Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Loratadine, a widely prescribed second-generation antihistamine, has maintained a pivotal role in allergy management since its marketing authorization in the late 1990s. Its unique pharmacological profile, characterized by selective peripheral H1 receptor antagonism, offers effective relief for allergic rhinitis, chronic urticaria, and other allergic conditions without significant sedative effects. This analysis explores the evolving market dynamics and financial trajectory of loratadine, emphasizing factors influencing market growth, competitive landscape, regional trends, patent status, and future outlook.
Market Overview and Historical Context
Loratadine's initial success was driven by unmet clinical needs for non-sedating antihistamines, resulting in rapid uptake globally, notably through prominent brands such as Claritin (manufactured by Schering-Plough/Merck) and its generic counterparts. Driven by an expanding allergy prevalence, increasing awareness, and expanding over-the-counter (OTC) availability in multiple countries, loratadine cemented its position as a treatment mainstay for allergic conditions by the early 2000s. The compound's favorable safety profile further enhanced its acceptance across diverse patient populations.
Initially, patent protections provided a competitive moat, allowing pharmaceutical companies to capitalize on brand value for approximately a decade. As patents expired in many key markets, the emergence of numerous generics significantly shifted the market dynamics, impacting sales revenues for originator companies.
Market Dynamics Influencing Loratadine's Trajectory
1. Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
The expiration of loratadine patents, notably in North America and Europe around the late 2000s to early 2010s, catalyzed a wave of generic entrants. This proliferation of lower-cost formulations led to a sharp decline in brand-name sales, compelling originators to adopt strategies such as price reductions, promoting OTC access, or diversifying their product portfolios. Market share shifted rapidly toward generics, with price competition becoming the dominant dynamic.
2. Regulatory Approvals and OTC Transition
Loratadine's transition from prescription to OTC in various jurisdictions expanded its accessibility, notably in the United States (FDA approved OTC status in 2002). OTC status broadened the consumer base, increased sales volume, and mitigated some losses incurred from generic competition. However, it also placed downward pressure on prices, affecting overall revenue.
3. Regional Market Variations
Market size, prescription versus OTC status, and regulatory policies vary globally. North America and Europe constitute mature markets with intense generic competition, leading to reliance on volume sales and diversification strategies. In comparison, emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific present growth opportunities driven by rising allergy prevalence, increasing healthcare awareness, and expanding OTC drug markets. For example, China's allergy drug market is projected to grow sharply, driven by urbanization and environmental factors.
4. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
While loratadine remains a staple in allergy pharmacotherapy, new-generation antihistamines like levocetirizine, desloratadine, and fexofenadine offer comparable or superior efficacy with potential for longer-lasting effects. These alternatives influence consumer preferences and prescribing patterns, thereby shaping loratadine's market share. Additionally, combination products featuring loratadine with other agents (e.g., pseudoephedrine) impact its sales dynamics in specific segments.
5. Impact of Pharmacoeconomics and Healthcare Policies
Reimbursement policies favoring generic drugs and price controls accelerate volume-driven markets. Healthcare providers' prescribing behaviors are also influenced by clinical guidelines, safety profiles, and cost considerations. The emphasis on value-based care encourages use of cost-effective antihistamines like loratadine, especially where clinical equivalence with newer agents exists.
Financial Trajectory: Revenue Trends and Market Opportunities
1. Revenue Decline Post-Patent Expiry
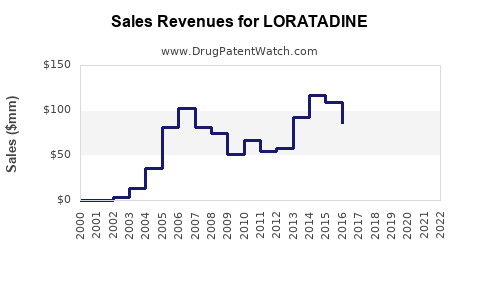
Originator companies historically experienced revenue erosion following patent cliffs, with brand sales decreasing by double digits within years of generic entry. For instance, Schering-Plough's Claritin experienced a decline after patent expiration, although OTC sales partially offset this reduction via increased accessibility. Overall, the shift to generics led to a notable contraction in brand-name revenues, with estimates indicating a 50-60% decline within five years post-patent expiry in mature markets.
