1. Introduction
Drug repurposing, a pivotal strategy in pharmaceutical development, involves the identification of new therapeutic applications for existing drugs or the advancement of previously studied but unapproved drugs for indications beyond their original scope.1 This approach, also referred to as drug repositioning, reprofiling, or retasking, encompasses not only discovering entirely new uses for approved medicines but also exploring different formulations of the same medicine or creating novel combinations of medicines, sometimes even with medical devices.2 The core significance of drug repurposing lies in its potential to offer a more expeditious, cost-effective, and less risky pathway for drug development with a potentially higher rate of success compared to the traditional de novo drug discovery process.1 A key advantage of this strategy is the ability to leverage the extensive existing knowledge base surrounding these drugs, including their safety profiles, pharmacological properties, and established manufacturing processes.1
The importance of drug repurposing has steadily grown within the pharmaceutical development landscape. This surge in interest is partly attributed to the escalating costs and protracted timelines associated with bringing novel drugs to market through traditional methods.1 Furthermore, major pharmaceutical companies have faced challenges in maintaining high levels of productivity in their drug discovery pipelines, making drug repurposing an appealing alternative.4 The strategic value of drug repurposing became particularly evident during health crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic, where the urgent need for effective treatments propelled the rapid investigation and deployment of existing drugs for new uses.1 This approach is also exceptionally relevant for addressing rare and neglected diseases, conditions for which the conventional drug development model often proves financially unviable due to smaller patient populations and potentially lower market returns.2 Notably, drugs identified through repurposing contribute significantly to the pharmaceutical industry’s annual revenue, underscoring their economic importance.8 The confluence of these factors has firmly established drug repurposing as a critical and increasingly pursued strategy in the ongoing efforts to develop new and effective therapies.
2. The Advantages of Drug Repurposing
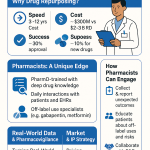
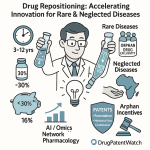
Drug repurposing offers a compelling array of advantages over traditional drug development, primarily in terms of reduced timelines and costs. On average, repurposing can shave off 5 to 7 years from the typical drug development timeline.8 This acceleration is accompanied by a substantial reduction in overall development expenses, estimated to be 50-60% lower, translating to approximately $300 million compared to the staggering $2-3 billion often required to bring a novel drug to market.8 This efficiency is largely due to the fact that drug repurposing allows researchers to bypass the early, resource-intensive stages of development, such as preclinical compound discovery and Phase I safety studies, as these have often already been completed for the drug in its original indication.1 In some cases, the well-established safety profile of a repurposed drug may even allow for skipping preclinical and Phase I trials altogether, enabling a direct progression to Phase II clinical studies focused on efficacy for the new indication.6 This streamlined process leads to development programs that are not only faster but also significantly less expensive.6
Another significant advantage of drug repurposing is the lower risk of failure. This reduced risk stems from the fact that repurposed drugs have already undergone substantial testing and have established safety and toxicity profiles.1 This contrasts sharply with traditional drug development, where a significant number of candidates fail due to unacceptable safety profiles.6 Consequently, repurposed drugs often exhibit higher approval rates compared to novel chemical entities.8 For instance, the approval rate for repurposed drugs that have successfully completed Phase I trials can be as high as 30%, a notable improvement over the typical success rate of less than 10% for traditional new drug development.10
Furthermore, drug repurposing plays a crucial role in addressing unmet medical needs, particularly for rare or neglected diseases. Developing novel drugs for these conditions can be financially challenging due to small patient populations and uncertain market returns.1 Drug repurposing offers a more economically viable pathway to provide new treatments for these patient groups, often facilitating earlier access to much-needed medicines for serious and life-threatening diseases, including pediatric conditions.2
3. Challenges and Limitations in Drug Repurposing
Despite its numerous advantages, drug repurposing is not without its challenges and limitations. One significant hurdle revolves around intellectual property rights and patentability. Securing patents for new medical uses of existing compounds, especially generic drugs, can be difficult.7 Issues such as prior art and the obviousness of the new use can further limit the scope of patent protection.7 Moreover, the expiration of the original drug’s patent can restrict the period of market exclusivity for the repurposed indication.7 Enforcing method-of-use patents, particularly for off-patent drugs, can also prove challenging.7
Regulatory hurdles and approval processes also present limitations. While no specific regulatory pathways are solely dedicated to repurposed drugs, existing pathways can be utilized.2 However, demonstrating efficacy and safety for the new indication is still mandatory, often necessitating additional clinical trials.2 Determining the appropriate dosage and treatment regimen for the new patient population can also be a complex undertaking.6 In some cases, reformulation of the drug may be required for the new indication, adding another layer of complexity.2
