Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Amphetamine, a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant, has a complex history rooted in medicinal use, regulatory scrutiny, and evolving market dynamics. Originally synthesized in the late 19th century, it gained prominence in the mid-20th century as a treatment for narcolepsy, ADHD, and as a stimulant for various conditions. Its pharmacological profile and misuse potential have profoundly influenced its commercial viability, regulatory status, and market trajectory. This analysis explores the current state of amphetamine’s market dynamics, future outlook, and factors shaping its financial trajectory within the pharmaceutical landscape.
Historical Context and Pharmacological Profile
Amphetamine, chemically known as phenylpropan-2amine, was first synthesized in 1887 but remained understudied until the mid-20th century. It became widely prescribed in the 1950s and 1960s, notably under brand names such as Adderall (a mixture of amphetamine salts) and Dexedrine. Its stimulant properties increase the release of dopamine and norepinephrine, which alleviate fatigue, improve focus, and suppress appetite — traits adjunctively exploited in medical settings and illicit markets.
In the US, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved amphetamine-based formulations for ADHD and narcolepsy, positioning it as a cornerstone CNS stimulant. However, the potency and abuse potential led to strict regulatory controls, including classification as a Schedule II controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act (1970), limiting prescribing and manufacturing.
Current Market Landscape
Market Size and Segmentation
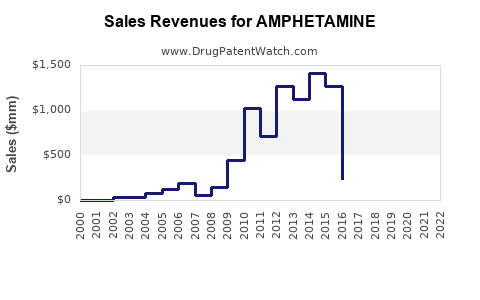
The global stimulant drug market, with amphetamine as a core component, is valued at approximately $4.2 billion in 2023, with growth projections exceeding 5% CAGR through 2028 (source: IBISWorld). The segment primarily comprises:
-
Prescription Medications: ADHD medications accounting for the largest share, driven by rising diagnosis rates. In the US, ADHD diagnoses are reported at over 6 million children and 10 million adults, fueling pharmaceutical sales (~$9 billion globally for all ADHD drugs) [1].
-
Illicit Market: The non-medical misuse and trafficking of illicit amphetamine and methamphetamine pose substantial challenges, influencing regulatory and market dynamics.
Key Players and Supply Chains
Leading pharmaceutical companies, such as Teva Pharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, and Alcoby, manufacture amphetamine-based formulations. Generic manufacturers dominate due to patent expirations, reducing costs and expanding access. Notably, illicit production often surpasses legal supplies, especially in regions with lax controls, impacting drug availability and market regulation.
Regulatory and Legal Dynamics
Legal Controls and Impact
The Schedule II status imposes strict prescription protocols, including limitations on refills and mandated DEA registration for manufacturers, distributors, and dispensers. This regulatory framework constrains rapid market expansion but maintains a degree of stability for licensed producers.
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
Patent cliffs have led to increased generic penetration, reducing prices and profit margins for branded formulations. For instance, Adderall XR patents expired in 2023 in the US, prompting intensified generic launches, diluting revenue streams.
Emerging Regulations and Oversight
In response to rising misuse, authorities globally have tightened controls. Recent measures include large-scale interdictions, prescription monitoring programs, and restrictions on non-medical uses, all impacting supply and demand dynamics.
Market Drivers
Growing Diagnostic Rates
Enhanced awareness, reduced stigma, and diagnostic criteria updates have increased ADHD diagnoses, notably among adults. This demographic shift amplifies demand for prescription stimulants, including amphetamine formulations.
Medical Therapeutic Research
Research exploring novel formulations (e.g., extended-release, transdermal patches) and combination therapies aims to optimize efficacy and minimize abuse potential, thus positively influencing market growth.
Institutional and Military Use
Certain military and institutional applications continue to use regulated doses of amphetamine for alertness and performance enhancement, though these are niche markets.
