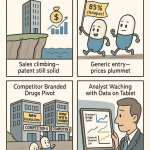
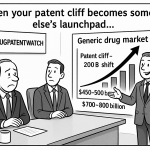
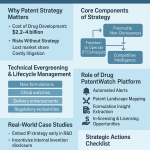
The pharmaceutical industry faces a critical financial challenge when drug patents expire, often referred to as the “patent cliff.” When pharmaceutical patents reach the end of their 20-year protection period, companies typically experience a dramatic revenue decline of up to 90% as generic competitors enter the market with substantially lower-priced alternatives[1]. The global pharmaceutical industry is heading toward a massive $236 billion patent cliff between 2025 and 2030, with nearly 70 high-revenue products facing potential competition[4]. This comprehensive guide explores the five strategic steps pharmaceutical companies can take to navigate the challenging transition from patent protection to open market competition, presenting innovative approaches to maintaining profitability and market presence even after losing exclusivity.
Understanding the Patent Cliff Challenge
Before diving into specific strategies, it’s essential to understand the full scope of the patent cliff challenge facing pharmaceutical companies today. Patent expiration represents one of the most significant turning points in a drug’s commercial lifecycle, transforming exclusive, high-margin products into commodities faced with intense price competition[3].
The Financial Impact of Patent Expiration
The financial implications of patent expiration extend far beyond immediate revenue loss. When patents lapse, generics and biosimilars enter with lower prices, slashing sales of branded drugs. Small-molecule drugs typically lose 90% of their market share within months, while biologics decline by 30% to 70% in the first year due to complex production and slower adoption[4].
Research shows that the average price of physician-administered drugs declined by between 38 and 48 percent following patent expiration, while oral medications saw a more modest reduction of about 25 percent[2]. This dramatic price erosion creates an urgent need for pharmaceutical companies to develop effective strategies to maintain revenue streams and protect shareholder value.
Current Market Trends in Pharmaceutical Patent Expirations
The current wave of patent expirations differs significantly from previous cycles. Unlike the 2008 patent cliff, this period features a higher share of biologics, which face slower but substantial erosion from biosimilars[4]. This shift is driven by faster regulatory approvals from regulatory agencies worldwide and growing acceptance of biosimilars among healthcare providers and patients.
Leading the losses are drugs like Merck’s Keytruda, with $25 billion in 2023 sales, set to expire in 2028, and Bristol-Myers Squibb’s Eliquis, at $12 billion, due by 2027 or 2028[4]. These patent expirations will reshape markets for critical treatments, including cancer and diabetes drugs, while forcing companies to adapt swiftly to maintain their competitive edge.
The Regulatory Landscape for Post-Patent Drugs
The regulatory environment plays a crucial role in determining how quickly generics can enter the market after patent expiration. The Hatch-Waxman Act of 1984 established an abbreviated FDA approval process for generic drugs, allowing generic manufacturers to apply for FDA approval and conduct bioequivalence testing without repeating costly clinical trials[5]. This legislation significantly increased the availability of generic medications and transformed the pharmaceutical landscape.
For biologics, the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act created a pathway for biosimilar approvals, though with more rigorous requirements than for small-molecule generics. Understanding these regulatory frameworks is essential for pharmaceutical companies planning their post-patent strategies.
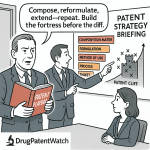
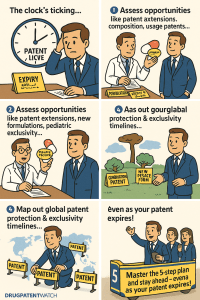
Step 1: Develop a Comprehensive Patent Expiration Strategy
The first and most crucial step in addressing patent expiration is developing a comprehensive strategy well before the patent’s end date. This strategic planning process should begin years in advance to ensure adequate time for implementation and market adaptation.
Timing Your Strategic Response
Timing is everything when preparing for patent expiration. A well-structured approach typically begins 3-5 years before patent expiration, allowing sufficient time to implement various defensive and adaptive strategies. This advance planning provides companies with the opportunity to maximize returns during the remaining exclusivity period while preparing for the post-patent landscape.