Financial incentives and market viability pose further challenges. Repurposing off-patent drugs often yields limited financial returns due to competition from generic manufacturers.4 The pharmaceutical industry’s primary focus on diseases with greater profit potential can also limit repurposing efforts for less commercially attractive conditions, such as rare or neglected diseases.51 Uncertainty regarding the market value and potential return on investment for a repurposed drug can also deter companies from pursuing this strategy.1
From a scientific standpoint, several challenges exist. A repurposed drug might not exhibit sufficient specificity for the new indication.6 Efficacy challenges and a lack of superiority compared to existing treatments can also lead to the abandonment of promising candidates.1 A thorough understanding of the underlying biological mechanisms of the drug’s action in the new indication is crucial but can sometimes be elusive.1 Finally, data availability and its heterogeneity can pose challenges. Access to certain types of data, such as detailed clinical patient information, might be limited.9 The diverse nature of data from various sources can also create computational hurdles in effectively integrating and analyzing information.2 The potential for generating false-positive signals during data mining also necessitates careful validation.51
4. Strategies and Approaches for Identifying Repurposing Opportunities
Identifying opportunities for drug repurposing involves several strategic approaches. Target-based screening is a key method that focuses on identifying existing compounds capable of interacting with a newly identified disease target.4 This often involves in vitro and in vivo high-throughput screening (HTS/HCS) of drug libraries against the target 4, as well as in silico techniques like ligand-based screening and molecular docking to predict potential interactions.4 A significant advantage of this approach is its direct link between drugs and disease mechanisms, thereby increasing the likelihood of discovering therapeutically beneficial compounds.4 However, it requires specific knowledge about the target, such as its three-dimensional structure, and might overlook potential off-target effects that could be therapeutically relevant.6
Phenotypic screening offers an alternative strategy by identifying compounds that can alter the observable characteristics (phenotype) of a cell or organism in a desired way.4 This can involve various techniques using cell-based assays (including 2D and 3D cultures, organoids, iPSC-derived models, patient-derived primary cells, and organ-on-a-chip systems) and in vivo models (such as zebrafish, C. elegans, rodents, non-human primates, and Drosophila).4 The key advantage of phenotypic screening is that it does not require prior knowledge of a specific drug target and can uncover novel mechanisms of action, making it particularly useful when no attractive target is known for a disease.4 However, elucidating the mechanism of action of a hit compound from a phenotypic screen can be challenging, and the setup and interpretation of these assays, especially with in vivo models, can be complex.4
Computational methods have become increasingly powerful in identifying drug repurposing opportunities. These approaches utilize bioinformatics, cheminformatics, machine learning, network analysis, and data mining to predict potential drug-disease associations based on the vast amounts of available biological and chemical data.1 These methods include machine learning algorithms (like logistic regression, support vector machines, random forests, neural networks, and deep learning), network models (analyzing drug-drug, drug-target, drug-disease, and protein-protein interactions), signature-based methods (comparing gene expression signatures), and molecular docking (predicting drug-target binding). Computational approaches offer the advantages of rapid processing of large datasets, identification of non-obvious connections, and cost-effectiveness.1 However, these methods heavily depend on the quality and availability of input data, can produce false positives, and often require experimental validation.
Finally, clinical observation plays a vital role, where unexpected benefits of a drug are noticed during clinical trials for its original indication or through off-label use by clinicians.1 Well-known examples include the discovery of Sildenafil’s effect on erectile dysfunction and Semaglutide’s effect on weight loss.1 While this approach can lead to the discovery of entirely new therapeutic uses, it inherently relies on chance and may not be a systematic method.
5. Successful Examples of Drug Repurposing and their Impact
The history of medicine is replete with successful examples of drug repurposing, demonstrating its profound impact on patient care. Sildenafil, marketed as Viagra®, stands out as a prime example. Originally developed by Pfizer for the treatment of hypertension and angina 1, its unexpected efficacy in treating erectile dysfunction was observed during clinical trials.1 This serendipitous finding led to its successful repurposing, demonstrating the potential for significant market success and addressing different medical needs. Furthermore, Sildenafil was later repurposed again for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension 3, and is being investigated for other potential uses, including Alzheimer’s disease and peripheral neuropathy.68
Thalidomide offers another compelling example. Initially marketed as a sedative and treatment for morning sickness 1, it was withdrawn from the market due to its devastating association with severe birth defects.6 However, decades later, thalidomide was successfully repurposed for the treatment of leprosy (specifically, erythema nodosum leprosum) and multiple myeloma.1 This example underscores the potential for finding new therapeutic uses even for drugs with a troubled history.
Metformin, a widely prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes 4, is also showing significant promise in areas beyond glucose control. Research suggests its potential in cancer prevention and treatment 7, as well as potential benefits in cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative conditions, and even aging.81 Metformin’s broad therapeutic potential highlights the value of investigating drugs that target fundamental metabolic pathways.
