but rather a sophisticated response to the complex and ever-evolving dynamics of the pharmaceutical industry. The company’s future trajectory will be defined by its ability to navigate these pressures while capitalizing on transformative opportunities.
Navigating Regulatory Headwinds and Market Pressures
The pharmaceutical industry operates under increasing scrutiny from regulators and governments, leading to significant market pressures. The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), with its provisions for Medicare Part D changes, and the Most-Favored-Nation (MFN) executive order, are expected to create substantial “headwinds” for pharmaceutical companies, potentially impacting revenues and R&D spending.6 Albert Bourla noted that the MFN order, which mandates U.S. drug prices align with the lowest prices in certain OECD countries, could lead to “downward pressure on U.S. prices and uncertain trade negotiations” to raise international prices. This creates a challenging environment where pricing power is constrained and margins are squeezed.
In response to these formidable challenges, pharmaceutical companies are proactively adapting their strategies. This involves a heightened focus on rigorous cost control, strategic pipeline diversification, and targeted mergers and acquisitions to offset potential revenue declines.5 The external pressure exerted by regulatory changes like the IRA and MFN, while challenging, compels pharmaceutical companies to become more efficient and precise in their operations and investments. When pricing power diminishes and margins are squeezed, every R&D dollar and every capital allocation decision must be optimized with greater care. This external pressure acts as a powerful catalyst, compelling companies like Pfizer to double down on “precision” as a core survival and growth strategy, effectively transforming a significant threat into an impetus for strategic evolution and enhanced operational discipline.
The Transformative Impact of AI on Pharma Investment
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not merely an incremental improvement; it is a transformative force reshaping the pharmaceutical industry and, critically, investment strategies within it. AI is emerging as a major deal driver and a foundational trend that will define the future of pharma.3 Its capabilities are revolutionizing how pharmaceutical portfolios are optimized, how investment decisions are made, and how R&D efficiency is improved, ultimately leading to significant cost reductions.19
The applications of AI are diverse and profound. In R&D, AI is utilized to design clinical trials with greater precision, predict the efficacy and safety profiles of drug candidates, and synthesize vast amounts of multi-omic data to gain deeper biological insights.18 Operationally, AI-powered tools automate complex and time-consuming tasks, streamlining processes in R&D and manufacturing, which Pfizer is actively leveraging to drive improvements.19 Looking ahead, the industry anticipates a wave of acquisitions in pharma services and operations, specifically aimed at integrating AI into every stage of drug development and expanding AI-driven value chains.
AI’s capabilities extend far beyond traditional analytics; it can “discern complex, non-linear relationships within datasets” that human analysis might easily overlook.19 This enables a level of “hyper-precision” in identifying optimal investment targets, accurately assessing risks, and dynamically optimizing portfolios that was previously unimaginable. For investors, this implies that companies effectively leveraging AI will possess a significant competitive advantage in making more accurate, data-driven investment decisions. This heightened accuracy, driven by AI’s analytical prowess, is expected to lead to demonstrably superior returns. Therefore, AI is not simply a tool; it represents a paradigm shift for investment precision, fundamentally altering the landscape of pharmaceutical investment.
Cultivating Agility: A Prerequisite for Sustained Success
In a rapidly evolving and often unpredictable industry like pharmaceuticals, precision alone is insufficient without a parallel commitment to agility. While precision implies a fixed, accurate target, agility provides the necessary flexibility to adapt to unforeseen circumstances and capitalize on emergent opportunities. The market often rewards discipline more than brilliance, and organizational agility is increasingly recognized as a key differentiator for sustained success.5
The ability to navigate, pivot, and bounce back from setbacks is crucial. Pfizer’s experience with the discontinuation of its oral GLP-1R agonist, danuglipron, serves as a case in point; rather than derailing its metabolic therapy strategy, the company continues to invest in other promising candidates in the space.5 This demonstrates the strategic flexibility to shift focus, adapt its pipeline, and reallocate resources in real-time.
Agility allows a company to re-calibrate its precision in real-time. It enables swift pivots away from failing assets or rapid capitalization on emerging scientific breakthroughs or significant market shifts. Therefore, true “precision in pharma investments” is not a static concept; it is a dynamic capability that seamlessly combines accurate targeting with the flexibility to adapt. This ensures sustained success in a volatile and highly competitive environment, allowing companies to maintain their strategic focus while remaining responsive to the ever-changing landscape.