“Declining R&D productivity, rising costs of commercialization, near-term patent expirations for many top-selling drugs are forcing companies to adopt new systems to introduce innovative products to market and to focus on strategies that increase the returns from the existing product portfolio.”[6]
This quote highlights the urgency with which pharmaceutical companies must approach patent expiration planning, recognizing it as not just a defensive measure but an opportunity to reimagine their business model and product portfolio.
Assembling Your Patent Cliff Response Team
Creating a dedicated cross-functional team is essential for effective patent cliff navigation. This team should include representatives from:
- Research and development
- Marketing and sales
- Legal and intellectual property
- Manufacturing and supply chain
- Finance and strategic planning
- Regulatory affairs
By bringing together expertise from across the organization, companies can develop more robust and innovative approaches to addressing patent expiration challenges. This collaborative approach ensures that all aspects of the business are aligned with the post-patent strategy.
Conducting a Thorough Market Analysis
A comprehensive market analysis provides the foundation for an effective patent expiration strategy. This analysis should include:
- Assessment of potential generic competitors and their capabilities
- Evaluation of market dynamics and pricing sensitivities
- Understanding of payer and provider perspectives on generic substitution
- Analysis of patient loyalty and switching behaviors
- Identification of unmet needs that could drive product differentiation
This market intelligence helps companies identify the most promising approaches for maintaining market share and profitability after patent expiration. By understanding the competitive landscape, companies can develop targeted strategies that address specific market realities.
Step 2: Maximize Brand Loyalty Before Patent Expiration
Building strong brand loyalty before patent expiration can significantly impact a drug’s market performance after generics enter the competition. Companies that successfully develop deep relationships with patients, providers, and payers may retain substantial market share despite lower-priced alternatives.
Implementing Patient Support Programs
As patent expiration approaches, many companies invest heavily in brand loyalty programs designed to maintain market share despite generic competition. These programs typically offer discounts, patient support services, or other benefits that generic manufacturers may struggle to match[1].
Effective patient support programs might include:
- Copay assistance and financial support
- Medication adherence tools and resources
- Disease management education and resources
- Patient communities and support networks
- Direct-to-patient communication channels
By creating value beyond the medication itself, pharmaceutical companies can build relationships that survive the transition to a competitive market environment. Patients who experience benefits from these programs may be reluctant to switch to generic alternatives, even with potential cost savings.
Leveraging Healthcare Provider Relationships
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in prescribing decisions and can significantly influence whether patients receive brand-name drugs or generic alternatives. Building strong relationships with key opinion leaders and prescribers can help maintain prescription volumes after patent expiration.
Strategies for strengthening provider relationships include:
- Developing valuable educational resources
- Supporting continuing medical education initiatives
- Providing robust clinical data demonstrating the drug’s value
- Creating prescriber support tools that simplify patient management
- Establishing scientific exchange programs that highlight therapeutic expertise
Providers who view a pharmaceutical company as a valuable partner in patient care may be more inclined to continue prescribing branded medications even when generic alternatives are available.
Strategic Pricing Adjustments
Proactive pricing strategies can help companies maintain market share while adapting to the new competitive landscape. Research shows that for oral drugs after generic entry, high and increasing brand prices partly offset low and decreasing generic prices[2]. While this approach may not maintain pre-expiration revenue levels, it can help minimize losses and create a more sustainable transition.
Strategic pricing options include:
- Gradual price adjustments to reduce the shock of patent expiration
- Tiered pricing strategies for different market segments
- Value-based pricing arrangements tied to clinical outcomes
- Rebate and discount programs for loyal customers
- Bundle pricing with complementary products or services
These pricing approaches should be carefully calibrated to balance short-term revenue protection with long-term market sustainability. Too aggressive a stance may accelerate market share erosion, while too passive an approach may surrender profit unnecessarily.
Step 3: Consider Product Lifecycle Extensions
One of the most effective strategies for mitigating patent expiration is extending the product lifecycle through innovation and product development. These approaches can create new periods of exclusivity or strengthen market differentiation against generic competitors.