Beyond these prominent examples, numerous other drugs have been successfully repurposed. Aspirin, initially an analgesic, is now widely used as an antiplatelet drug and is being explored for its potential in oncology.4 Minoxidil, first developed for hypertension, found a new application in treating alopecia.3 Propranolol, a beta-blocker used for hypertension, was repurposed for the treatment of infantile hemangiomas.18 Fenfluramine, initially an appetite suppressant, is now used to treat Dravet syndrome.18 Furthermore, several drugs like Nitisinone, Everolimus, and Sirolimus have been successfully repurposed to treat rare diseases.132 The COVID-19 pandemic also spurred significant drug repurposing efforts, leading to the use of drugs like Remdesivir and Dexamethasone in treating the virus.1 These diverse examples underscore the wide-ranging potential and significant impact of drug repurposing across various therapeutic areas.
6. The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data in Drug Repurposing
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques are playing an increasingly vital role in the field of drug repurposing.1 These technologies excel at processing vast amounts of real-world data and complex biological datasets 1, significantly improving the efficiency and accuracy of predicting new drug-disease associations. For instance, AI models like TxGNN have been specifically developed to identify drug candidates for rare diseases, a task that often presents significant challenges.110
Big data analytics plays a crucial role by streamlining the identification of potential drug candidates through the analysis of extensive datasets, including genetic information, clinical trial results, and real-world patient data.1 This capability enables personalized medicine by tailoring treatments to individual patient profiles.37 Furthermore, big data analytics aids in predicting patient recruitment and retention for clinical trials of repurposed drugs, optimizing the trial process.111
Several computational tools and platforms have been developed to support drug repurposing efforts. Databases and web-based resources such as DrugRepo, Drug Repurposing Hub, repoDB, and RepurposeDB provide valuable information and facilitate the identification of potential candidates.53 AI-driven platforms like REPO4EU are being developed with the goal of creating industry-level online platforms for validated precision drug repurposing.2 Overall, the integration of AI and big data analytics is revolutionizing the field by enabling faster, cheaper, and more effective identification of potential therapies, particularly for rare and neglected diseases, and by contributing to the advancement of personalized medicine.
7. Regulatory Pathways for Drug Repurposing
The regulatory landscape for drug repurposing involves navigating the existing frameworks provided by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). While neither agency has established specific regulatory pathways solely for repurposed drugs, the current pathways available for drug approval can be effectively utilized for this purpose.2 Obtaining regulatory approval invariably requires demonstrating sufficient efficacy and safety for the new indication, which often necessitates conducting additional clinical trials, even for drugs with established safety profiles for other uses.2 Notably, the EMA appears to offer a slightly greater number of options for pursuing drug repurposing compared to the FDA.58
In the United States, the 505(b)(2) pathway provides a streamlined route for the approval of repurposed drugs. This pathway allows applicants to rely, in part, on data from previously approved products, including safety and efficacy data not generated by the applicant.7 This can significantly expedite the approval process by reducing the need for extensive new preclinical and clinical studies. Similarly, the EMA has introduced adaptive pathways aimed at facilitating faster approval of drugs that address urgent medical needs, including repurposed medicines.7
Furthermore, repurposed drugs targeting rare diseases may qualify for orphan drug designation in both the US and Europe. This designation offers several attractive incentives, such as extended periods of market exclusivity, potential tax credits for clinical research expenses, and regulatory assistance from the agencies.7 In the European Union, the EMA also provides an additional year of market exclusivity for the original product if a new indication demonstrating significant clinical benefit is added within the first eight years of the product’s authorization.58 These regulatory mechanisms and incentives play a crucial role in encouraging and facilitating the development and approval of repurposed drugs, particularly in areas of high unmet medical need.
8. Drug Repurposing for Unmet Medical Needs and Emerging Health Crises
Drug repurposing presents a particularly promising avenue for addressing unmet medical needs, especially in the context of rare and neglected diseases. For these conditions, where patient populations are small and traditional drug development often faces significant economic hurdles, repurposing offers a more cost-effective and potentially faster route to identifying and providing much-needed treatments.1 By leveraging the existing knowledge about the safety and pharmacokinetics of approved or well-studied drugs, researchers can accelerate the process of finding new therapies for these challenging conditions.1 Successful examples in this area include the repurposing of Nitisinone for alkaptonuria, Everolimus for tuberous sclerosis, and Sirolimus for autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS).132
Furthermore, drug repurposing plays a critical role in pandemic preparedness and response. During emerging health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, the ability to rapidly identify potential treatments is paramount. Drug repurposing offers a crucial pathway to quickly evaluate and deploy existing drugs that might have activity against the novel pathogen or the symptoms it causes.1 In the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, numerous repurposed drugs were rapidly moved into clinical trials to assess their efficacy.1 Notable examples of repurposed drugs used in the fight against COVID-19 include Remdesivir and Dexamethasone.1 These efforts highlight the strategic importance of drug repurposing as a first line of defense against new and emerging health threats, complementing the longer timelines associated with de novo drug development.