Key Takeaways: Lessons from Pfizer’s Precision Playbook
Pfizer’s strategic evolution provides a compelling model for precision in pharmaceutical investments, offering valuable lessons for business professionals navigating this complex industry.
- Strategic Re-anchoring: Precision investment involves a deliberate shift from opportunistic, short-term revenue drivers (like pandemic-era products) to a re-anchored focus on sustainable, core business growth through a diversified, high-potential pipeline.
- Targeted R&D: Success hinges on meticulously targeted R&D, focusing on areas of high unmet medical need (e.g., oncology, rare diseases) and leveraging cutting-edge science like precision medicine, gene therapy, and advanced mRNA platforms.
- Financial Discipline as an Enabler: Aggressive cost realignment and operational efficiencies are not just about the bottom line; they are strategic maneuvers that free up capital for precise reinvestment into high-potential R&D and strategic M&A.
- M&A as a Strategic Tool: Mergers and acquisitions, exemplified by the Seagen acquisition, are deployed as precision instruments to proactively address looming patent cliffs, acquire complementary expertise, and bolster core therapeutic areas, rather than merely for revenue growth.
- The Power of Patent Intelligence: Intellectual property is the lifeblood of pharmaceutical value. Leveraging comprehensive patent data, through platforms like DrugPatentWatch, is crucial for anticipating market shifts, de-risking investments, and identifying undervalued assets, thereby gaining a significant competitive edge.
- AI for Hyper-Precision: Artificial Intelligence is transforming investment decisions by enabling a level of “hyper-precision” in R&D and portfolio management. Companies that effectively integrate AI will have a distinct advantage in identifying opportunities and mitigating risks.
- Agility is Paramount: In a volatile industry, true precision is dynamic. The ability to pivot quickly from setbacks, adapt to regulatory changes, and reallocate resources swiftly is essential for sustained success and for maintaining a precise course in an unpredictable market.
By integrating these principles, business professionals can develop more robust and resilient investment strategies, transforming complex data into actionable insights and fostering competitive advantage in the ever-evolving pharmaceutical landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How does Pfizer’s post-pandemic strategy demonstrate a shift towards “precision investment”?
Pfizer’s post-pandemic strategy showcases a clear pivot towards “precision investment” by consciously de-emphasizing pandemic-era revenue drivers like Paxlovid and Comirnaty in its financial reporting, instead highlighting operational growth excluding these products.9 This signifies a deliberate re-anchoring to sustainable core business growth. Furthermore, the company is implementing aggressive cost-cutting programs with explicit plans to reinvest savings back into its R&D pipeline.22 The transformative $45.7 billion acquisition of Seagen in 2023, specifically aimed at bolstering its oncology portfolio, exemplifies a precise strategic M&A move to fill pipeline gaps and secure future growth in high-value therapeutic areas.23
What specific role does AI play in enhancing precision in Pfizer’s R&D and portfolio management?
AI plays a multifaceted and critical role in enhancing precision across Pfizer’s R&D and portfolio management. It is leveraged to analyze massive datasets, identify complex, non-linear patterns, and predict the potential efficacy and safety profiles of drug candidates.18 This allows for more informed decisions in designing clinical trials, optimizing resource allocation, and de-risking investments by identifying potential failures early. In portfolio management, AI enhances decision-making, improves R&D efficiency, and contributes to cost reductions by automating complex tasks and providing data-driven insights.19
How can patent data, particularly through platforms like DrugPatentWatch, inform and de-risk pharmaceutical investment decisions?
Patent data is crucial for informed pharmaceutical investment decisions. Platforms like DrugPatentWatch provide deep analytics on patent lifecycles, allowing investors to predict branded drug patent expirations and anticipate generic entry, which is vital for forecasting revenue erosion and market shifts.25 It also offers insights into patent litigation and regulatory landscapes, enabling investors to precisely assess intellectual property-related risks and understand competitor strategies.1 By illuminating these critical aspects, patent data helps de-risk investments and identify undervalued assets or emerging opportunities, leading to more precise and strategic capital deployment.
