The pharmaceutical industry is on the brink of a revolution. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are emerging as powerful engines that can overhaul the early stages of drug R&D, transforming how targets are identified, molecules are designed, and data is analyzed (1, 2, 3). For a busy pharma executive, the big question is: how can AI/ML truly impact our drug pipelines? The answer spans from accelerated target identification to generative design of novel compounds, with case studies already demonstrating dramatic results (4, 5).
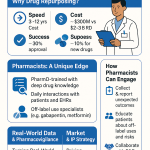
Imagine AI as a virtual chemist and data analyst rolled into one. It can scan billions of molecular combinations, predict properties, and highlight the most promising candidates — all in a fraction of the time it would take humans (6). In practical terms, this means potentially reducing a process that traditionally took 10–15 years and over $2.6 billion (2) into something much faster and cheaper.
The Challenge of Traditional Drug Discovery
Drug discovery has been painfully slow and risky. Between 2000 and 2015, over 86% of drug candidates failed to meet clinical endpoints (2). Only about 14% would ever reach patients. Typically, a new drug goes through these steps:
- Target identification
- Target validation
- Lead compound discovery
- Lead optimization
- Preclinical studies
- Clinical trials
Out of thousands of projects, only a handful pay off, at a cost of billions of dollars and over a decade per success (2). AI/ML promises to shift the odds, making discovery less random (3, 4).
How AI and ML Accelerate Early-Stage R&D
AI and ML tools shine in data-rich, pattern-finding tasks. In early drug discovery, this means everywhere from mining genomics data for targets to screening virtual molecules (5, 6).
Target Identification and Validation
AI excels at scanning complex biological data to suggest novel targets (3). ML algorithms can uncover hidden relationships between diseases and molecular pathways that human analysts might miss (5). For example, DeepMind’s AlphaFold uses deep learning to predict protein 3D structures with near-experimental accuracy (15).
Virtual Screening and Lead Discovery
Once a target is chosen, AI performs in silico screening of virtual compound libraries (4). For instance, MIT researchers used an ML model to evaluate over 100 million molecules in a matter of days, identifying a novel antibiotic (halicin) (6).
De Novo Drug Design (Generative Chemistry)
Advances in AI such as variational autoencoders and reinforcement learning allow models to sample chemical space creatively (5). Insilico Medicine, for example, used its AI platform to discover a first-in-class anti-fibrotic compound for pulmonary fibrosis in under 30 months (4).
Predicting ADMET and Side Effects
AI plays a crucial role in predicting absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) before any animal tests (14). Atomwise’s AI predicted toxic liabilities for candidate compounds, weeding out those likely to fail in safety trials (3).
Data Infrastructure and AI: Fueling Discovery
Pharmaceutical companies sit on enormous proprietary datasets (8). Leading AI drug discovery firms are amassing petabytes of data (10). Recursion, for example, processes over 2 million experiments per week (10).
Real-World Case Studies: Pharma Companies Leveraging AI/ML
Recursion Pharmaceuticals
Recursion has built an AI-driven platform combining high-content cell imaging with deep learning (10).
BenevolentAI
BenevolentAI combines unstructured literature with databases using AI to make connections between disease pathways (9).
Insilico Medicine
Insilico advanced an AI-designed anti-fibrotic molecule into Phase I trials after only ~30 months (4).
Exscientia & Sumitomo
Exscientia partnered with Sumitomo Dainippon to use AI/ML in designing DSP-1181, a long-acting 5-HT1A agonist for OCD, achieved in under 12 months (7).
Lantern Pharma
Lantern Pharma focuses on repurposing oncology drugs using its RADR platform (11).
Big Pharma Moving In
Eli Lilly and Novartis each struck deals with Google’s AI spinout Isomorphic Labs in 2024 (12). NVIDIA supports these efforts with its DGX Cloud for AI drug discovery (13).
Benefits of AI/ML in Drug Discovery
- Speed and efficiency: Faster target-to-candidate timelines (2, 4).
- Cost savings: AI can slash R&D costs (4).
- Higher success rates (early stages): AI-derived candidates have had unusually high Phase I success rates (2).
- Competitive advantage: AI can broaden pipelines and reduce risk (8).
Challenges and Considerations
- Data quality and bias
- Interpretability
- Regulatory hurdles (3)
- Intellectual property
- Skill gap and culture (8)
The Future: Towards Fully Autonomous Discovery
Expect more AI integration through LLMs, quantum computing, digital twins, and personalized medicine strategies (1, 2, 3).
Key Takeaways
- AI/ML are reshaping early drug R&D (1-4)
- Real-world successes demonstrate AI’s potential (4, 6, 7, 10)
- Top pharma firms are investing heavily in AI platforms (8, 12, 13)
- AI-designed molecules show high Phase I success rates (2)
- Integration challenges require robust strategies (3, 8)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How quickly can AI reduce drug development time?
Examples show timelines reduced to months from years (4, 7).
Q2: What success rates do AI-designed drugs have in clinical trials?
AI-derived molecules have shown up to 80-90% Phase I success (2).
Q3: Are big pharmaceutical companies already using AI?
Yes, with partnerships and internal programs (8, 12).
Q4: What are the main challenges when implementing AI in drug discovery?
Data quality, explainability, and IP remain key hurdles (3, 8).
Q5: How does AI fit into the larger pharmaceutical R&D strategy?
AI augments human decision-making throughout the pipeline (1-4).
Sources
- DrugPatentWatch — https://www.drugpatentwatch.com
- Boston Consulting Group (BCG), AI in Biopharma R&D: Delivering on the Promise (2023)
- U.S. FDA, Artificial Intelligence in Drug Development: Current Status and Future Directions (2024)
- Insilico Medicine, First AI-Discovered and AI-Designed Drug Candidate Enters Clinical Trials (2022)
- Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery: Progress and Challenges (2023)
- MIT News, AI System Identifies Promising New Antibiotic (2020)
- Exscientia Press Release, First AI-Designed Drug Moves to Clinical Trials in Partnership with Sumitomo Dainippon (2020)
- McKinsey & Company, Scaling AI in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Lessons from the Field (2024)
- BenevolentAI Corporate Website and Investor Reports (2024)
- Recursion Pharmaceuticals Corporate Website and Investor Reports (2024)
- Lantern Pharma Corporate Reports and RADR Platform Overview (2024)
- DeepMind / Isomorphic Labs, Press Releases on Pharma Collaborations (2024)
- NVIDIA, DGX Cloud for AI Drug Discovery (2024)
- Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, Machine Learning for ADMET Predictions (2023)
- Science, AI Predicts Protein Structures with Near-Experimental Accuracy (2020)