9. Considerations for Successful Drug Repurposing Initiatives
Successful drug repurposing initiatives require careful consideration of several key factors. First and foremost, the repurposed drug must offer a clear value proposition and address a genuine clinical need for patients or physicians.4 Ideally, it should target a significant unmet medical need, providing a treatment option where none or few exist.1
Demonstrating sufficient evidence of safety and efficacy for the new indication is also crucial. While the existing safety data from the original approval can be leveraged 1, bridging studies and often new clinical trials are necessary to specifically demonstrate efficacy in the target patient population.2
Developing robust intellectual property and market access strategies is also essential for the success of a repurposed drug. This may involve seeking patent protection for the new indication through method-of-use, formulation, or combination patents.4 Furthermore, establishing clear strategies for pricing and market access from the outset is vital to ensure the repurposed drug can reach the patients who need it.4
Finally, early and consistent engagement with regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA is highly recommended to discuss development plans and ensure alignment on the requirements for approval.7 Collaboration with patient groups, academics, and other relevant stakeholders can also significantly contribute to the success of a drug repurposing initiative by providing valuable insights, support, and resources.12
10. Future Trends and Perspectives in Drug Repurposing
The future of drug repurposing is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by several key trends. The increasing integration of multi-omics data, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, holds immense potential for identifying more precise repurposing candidates and advancing personalized medicine approaches.10 This will allow for tailoring repurposed drugs to specific patient populations based on their unique genetic profiles and biomarkers.
Advancements in computational methods and AI-driven discovery are also expected to revolutionize the field.1 The development of new computational tools and platforms specifically designed for drug repurposing will further enhance the efficiency and accuracy of identifying novel therapeutic uses for existing drugs.1
Finally, an increasing trend towards collaboration and the formation of public-private partnerships is expected to accelerate progress in drug repurposing.4 Financial support and incentives from organizations like the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) will continue to play a crucial role in fostering innovation and driving drug repurposing efforts.4
11. Conclusion
Drug repurposing stands as a vital and increasingly recognized strategy in the landscape of pharmaceutical development. Its inherent advantages in terms of reduced development timelines, lower costs, and a higher likelihood of success compared to traditional de novo drug discovery make it an attractive approach for addressing a wide range of medical needs. The ability to leverage the established safety profiles and existing knowledge of approved or well-studied drugs significantly de-risks the development process, allowing for a more efficient pathway to new therapies.
The successful examples of repurposed drugs, such as Sildenafil and Thalidomide, underscore the transformative potential of this strategy in treating diverse conditions, from common ailments to rare diseases. The advent of sophisticated computational methods, particularly those powered by artificial intelligence and big data analytics, is further enhancing the ability to identify promising repurposing candidates and predict their efficacy with greater accuracy and speed. These technological advancements are paving the way for a more systematic and data-driven approach to drug repurposing, moving beyond serendipitous discoveries towards rational and targeted identification of new therapeutic uses.
Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA are also playing a crucial role by providing pathways and incentives that facilitate the approval of repurposed drugs, especially for unmet medical needs and rare diseases. The continued evolution of these regulatory frameworks will be essential in further streamlining the process and encouraging innovation in this field.
Looking ahead, the integration of multi-omics data, the advancement of AI-driven discovery tools, and the fostering of increased collaboration across academia, industry, and government will be key drivers in shaping the future of drug repurposing. This dynamic field holds significant promise for accelerating the development of new treatments, addressing unmet medical needs, and enhancing our preparedness for emerging health crises, ultimately benefiting patients worldwide.
