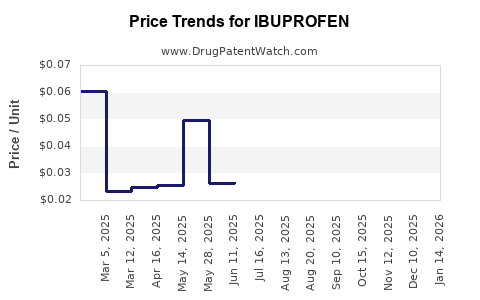
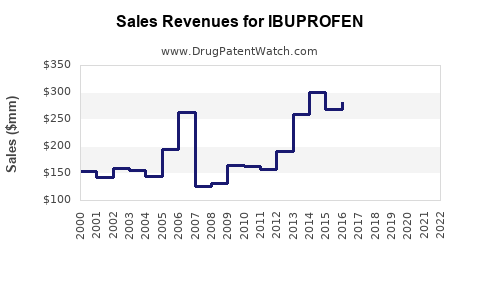
Last updated: October 30, 2025
Introduction
Ibuprofen, an over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), has become one of the most widely used analgesic and antipyretic medications globally. Its broad application in pain management, inflammation reduction, and fever control has secured a dominant market presence. This analysis explores the evolving market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and financial trajectory shaping ibuprofen’s future in the global pharmaceutical sector.
Market Overview for Ibuprofen
Global Market Size and Growth
The ibuprofen market has demonstrated steady growth driven by escalating prevalence of chronic inflammatory conditions, increasing demand for OTC analgesics, and expanding healthcare access in emerging economies. According to a 2022 report by Grand View Research, the global NSAID market, dominated by ibuprofen, was valued at approximately USD 10.8 billion with an expected CAGR of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. The OTC segment commands a substantial share, reflecting consumer preference for accessible, low-cost medications.
Key Market Segments
- OTC vs. Prescription: Most ibuprofen sales occur OTC, favored for self-medication due to safety profiles, affordability, and ease of access.
- Formulations: Tablets, caplets, suspensions, gels, and topical creams cater to diverse patient needs.
- End-User Demographics: Wide application across age groups, from pediatrics to geriatrics, enhances market penetration.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
- Rising Chronic Disease Incidence: Increasing cases of arthritis, musculoskeletal disorders, and fever-related illnesses sustain demand.
- Expanding OTC Market: Growing consumer preference for self-care and OTC analgesics boosts sales.
- Developing Economies: Emerging markets such as China, India, and Brazil exhibit rapid pharmaceutical consumption growth, driven by increasing health awareness and disposable income.
- Product Pipeline and Innovation: Development of formulations with improved bioavailability, reduced gastrointestinal side effects, and combination therapies expand market opportunities.
Restraints
- Safety Concerns and Regulatory Scrutiny: Long-term use risks, such as gastrointestinal bleeding, cardiovascular events, and renal complications, attract regulatory attention, leading to dosage and labeling restrictions.
- Generic Competition: The expiry of key patents in the past decade has intensified competition, leading to price erosion.
- Market Saturation: Mature markets, particularly in North America and Europe, face saturation, limiting growth potential.
Opportunities
- Novel Delivery Systems: Transdermal patches, soft gels, and inhalable forms offer convenience and improved compliance.
- Expanding Indications: Research exploring ibuprofen’s role in oncology, neurodegenerative diseases, and COVID-19 related symptoms creates new therapeutic avenues.
- Strategic Partnerships and M&A: Collaborations for manufacturing, distribution, and innovation can enhance market share.
Competitive Landscape
Major pharmaceutical companies manufacturing ibuprofen include Johnson & Johnson, Bayer, Pfizer, and Teva Pharmaceuticals. Many of these corporations hold legacy manufacturing rights, alongside a proliferation of generic producers driving price competition. Patent expirations have led to a biosimilar and generic flood, intensifying downward pricing pressure.