Developing Next-Generation Products
Pharmaceutical companies often focus on developing next-generation products that offer meaningful improvements over the original formulation. This approach involves significant R&D investment but can create a smooth transition path for patients from the original product to the improved version before generics enter the market.
Next-generation product development might focus on:
- Enhanced efficacy through improved molecular design
- Reduced side effects or improved safety profile
- More convenient dosing schedules
- Addressing secondary conditions or comorbidities
- Improved bioavailability or pharmacokinetics
If successful, this strategy can shift market demand to the new, patent-protected product, essentially rendering generic versions of the original formulation less relevant in the marketplace.
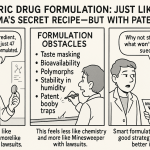
Exploring New Formulations and Delivery Systems
Another approach is to create different formulations of an existing product, often with a different delivery system, to extend patent life. This strategy involves lower developmental costs compared to creating a completely new molecular entity[5]. Modified-release formulations, injectable versions of oral medications, or novel delivery devices can all provide additional patent protection while offering tangible benefits to patients.
Examples of successful delivery innovations include:
- Extended-release formulations that reduce dosing frequency
- Transdermal patches that replace oral medications
- Implantable or injectable long-acting formulations
- Inhalation devices that improve drug delivery
- Combination delivery systems that enhance patient adherence
These innovations not only extend patent protection but can also address specific patient needs, creating meaningful differentiation from generic versions of the original product.
Seeking New Indications and Uses
Expanding approved indications for an existing drug can open new markets and potentially extend market exclusivity. This approach requires additional clinical trials but leverages the existing safety data and company knowledge about the molecule.
Strategies for indication expansion include:
- Investigating use in related disease states
- Exploring applications in different patient populations
- Evaluating effectiveness for different disease stages
- Researching preventative applications
- Investigating use in rare diseases or orphan indications
Each new approved indication can potentially come with its own period of market exclusivity, creating a patchwork of protection that extends beyond the original patent expiration.
The Value of Combination Therapies
Combination therapies represent a particularly valuable approach to lifecycle extension. By combining the original drug with other active ingredients, companies can create new patent-protected products that offer enhanced efficacy or address multiple aspects of a disease state.
Combination therapy advantages include:
- New patent protection for the specific combination
- Enhanced efficacy through synergistic effects
- Improved patient convenience with fewer pills or injections
- Reduced side effects through lower individual drug doses
- Potential for premium pricing based on enhanced value
Major pharmaceutical companies have successfully used combination therapies to extend franchises well beyond the patent life of the original molecule, particularly in therapeutic areas like hypertension, diabetes, and infectious disease.
Step 4: Explore Strategic Business Adaptations
Beyond product-specific strategies, pharmaceutical companies can implement broader business adaptations to navigate patent expirations successfully. These approaches often involve rethinking the company’s position in the market and exploring new business models.
Launching Authorized Generics
One tactic is for branded manufacturers to launch their own authorized generic versions of a product at the same time the first generic version hits the market. This move decreases the financial benefit of the period of exclusivity for the generic manufacturer and may discourage patent challenges[5].
Authorized generics offer several advantages:
- Capture a portion of the generic market
- Maintain manufacturing volume and efficiency
- Preserve relationships with distribution channels
- Generate data on post-patent market dynamics
- Potentially discourage aggressive generic competition
By participating in both the branded and generic segments, pharmaceutical companies can manage the transition more effectively and maintain a larger overall market share.
Pursuing Licensing and Partnership Opportunities
Strategic partnerships can help pharmaceutical companies leverage external innovation and capabilities to address patent expiration challenges. These partnerships might include in-licensing promising compounds to fill pipeline gaps, co-development agreements to share costs and risks, or out-licensing declining products to companies better positioned to maximize their remaining value.
Effective partnership strategies might include:
- In-licensing late-stage assets to fill revenue gaps
- Forming co-promotion agreements for complementary products
- Establishing research collaborations focused on life-cycle management
- Creating joint ventures for specific geographic markets
- Developing risk-sharing agreements with payers or providers
These collaborative approaches can provide access to innovation and capabilities beyond what the company could develop internally, potentially accelerating the response to patent expiration challenges.