What are the primary challenges Pfizer and the broader pharmaceutical industry face in maintaining investment precision, and how are they addressing them?
Pfizer and the pharmaceutical industry face significant challenges in maintaining investment precision, primarily from looming patent cliffs (potential revenue losses exceeding $300 billion by 2030) and increasing regulatory pressures, such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and the Most-Favored-Nation executive order, which impact drug pricing and R&D investment.3 They are addressing these by executing strategic M&A (like the Seagen acquisition), implementing aggressive cost realignment programs to enhance operational efficiency, diversifying R&D pipelines across multiple therapeutic areas, and extensively leveraging advanced technologies like AI to improve efficiency and identify new growth drivers.10
Beyond financial returns, what broader impact does a precision investment model like Pfizer’s have on patient outcomes and public health?
Beyond financial returns, a precision investment model like Pfizer’s has a profound broader impact on patient outcomes and public health. By precisely targeting areas of high unmet medical need, such as specific cancers, rare genetic diseases, and chronic inflammatory conditions, the model accelerates the development of highly effective, targeted therapies.12 This focus on understanding the biological basis of disease and leveraging cutting-edge science (e.g., precision medicine, gene therapy, mRNA technology) leads to the creation of breakthrough medicines that offer improved efficacy, reduced side effects, and ultimately, a better quality of life for patients globally. It ensures that R&D resources are directed towards innovations that address critical health challenges, fostering a healthier future.
References
9
14
11
13
8
3
2
7
1
Works cited
- Leveraging Drug Patent Data for Strategic Investment Decisions: A Comprehensive Analysis, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/leveraging-drug-patent-data-for-strategic-investment-decisions-a-comprehensive-analysis/
- Measuring the return from pharmaceutical innovation 2025 | Deloitte Switzerland, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.deloitte.com/ch/en/Industries/life-sciences-health-care/research/measuring-return-from-pharmaceutical-innovation.html
- M&A Trends in Turbulent Times – Taylor Wessing, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.taylorwessing.com/en/insights-and-events/insights/2025/03/m-and-a-trends-in-turbulent-times
- Biopharma M&A: Outlook for 2025 – IQVIA, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.iqvia.com/locations/emea/blogs/2025/01/biopharma-m-and-a-outlook-for-2025
- Next in pharma 2025: The future is now – PwC, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industries/pharma-life-sciences/pharmaceutical-industry-trends.html
- Pharmaceutical Innovation and the Inflation Reduction Act | ATI Advisory, accessed July 16, 2025, https://atiadvisory.com/resources/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/Pharmaceutical-Innovation-and-the-Inflation-Reduction-Act.pdf
- Pfizer Conference Insights: Analyzing Bourla’s Strategic Vision Amid Policy Changes, accessed July 16, 2025, https://news.syenza.com/pfizer-conference-insights-bourla-strategic-vision/
- Pfizer Net Acquisitions/Divestitures 2010-2025 | PFE | MacroTrends, accessed July 16, 2025, https://macrotrends.net/stocks/charts/PFE/pfizer/net-acquisitions-divestitures
- Pfizer Reports Strong Full-Year 2024 Results And Reaffirms 2025 …, accessed July 16, 2025, https://s206.q4cdn.com/795948973/files/doc_financials/2024/q4/Q4-2024-PFE-Earnings-Release-Final.pdf
- Pfizer Reports Strong Full-Year 2024 Results And Reaffirms 2025 Guidance – Business Wire, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250204537410/en/Pfizer-Reports-Strong-Full-Year-2024-Results-And-Reaffirms-2025-Guidance
- Our Therapy Areas | Pfizer UK, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.pfizer.co.uk/science/our-therapy-areas
- Partners | Pfizer, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.pfizer.com/about/partners/research-and-business-development-partnerships
- Pfizer’s Strategic Crossroads: Can Pipeline Milestones and Cost …, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.ainvest.com/news/pfizer-strategic-crossroads-pipeline-milestones-cost-discipline-drive-post-pandemic-growth-2506/