Works cited
- Drug repurposing: a systematic review on root causes, barriers and facilitators – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9336118/
- Accelerating Drug Development: Unleashing the Power of Drug Repurposing, accessed May 8, 2025, https://drugrepocentral.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.58647/DRUGREPO.24.1.0013
- Advancements in Drug Repurposing: Examples in Psychiatric Medications – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10341557/
- Repurposing – second life for drugs – Pharmacia, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pharmacia.pensoft.net/article/72548/
- Drug Repurposing – Foundation to Fight H-ABC / Tubb4A, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.h-abc.org/drug-repurposing
- Drug Repurposing Strategies, Challenges and Successes | Technology Networks, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.technologynetworks.com/drug-discovery/articles/drug-repurposing-strategies-challenges-and-successes-384263
- Intellectual Property Rights and Regulatory Considerations for Drug Repurposing, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/intellectual-property-rights-and-regulatory-considerations-for-drug-repurposing/
- Advantages of Drug Repurposing – pharm-int – Pharmaceutics International, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.pharm-int.com/resources/advantages-of-drug-repurposing/
- Drug Repurposing for Pandemic Innovation: Establishing an Effective and Efficient Ecosystem, accessed May 8, 2025, https://healthpolicy.duke.edu/publications/drug-repurposing-pandemic-innovation
- Drug Repurposing: An Effective Tool in Modern Drug Discovery – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9945820/
- How drug repurposing can advance drug discovery: challenges and opportunities – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/drug-discovery/articles/10.3389/fddsv.2024.1460100/full
- The Benefits and Pitfalls of Repurposing Drugs – PHETAIROS, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.phetairos.com/insights/integrated-product-development/the-benefits-and-pitfalls-of-repurposing-drugs/
- Traditional drug discovery vs. drug repurposing. | Download Scientific Diagram – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Traditional-drug-discovery-vs-drug-repurposing_fig1_342991385
- Drug Repurposing: Claiming the Full Benefit from Drug Development – PubMed, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33961142/
- Is drug repurposing really the future of drug discovery or is new innovation truly the way forward?, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17460441.2021.1912733
- Opportunities and Challenges in Drug Repurposing – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/research-topics/64551/opportunities-and-challenges-in-drug-repurposing
- Repurposing medicines: the opportunity and the challenges – LifeArc, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.lifearc.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/LifeArc-Repurposing-digital_FINAL.pdf
- Drug repurposing for rare: progress and opportunities for the rare disease community – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1352803/full
- Drug Repurposing: Sustainably Accelerating Drug Discovery – AZoLifeSciences, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.azolifesciences.com/article/Drug-Repurposing-Sustainably-Accelerating-Drug-Discovery.aspx
- Drug Repurposing: A Smart Drug Development Strategy – Dalton Pharma Services, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.dalton.com/drug-repurposing-a-smart-drug-development-strategy
- Phenotypic screening of 1,953 FDA-approved drugs reveals 26 hits …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0277646
- Drug Repurposing Strategy (DRS): Emerging Approach to Identify Potential Therapeutics for Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Infection, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7953054/
- The Utility of Drug Repurposing in Orphan Disease Research – Worldwide Clinical Trials, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.worldwide.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Rare-Disease-Whitepaper-Drug-Repurposing-In-Orphan-Disease-Research-20230327.pdf
- Drug Repurposing: An Overview – DrugPatentWatch, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/drug-repurposing-an-overview/
- International regulatory and publicly-funded initiatives to advance drug repurposing, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1387517/full
- ER2 – The second life of drugs: opportunities and challenges of drug repurposing – EAHP — European Association of Hospital Pharmacists, accessed May 8, 2025, https://eahp.eu/congress_goal/er2-the-second-life-of-drugs-opportunities-and-challenges-of-drug-repurposing/
- Drug Repurposing for Pandemic Innovation: Establishing an Effective and Efficient Ecosystem – Duke-Margolis Institute for Health Policy, accessed May 8, 2025, https://healthpolicy.duke.edu/sites/default/files/2023-06/Drug%20Repurposing%20for%20Pandemic%20Innovation.pdf
- Drug repurposing for COVID-19: Approaches, challenges and promising candidates – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8220862/
- (PDF) Drug repurposing and phenotypic screening: innovative strategies for treating ultra-rare disorders – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/385562624_Drug_repurposing_and_phenotypic_screening_innovative_strategies_for_treating_ultra-rare_disorders
- Drug repurposing and phenotypic screening: innovative strategies for treating ultra-rare disorders – PMC – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11537879/
- Computational Approaches to Drug Repurposing: Methods, Challenges, and Opportunities – Annual Reviews, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.annualreviews.org/content/journals/10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-110123-025333?crawler=true&mimetype=application/pdf
- Challenges and opportunities with drug repurposing: finding strategies to find alternative uses of therapeutics, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17460441.2020.1704729
- New REMEDi4ALL resource for navigating the complex landscape of computational drug repurposing, accessed May 8, 2025, https://remedi4all.org/new-remedi4all-resource-for-navigating-the-complex-landscape-of-computational-drug-repurposing/