Acquisition Strategies for Portfolio Diversity
Strategic acquisitions represent another approach to addressing revenue gaps created by patent expirations. By acquiring companies with complementary products, promising pipelines, or specific technological capabilities, pharmaceutical companies can diversify their portfolio and reduce reliance on any single patent-protected product.
For example, in early 2024, Merck entered a definitive agreement to acquire US Harpoon Therapeutics for $680 million to further advance its oncology portfolio, helping offset potential revenue losses when Keytruda loses patent protection in 2028[7].
Effective acquisition strategies consider:
- Pipeline synchronization to ensure continuous revenue flow
- Therapeutic area focus to leverage existing expertise
- Technology platform acquisition for future innovation
- Geographic expansion opportunities
- Scale advantages in research, manufacturing, or commercialization
While acquisitions require significant investment, they can provide immediate revenue diversification and long-term strategic benefits that help companies weather patent expirations more effectively.
Step 5: Optimize Manufacturing and Supply Chain
The final step in preparing for patent expiration involves optimizing manufacturing and supply chain operations to improve cost competitiveness and operational flexibility. As price pressures increase after patent expiration, manufacturing efficiency becomes increasingly important for maintaining profitability.
Cost Reduction Strategies
Implementing comprehensive cost reduction initiatives across the value chain can help preserve margins even as prices decline. These initiatives might include:
- Process optimization to improve manufacturing efficiency
- Raw material sourcing improvements
- Technology upgrades to reduce production costs
- Scale adjustments to match post-patent demand patterns
- Workforce realignment to match new market realities
By systematically addressing cost drivers, pharmaceutical companies can create a more competitive cost structure that supports profitability even in a more price-sensitive environment.
Supply Chain Resilience for Post-Patent Competition
Building supply chain resilience is critical for competing effectively after patent expiration. A robust and flexible supply chain can help companies respond quickly to market changes, maintain reliable product availability, and potentially create competitive advantages against generic manufacturers with less sophisticated supply networks.
Key elements of supply chain resilience include:
- Diversified supplier relationships to reduce dependency
- Flexible manufacturing capacity that can scale to match demand
- Streamlined distribution channels with reduced intermediaries
- Advanced inventory management systems to optimize working capital
- End-to-end visibility through digital supply chain technologies
These capabilities help pharmaceutical companies maintain reliable product supply while adapting to the changing competitive landscape after patent expiration.
Leveraging Manufacturing Expertise as a Competitive Advantage
For some products, particularly complex biologics or drugs with challenging manufacturing requirements, production expertise can serve as a barrier to generic competition. By continuously advancing manufacturing capabilities, pharmaceutical companies can create sustainable advantages that persist beyond patent expiration.
Approaches to leveraging manufacturing expertise include:
- Continuous process improvement and innovation
- Advanced analytics and AI implementation in production
- End-to-end quality systems that ensure consistent product quality
- Specialized capabilities for complex formulations or delivery systems
- Sustainability initiatives that create additional value
While generic manufacturers can replicate drug formulations, they may struggle to match the manufacturing efficiency and quality systems of experienced producers, creating an ongoing competitive advantage for the original manufacturer.
Measuring Success in Post-Patent Strategy
Implementing effective strategies is only part of the challenge—measuring their impact and making continuous adjustments is equally important for navigating patent expiration successfully.
Key Performance Indicators for Patent Cliff Navigation
Establishing clear metrics to evaluate strategy effectiveness helps companies track progress and make necessary adjustments. Key performance indicators might include:
- Market share retention compared to historical averages
- Revenue preservation percentage
- Profit margin maintenance
- Successful transition rate to next-generation products
- Speed of implementation for strategic initiatives
- Return on investment for lifecycle management efforts
Regular review of these metrics allows companies to identify which strategies are delivering the expected results and which require modification or replacement.