Market Positioning Strategies
- Brand Differentiation: Proprietary formulations or combination products.
- Cost Leadership: Strategies to optimize manufacturing costs for competitive pricing.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring safety and efficacy standards to maintain market access.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies like the FDA (U.S.), EMA (Europe), and MHRA (UK) enforce strict guidelines on dosage, labeling, and safety warnings for NSAIDs, including ibuprofen. Recent regulatory considerations focus on cardiovascular and gastrointestinal risks, prompting manufacturers to revise labeling and conduct post-market surveillance.
Emerging regulations in developing regions aim to improve OTC drug standards, which may require investment in compliance protocols. The global trend emphasizes balanced risk-benefit assessments to ensure patient safety while maintaining accessibility.
Financial Trajectory
Historical Performance
Companies generating significant revenue from ibuprofen benefit from stable cash flows. For instance, Johnson & Johnson’s Consumer segment reported robust OTC revenues, with ibuprofen products being core contributors. Generic manufacturers have achieved high-volume, low-margin sales, leveraging manufacturing efficiencies.
Future Revenue Streams
- Generic and OTC Sales: As patents expire, generics will dominate sales, potentially sustaining volume growth but exerting price pressures.
- Innovative Formulations: Premium-priced formulations with enhanced safety profiles or novel delivery methods present revenue expansion opportunities.
- Regional Market Expansion: Entry into underserved markets with increasing healthcare infrastructure can lead to incremental revenue.
Profitability Factors
- Manufacturing Costs: Automation and optimization are critical to maintain margins amidst volume-driven competition.
- Regulatory Costs: Compliance and post-market monitoring increase operational expenses but are crucial for sustained market access.
- Pricing Strategies: Transparent, value-based pricing, especially for premium formulations, can improve profitability.
Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations
The outlook for ibuprofen remains cautiously optimistic. Mature markets will see volume maintenance with slim margins, necessitating innovation and diversification. Emerging markets are poised for rapid growth, driven by expanding healthcare access and increasing health awareness.
Companies should prioritize R&D investments into safer formulations, alternative delivery mechanisms, and broader therapeutic indications. Strategic partnerships, licensing, and acquisitions can facilitate market penetration and diversify product portfolios.
Key Takeaways
- The ibuprofen market exhibits steady growth driven by increasing demand across global markets, with significant opportunities in emerging economies.
- Price competition from generics continues to pressure margins, necessitating cost-efficient manufacturing and innovation.
- Regulatory scrutiny around safety profiles influences formulation development, marketing, and labeling strategies.
- Expansion into novel formulations and new therapeutic indications offers avenues for revenue growth.
- Companies that focus on regional market expansion, regulatory compliance, and product differentiation are best positioned for financial success.
FAQs
-
What are the main factors influencing ibuprofen’s market growth?
Rising prevalence of inflammatory conditions, expanding OTC use, and growth in emerging markets are primary drivers.
-
How do patent expirations affect ibuprofen’s market dynamics?
They enable generic manufacturers to enter, increasing competition, reducing prices, and squeezing profit margins for branded products.
-
What safety concerns impact ibuprofen’s regulatory status?
Long-term use risks like gastrointestinal bleeding and cardiovascular events result in tighter regulations and labeling requirements.
-
What innovations are emerging in the ibuprofen segment?
New delivery systems such as topical patches, controlled-release formulations, and combination drugs are under development.
-
How can companies capitalize on future opportunities in the ibuprofen market?
By investing in safer formulations, exploring new indications, expanding geographically, and forming strategic alliances.
References
- Grand View Research. (2022). NSAID Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2023). Labeling and Safety Guidelines for NSAIDs.
- MarketWatch. (2022). OTC Pain Management Market Overview and Trends.
- GlobalData. (2023). Pharmaceutical Industry Outlook: Focus on NSAID Innovations.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). (2023). NSAID Safety Monitoring Reports.