- Pfizer’s Strong Late-Stage Pipeline Can Drive Long-Term Growth …, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/pfizers-strong-late-stage-pipeline-can-drive-long-term-growth
- News – Pfizer Inc. – Investor Relations, accessed July 16, 2025, https://investors.pfizer.com/Investors/News/default.aspx
- Our Science: Pharmaceutical Development | Pfizer | Pfizer, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.pfizer.com/science
- New Drug Development Pipeline: Pfizer’s Medicine, Vaccine …, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.pfizer.com/science/drug-product-pipeline
- As AI Dawns in Precision Oncology, 2025 Expected To Be a ‘Turning Point’ – BioSpace, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.biospace.com/drug-development/as-ai-dawns-in-precision-oncology-2025-expected-to-be-a-turning-point
- AI-Powered Portfolio Management in Pharmaceuticals …, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/ai-powered-portfolio-management-in-pharmaceuticals/
- Pfizer’s 2025 Priorities: A Roadmap to Innovation and Excellence, accessed July 16, 2025, https://insights.pfizer.com/jpm-2025
- Global Trends in R&D 2025: Signs of Higher Efficiency and Productivity – IQVIA, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.iqvia.com/blogs/2025/06/global-trends-in-r-and-d-2025-signs-of-higher-efficiency-and-productivity
- Pfizer Reports Solid First-Quarter 2025 Results And Reaffirms 2025 …, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.biospace.com/press-releases/pfizer-reports-solid-first-quarter-2025-results-and-reaffirms-2025-guidance
- Life sciences: Primed for an increase | McKinsey, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/m-and-a/our-insights/life-sciences-primed-for-an-increase
- Managing Patent Portfolios in the Pharmaceutical Industry – PatentPC, accessed July 16, 2025, https://patentpc.com/blog/managing-patent-portfolios-in-the-pharmaceutical-industry
- DrugPatentWatch | Software Reviews & Alternatives – Crozdesk, accessed July 16, 2025, https://crozdesk.com/software/drugpatentwatch
- DrugPatentWatch Reviews – 2025 – Slashdot, accessed July 16, 2025, https://slashdot.org/software/p/DrugPatentWatch/
- DrugPatentWatch Pricing, Features, and Reviews (Jun 2025) – SoftwareSuggest, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.softwaresuggest.com/drugpatentwatch
- DrugPatentWatch – Rapid API, accessed July 16, 2025, https://rapidapi.com/drugpatentwatch/api/drugpatentwatch
- Top 200 Investing Quotes [2025] – DigitalDefynd, accessed July 16, 2025, https://digitaldefynd.com/IQ/investing-quotes/
- Undeterred by Political, Economic Headwinds, Pharma Ups R&D Investment in 2024 and Beyond – BioSpace, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.biospace.com/business/undeterred-by-political-economic-headwinds-pharma-ups-r-d-investment-in-2024-and-beyond
- Measuring the return from pharmaceutical innovation 2024 | Deloitte US, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/Industries/life-sciences-health-care/articles/measuring-return-from-pharmaceutical-innovation.html
- Pharmaceutical Industry Quotes – BrainyQuote, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.brainyquote.com/topics/pharmaceutical-industry-quotes
- 30 Quotes About the Future of Healthcare: Expert Takes, accessed July 16, 2025, https://deliberatedirections.com/quotes-future-of-healthcare/
- The Future of Healthcare Innovation 2025 – Cure, accessed July 16, 2025, https://wewillcure.com/insights/healthcare-innovation-report
- Teva Reaffirms “Pivot to Growth” Strategy Progress with Launch of Acceleration Phase at 2025 Innovation and Strategy Day – Teva’s Investor, accessed July 16, 2025, https://ir.tevapharm.com/news-and-events/press-releases/press-release-details/2025/Teva-Reaffirms-Pivot-to-Growth-Strategy-Progress-with-Launch-of-Acceleration-Phase-at-2025-Innovation-and-Strategy-Day/default.aspx
- Pioneering Portfolio Management Quotes by David F. Swensen – Goodreads, accessed July 16, 2025, https://www.goodreads.com/work/quotes/18936-pioneering-portfolio-management-an-unconventional-approach-to-instituti
- Best Inspirational Mutual Fund Investment Quotes in 2025 – Scripbox, accessed July 16, 2025, https://scripbox.com/mf/investment-quotes/