- Drug Repositioning: Exploring New Indications for Existing Drug-Disease Relationships – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8901967/
- Drug Repurposing: Potential to Expand Rare Disease Treatment – Avalere Health Advisory, accessed May 8, 2025, https://avalere.com/insights/drug-repurposing-potential-to-expand-rare-disease-treatment
- The many advantages of repurposing existing drugs – European Pharmaceutical Review, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/article/122023/the-many-advantages-of-repurposing-existing-drugs/
- Drug Repurposing for Faster, Greener, and Affordable Treatments | DataDrivenInvestor, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.datadriveninvestor.com/2023/04/20/drug-repurposing-for-faster-greener-and-affordable-treatments/
- Drug Repurposing: Harnessing the Power of Existing Drugs through Innovative Tools, accessed May 8, 2025, https://revvitysignals.com/blog/drug-repurposing-harnessing-power-existing-drugs-through-innovative-tools
- Is drug repurposing worth the effort? – C&EN – American Chemical Society, accessed May 8, 2025, https://cen.acs.org/pharmaceuticals/drug-discovery/Is-drug-repurposing-worth-the-effort/99/i3
- Computational approaches for drug repositioning and repurposing to combat SARS-CoV-2 infection – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9300474/
- Drug Repurposing During The COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons For Expediting Drug Development And Access | Health Affairs, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.healthaffairs.org/doi/10.1377/hlthaff.2022.01083
- Drug Repurposing During The COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons For Expediting Drug Development And Access | Health Affairs, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.healthaffairs.org/doi/abs/10.1377/hlthaff.2022.01083
- Full article: Drug repurposing strategies for COVID-19 – Taylor & Francis Online, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/fdd-2020-0010
- Drug Repositioning in Rare/Orphans and Neglected Diseases – DrugPatentWatch, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/drug-repositioning-concept-classification-methodology-and-importance-in-rare-orphans-and-neglected-diseases/
- Drug repositioning – Wikipedia, accessed May 8, 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drug_repositioning
- Exploring Drug Repositioning Approaches and Resources – DrugPatentWatch, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/review-of-drug-repositioning-approaches-and-resources/
- The Promise of Drug Repurposing: A Faster, Cost-Effective Path to New Therapies, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.agilisium.com/blogs/the-promise-of-drug-repurposing-a-faster-cost-effective-path-to-new-therapies
- Drug repositioning: a brief overview – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7262062/
- Drug Repurposing Market: Strategic Approaches, Technological, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/drug-repurposing-market/273130/
- R&D Trends: Maximizing dark data to enhance drug repurposing – CAS, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.cas.org/resources/cas-insights/rd-trends-maximizing-dark-data-enhance-drug-repurposing
- View of The dark side of drug repurposing. From clinical trial …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://journals.aboutscience.eu/index.php/dti/article/view/3019/3558
- Drug Repurposing: A New Life for Old Drugs – DrugBank Blog, accessed May 8, 2025, https://blog.drugbank.com/drug-repurposing-a-new-life-for-old-drugs/
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Drug Repurposing—Challenges and Perspectives, accessed May 8, 2025, https://drugrepocentral.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.58647/DRUGREPO.24.1.0004
- The Prospect and Challenges of Repurposing Established Drugs in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension – MDPI, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.mdpi.com/2673-6411/4/3/12
- The dark side of drug repurposing. From clinical trial challenges to antimicrobial resistance: analysis based on three major fields – AboutScience, accessed May 8, 2025, https://journals.aboutscience.eu/index.php/dti/article/view/3019
- Comparing Pathways for Making Repurposed Drugs Available In The EU, UK, And US – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11788669/
- Drug repurposing: Clinical practices and regulatory pathways – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12048090/
- Research and analysis of regulatory framework and harmonisation of repurposing, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pharmacia.pensoft.net/article/129020/
- Repurposing of established medicines/active substances Agenda item 5 The issue of repurposing of e – Public Health, accessed May 8, 2025, https://health.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2018-11/stamp_8_repurposing_established_medicines_background_0.pdf
- Comparing regulatory pathways for drug repurposing in the EU, UK, and US, accessed May 8, 2025, https://drugrepocentral.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.58647/REXPO.23000027.v1
- Editorial: Drug repurposing and polypharmacology: A synergistic approach in multi-target based drug discovery – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.1101007/full
- How To Navigate Drug Repurposing And Bridging Studies – Clinical Leader, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.clinicalleader.com/doc/how-to-navigate-drug-repurposing-and-bridging-studies-0001
- Computational Drug Repositioning: Current Progress and Challenges, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/15/5076
- Trends and Applications in Computationally Driven Drug Repurposing – MDPI, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/22/16511
- Unmet Medical Needs require sustainable and innovative solutions – Anticancer Fund, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.anticancerfund.org/en/blog/unmet-medical-needs-require-sustainable-and-innovative-solutions
- New Approaches in Oncology for Repositioning Drugs: The Case of PDE5 Inhibitor Sildenafil – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.627229/full