2. Growth in Generic Sales and Price Competition
Generics now dominate loratadine sales, capturing over 80-90% of market volume in key regions. Companies employ aggressive pricing, promotion, and supply chain efficiencies to maintain profit margins despite price erosion. The global loratadine generics market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2021, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4-5% forecasted over the next five years (2022-2027).
3. Market Expansion in Developing Countries
Emerging markets present lucrative opportunities. The increasing prevalence of allergy-related conditions, coupled with broader OTC availability, fosters growth. Companies investing in localized marketing and partnerships with healthcare providers aim to capture market share. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to lead growth, driven by population expansion and greater healthcare access.
4. Innovation and Combination Therapies
While loratadine itself faces limited innovation, product differentiation strategies—such as sustained-release formulations or combination therapies—could drive incremental revenues. These innovations aim to improve adherence, efficacy, and convenience, particularly for chronic allergic conditions.
5. Future Outlook and Challenges
Predicting loratadine's financial trajectory demands consideration of regulatory shifts, market saturation, and alternative therapies. The continued dominance of generics suggests stable low-margin volumes rather than high-margin brand revenues. However, strategic diversification, biosimilar competition, and potential new formulations may influence future profitability.
Conclusion
Loratadine's market journey reflects a classic path from innovative prescription drug to a globally available generic staple. Although patent expiries curtailed original brand revenues, expanded OTC access and regional growth opportunities sustain its relevance. Market dynamics now hinge on competitive pricing, regional market development, and incremental innovation. Industry participants must adapt to these evolving forces to optimize financial outcomes, leveraging loratadine's established efficacy profile within the broader allergy therapeutics landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expiries have led to a surge in generic loratadine options, reducing brand-name revenues significantly.
- OTC availability has expanded consumer access, supporting volume growth in mature and emerging markets.
- Regional disparities shape market strategies; emerging markets offer substantial growth potential, especially in Asia-Pacific.
- Competitive therapies and new formulations challenge loratadine's market share, emphasizing the need for strategic innovation.
- Pricing pressures and healthcare policies favor volume over margins, influencing the overall financial trajectory.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How has loratadine's patent expiration affected its market share?
Patent expirations have led to a rapid increase in generic competitors, causing a significant decline in brand-name market share in mature markets. Generics now dominate sales volumes; however, brand loyalty and OTC availability sustain some brand-value retention.
2. What regional factors influence loratadine's market growth?
Developed markets face intense generic competition, relying on volume sales and OTC channels, whereas emerging markets benefit from rising allergy prevalence, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and increasing OTC access, offering growth opportunities.
3. Are there any recent innovations related to loratadine?
Though direct innovation in loratadine is limited, combination formulations and extended-release variants are explored to improve efficacy and adherence, potentially creating niche markets and new revenue streams.
4. How does competition from newer antihistamines impact loratadine?
Newer agents like levocetirizine and fexofenadine offer longer duration and better side effect profiles, diverting some market share from loratadine, especially in segments seeking enhanced convenience or efficacy.
5. What is the outlook for loratadine in the next five years?
The outlook remains stable primarily through generic sales expansion, regional growth, and potential niche innovations. However, quote from generics' low-margin environment and evolving competitive landscape indicates limited upside for brand-name revenues.
Sources
[1] "Loratadine Market by Product Type, Distribution Channel, End User – Global Forecast to 2027," MarketsandMarkets.
[2] Food and Drug Administration (FDA). "OTC Drug Facts," 2002.
[3] Grand View Research. "Allergy Therapeutics Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report."
[4] IQVIA. "Global Market Enrollment and Sales Data," 2022.
[5] "Pharmaceutical Patent Expiry and Market Trends," patent analysis reports.