Case Studies: Successful Patent Expiration Responses
Learning from companies that have successfully navigated patent expirations provides valuable insights for developing effective strategies. While sales volume appears to increase substantially following generic entry, total revenue from sales of both branded and generic versions of drugs increased after patent expiration in many cases[2].
This counterintuitive finding suggests that well-executed post-patent strategies can create value even in a more competitive environment. By studying these success cases, pharmaceutical companies can identify approaches that might work for their specific products and market conditions.
Key Takeaways
Navigating the patent cliff requires a multifaceted approach that begins years before patent expiration and continues well into the post-patent period. Key takeaways from this analysis include:
- Start early: Begin planning at least 3-5 years before patent expiration to implement comprehensive strategies.
- Diversify approaches: Combine multiple strategies—from lifecycle management to business model innovation—for the most robust response.
- Build loyalty: Invest in patient and provider relationships that can withstand the introduction of lower-priced alternatives.
- Innovate continuously: Develop next-generation products and formulations that provide meaningful improvements over the original drug.
- Optimize operations: Create a competitive cost structure and resilient supply chain to compete effectively in the post-patent environment.
- Measure and adapt: Establish clear metrics to evaluate strategy effectiveness and make continuous adjustments.
- Learn from success: Study companies that have successfully navigated patent expirations to identify applicable approaches.
By implementing these strategic approaches, pharmaceutical companies can transform the challenge of patent expiration into an opportunity for innovation and business model evolution, ensuring sustained growth and profitability despite the inevitable loss of exclusivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long before patent expiration should pharmaceutical companies begin implementing strategies?
Pharmaceutical companies should ideally begin planning and implementing patent expiration strategies 3-5 years before the patent expires. This timeline provides sufficient opportunity to develop and launch next-generation products, build brand loyalty programs, optimize manufacturing processes, and implement other strategic initiatives that can help maintain market share and profitability after generics enter the market.
2. What is the typical revenue impact of patent expiration for pharmaceutical products?
The revenue impact varies by product type, but research shows that small-molecule drugs typically lose up to 90% of their market share within months of patent expiration, while biologics decline by 30% to 70% in the first year due to complex production and slower adoption of biosimilars. The average price of physician-administered drugs declines by between 38% and 48% following patent expiration, while oral medications see a more modest reduction of about 25%.
3. Can pharmaceutical companies prevent generic manufacturers from challenging their patents before expiration?
While pharmaceutical companies cannot prevent legitimate patent challenges, they can implement strategies to discourage early challenges or settle them advantageously. These approaches include robust patent portfolios with multiple layers of protection, launching authorized generics to reduce the financial incentive for first generic entrants, and strategic settlements that balance immediate competitive threats with long-term business objectives.
4. How effective are combination therapies in extending product lifecycles?
Combination therapies have proven highly effective in extending product lifecycles, particularly in therapeutic areas like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory conditions. By combining an off-patent molecule with other active ingredients, companies can create new patent-protected products that offer enhanced efficacy or convenience. The success of this approach depends on demonstrating meaningful clinical benefits that justify continued use despite the availability of generic versions of the original molecule.
5. What emerging strategies are pharmaceutical companies exploring to address future patent expirations?
Emerging strategies include value-based contracting that ties pricing to clinical outcomes, digital therapeutics that complement traditional medications, subscription-based pricing models for high-cost treatments, and advanced analytics to identify patient subpopulations with enhanced response. Companies are also increasingly exploring opportunities in precision medicine, where genetic or biomarker-based targeting may create sustained competitive advantages that transcend traditional patent protection.
Sources:
- https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/top-strategies-for-pharma-profitability-after-drug-patents-expire/
- https://www.nber.org/digest/sep14/patent-expiration-and-pharmaceutical-prices
- https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/what-happens-when-a-drug-patent-expires/
- https://www.geneonline.com/pharma-faces-236-billion-patent-cliff-by-2030-key-drugs-and-companies-at-risk/
- https://www.drugpatentwatch.com/blog/patent-expirations-seizing-opportunities-in-the-generic-drug-market/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4899342/
- https://www.proclinical.com/blogs/2024-2/top-10-drugs-with-patents-due-to-expire-in-the-next-5-years