- Sildenafil: from angina to erectile dysfunction to pulmonary hypertension and beyond – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7097805/
- Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors in Men With Erectile Dysfunction and the Risk of Alzheimer Disease: A Cohort Study – Neurology.org, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.neurology.org/doi/10.1212/WNL.0000000000209131
- Sildenafil: From angina to erectile dysfunction to pulmonary hypertension and beyond | Request PDF – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/6904062_Sildenafil_From_angina_to_erectile_dysfunction_to_pulmonary_hypertension_and_beyond
- Repurposing Viagra Reverses Peripheral Neuropathy – The Jackson Laboratory, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.jax.org/news-and-insights/2015/may/repurposing-viagra-reverses-peripheral-neuropathy
- Thalidomide–A Notorious Sedative to a Wonder Anticancer Drug – PMC – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4112512/
- Thalidomide (oral route) – Mayo Clinic, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/thalidomide-oral-route/description/drg-20066301
- Thalidomide – Knowledge and References – Taylor & Francis, accessed May 8, 2025, https://taylorandfrancis.com/knowledge/Medicine_and_healthcare/Pharmaceutical_medicine/Thalidomide/
- (PDF) Thalidomide–A Notorious Sedative to a Wonder Anticancer Drug – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255732600_Thalidomide-A_Notorious_Sedative_to_a_Wonder_Anticancer_Drug
- Thalidomide: history, withdrawal, renaissance, and safety concerns – Taylor & Francis Online, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14740338.2021.1991307
- Old drugs, new tricks: Thalidomide’s journey back from the wilderness – The Institute of Cancer Research, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.icr.ac.uk/research-and-discoveries/cancer-blogs/detail/science-talk/old-drugs-new-tricks-thalidomide-s-journey-back-from-the-wilderness
- Scientists discover how thalidomide-like drugs fight cancer – Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.dana-farber.org/newsroom/news-releases/2013/scientists-discover-how-thalidomide-like-drugs-fight-cancer
- Thalidomide in the treatment of leprosy – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11095814_Thalidomide_in_the_treatment_of_leprosy
- The Rise, Fall and Subsequent Triumph of Thalidomide: Lessons Learned in Drug Development – PMC – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3573415/
- Discovering Potential in Non-Cancer Medications: A Promising Breakthrough for Multiple Myeloma Patients. – Rowan Digital Works, accessed May 8, 2025, https://rdw.rowan.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1346&context=csm_facpub
- Metformin: Beyond Diabetes | Frontiers Research Topic, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/research-topics/7028/metformin-beyond-diabetes/magazine
- Editorial: Metformin: Beyond Diabetes – PMC – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6909380/
- Metformin beyond type 2 diabetes: Emerging and potential new indications – PubMed, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38965738/
- Metformin: Beyond Diabetes – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/research-topics/7028/metformin-beyond-diabetes
- Repurposing metformin for treatment of atrial fibrillation | VHRM – Dove Medical Press, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.dovepress.com/repurposing-metformin-for-the-treatment-of-atrial-fibrillation-current-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-VHRM
- Metformin in COVID-19: a magical role beyond the hyperglycemia, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.explorationpub.com/Journals/eds/Article/100855
- Metformin beyond type 2 diabetes: Emerging and potential new indications, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.sochob.cl/web1/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Metformin-beyond-type-2-diabetes-Emerging-and-potential-new-indications.pdf
- Beyond diabetes, metformin may prove to be a ‘wonder drug’ – Healio, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.healio.com/news/endocrinology/20170207/beyond-diabetes-metformin-may-prove-to-be-a-wonder-drug
- “Happy Accidents”: Repurposing Metformin – Psychiatric Times, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/happy-accidents-repurposing-metformin
- A Narrative Review: Repurposing Metformin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Oral Cancer – MDPI, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/16/17/3017
- Target-Based Drug Repositioning Using Large-Scale Chemical–Protein Interactome Data, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00330
- Drug repurposing: a promising tool to accelerate the drug discovery process – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11920972/
- Computational and chemical approaches to drug repurposing – KI Open Archive, accessed May 8, 2025, https://openarchive.ki.se/articles/thesis/Computational_and_chemical_approaches_to_drug_repurposing/26916481
- A review of computational drug repurposing – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6989243/
- Full article: Drug Repurposing and Computational Drug Discovery: Strategies and Advances – Taylor & Francis Online, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/0889311X.2024.2430996?src=exp-la
- Computational methods directed towards drug repurposing for COVID-19: advantages and limitations – RSC Publishing Home, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/ra/d1ra05320e
- Making the most effective use of available computational methods for drug repositioning, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17460441.2023.2198700
- Drug Discovery: Computational Chemistry-Based Drug Repurposing – Open Access Journals, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.openaccessjournals.com/articles/drug-discovery-computational-chemistrybased-drug-repurposing.pdf
- Approaches for drug repurposing. (a) Experimental based, (b) clinical… – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Approaches-for-drug-repurposing-a-Experimental-based-b-clinical-based-and-c_fig1_341156185
- Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods for Drug Repurposing and …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/15/5/2798
- Drug repurposing and phenotypic screening: innovative strategies for treating ultra-rare disorders – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1489094/pdf
- Phenotypic Screening in Drug Discovery: An Overview | Technology …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.technologynetworks.com/drug-discovery/articles/phenotypic-screening-a-powerful-tool-for-drug-discovery-398572
- Phenotypic screening – Wikipedia, accessed May 8, 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phenotypic_screening
- Phenotypic Drug Discovery: Recent successes, lessons learned and …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9708951/
- Phenotypic Screening of the Reframe Drug Repurposing Library to Discover New Drugs for Treating Sickle Cell Disease | Blood | American Society of Hematology, accessed May 8, 2025, https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/140/Supplement%201/11089/491712/Phenotypic-Screening-of-the-Reframe-Drug
- Validation approaches for computational drug repurposing: a review …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10785886/
- Computational Methods for Drug Repurposing (Methods in Molecular Biology, 1903) – Amazon.com, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.amazon.com/Computational-Methods-Repurposing-Molecular-Biology/dp/1493989545
- Computational approaches for drug repurposing in oncology: untapped opportunity for high value innovation – Frontiers, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2023.1198284/full
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in drug repurposing – challenges and perspectives, accessed May 8, 2025, https://drugrepocentral.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000007.v1
- Researchers Harness AI to Repurpose Existing Drugs for Treatment …, accessed May 8, 2025, https://hms.harvard.edu/news/researchers-harness-ai-repurpose-existing-drugs-treatment-rare-diseases
- Revolutionizing Pharmaceuticals: The Impact of Big Data, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.medicapharma.com/revolutionizing-pharmaceuticals-the-transformative-impact-of-big-data/
- The Benefits of Big Data in Drug Development | Contract Pharma, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.contractpharma.com/the-benefits-of-big-data-in-drug-development/
- 8 Use Cases For Data Analytics In Pharmaceutical Industry – Polestar Solutions, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.polestarllp.com/blog/analytics-in-pharmaceutical-companies
- Drug Repurposing Market Size, Industry Trends And Future Outlook By 2033, accessed May 8, 2025, https://straitsresearch.com/report/drug-repurposing-market
- Drug Repurposing Market to Grow by USD 8.57 Billion (2024-2028) as Cancer Treatment Applications Expand, AI-Driven Market Transformation Report – Technavio – PR Newswire, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/drug-repurposing-market-to-grow-by-usd-8-57-billion-2024-2028-as-cancer-treatment-applications-expand-ai-driven-market-transformation-report—technavio-302292477.html
- Drug repurposing: An effective strategy to accelerate contemporary drug discovery – PMC, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9155184/
- Current trends and future prospects of drug repositioning in gastrointestinal oncology, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38239190/
- Editorial: The Challenge of New Therapeutic Approaches for Unmet Therapeutic Needs – PMC – PubMed Central, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7554613/
- Advances of the Target-Based and Phenotypic Screenings and Strategies in Drug Discovery, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.sciltp.com/journals/ijddp/article/view/199
- pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10785886/#:~:text=Computational%20drug%20repurposing%20consists%20of,diseases%20that%20need%20drug%20treatments.
- Computational Approaches to Drug Repurposing: Methods, Challenges, and Opportunities, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.annualreviews.org/content/journals/10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-110123-025333
- Giving old drugs new life…to save lives – Wyss Institute, accessed May 8, 2025, https://wyss.harvard.edu/news/giving-old-drugs-new-life-to-save-lives/
- Examples of some FDA-approved repurposed drugs. – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Examples-of-some-FDA-approved-repurposed-drugs_tbl1_352482307
- Sildenafil – Wikipedia, accessed May 8, 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sildenafil
- Sildenafil – Pulmonary Hypertension Association, accessed May 8, 2025, https://phassociation.org/patients/treatments/sildenafil/
- Repurposing of the PDE5 Inhibitor Sildenafil for the Treatment of Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension in Neonates | Bentham Science, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.benthamscience.com/article/110180
- Repurposing of the PDE5 Inhibitor Sildenafil for the Treatment of Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension in Neonates – PubMed, accessed May 8, 2025, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32964819/
- Cleveland Clinic-Led Research Supports Repurposing Sildenafil (Viagra) For Alzheimer’s Treatment, accessed May 8, 2025, https://newsroom.clevelandclinic.org/2024/03/05/cleveland-clinic-led-research-supports-repurposing-sildenafil-viagra-for-alzheimers-treatment
- Advantages and Limitations of Drug Repositioning | Request PDF – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341541031_Advantages_and_Limitations_of_Drug_Repositioning
- Computational methods directed towards drug repurposing for COVID-19: advantages and limitations – ResearchGate, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356124596_Computational_methods_directed_towards_drug_repurposing_for_COVID-19_advantages_and_limitations
- Drug Discovery and Development: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Drug Repurposing, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/fmc-2024-0048
- Drug repurposing in rare diseases, accessed May 8, 2025, https://www.rarebeacon.org/research/drug-repurposing/