Constraints and Challenges
Abuse and Misuse
Non-medical use leads to societal and regulatory concerns, prompting restrictions that limit market expansion. The illicit trade not only challenges public health but also affects legitimate sales.
Regulatory Risks
Stringent oversight may lead to scheduling adjustments, manufacturing restrictions, or even bans in certain jurisdictions, contingent on misuse trends and public health findings.
Market Saturation and Price Erosion
Patent expirations and rising generic competition lead to erosion of high-margin sales, demanding efficiency gains and diversification strategies from manufacturers.
Financial Trajectory Outlook
Short-term Outlook (1-3 years)
In the near term, financial performance is projected to stabilize with moderate growth driven by increased ADHD diagnosis rates and new formulations. However, patent expirations and pricing pressures could temper revenue growth.
Medium-term Outlook (3-5 years)
The advent of novel formulations and improved delivery systems could offset declining revenues from traditional products. Regulatory tightening may moderately inhibit growth but also create barriers against illicit market expansion, indirectly supporting licensed product markets.
Long-term Outlook (5+ years)
The market may witness decreased growth in traditional amphetamine formulations due to regulatory constraints and societal shifts toward non-stimulant therapies for ADHD (such as Atomoxetine and Guanfacine). Nonetheless, niche markets—such as performance enhancement or special medical applications—may sustain some revenue streams.
Innovations and Future Opportunities
-
Alternative Delivery Systems: Transdermal patches, long-acting formulations, and injectable variants aim to improve compliance and reduce abuse potential, promising incremental market growth.
-
Digital Monitoring and Abuse Deterrents: Integration of digital adherence tools and abuse-deterrent formulations could mitigate misuse, fostering a more sustainable market environment.
-
Regulatory Approvals in Emerging Markets: Expanding access in underserved regions, with appropriate regulatory safeguards, offers growth opportunities, especially where ADHD awareness is increasing.
-
Biotech Developments: Ongoing research into non-stimulant alternatives with similar efficacy but lower abuse potential could impact long-term demand for traditional amphetamines.
Conclusion
Amphetamine's market dynamics hinge on balancing therapeutic demand with societal concerns over misuse. While regulatory constraints and patent cliffs challenge traditional revenue streams, ongoing medical innovation and expanding diagnostic criteria sustain a stable growth trajectory. Strategic positioning in research, formulation innovation, and compliance will be pivotal for pharmaceutical companies aiming to capitalize on this evolving landscape.
Key Takeaways
- The amphetamine market remains significant, with global revenues around $4.2 billion, driven chiefly by ADHD prescriptions.
- Patent expirations and generic competition are exerting downward pressure on prices, necessitating innovation.
- Regulatory oversight continues to tighten, especially concerning misuse, impacting supply and affordability.
- Growing diagnosis rates and novel formulations present growth opportunities—particularly in emerging markets.
- The future landscape may favor non-stimulant and abuse-deterrent formulations, possibly diminishing traditional amphetamine-based revenues.
FAQs
1. How does regulatory status influence the amphetamine market?
Regulatory controls, notably Schedule II classification, impose strict prescribing and manufacturing limitations, reducing illicit use but also constraining rapid market expansion. Tight controls can lead to shortages or decreased availability, influencing supply and pricing.
2. What are the main drivers of recent growth in the amphetamine market?
Increased ADHD diagnosis rates globally, the development of new formulations with improved delivery mechanisms, and expanding awareness all contribute to steady growth despite regulatory hurdles.
3. How do patent expirations affect market revenues?
Patent expirations enable generic manufacturers to launch cheaper versions, reducing prices and profit margins for branded products. This often results in revenue declines for original patent holders unless offset by new formulations or indications.
4. What role does illicit amphetamine trade play in market dynamics?
Illicit trade increases societal risks, prompts stricter regulations, and can disrupt legal supply chains—challenging manufacturers and regulators to balance access with misuse prevention.
5. What innovations are likely to shape the future of amphetamine-based therapies?
Development of abuse-deterrent formulations, long-acting delivery systems, and non-stimulant alternatives will influence future market dynamics, potentially reshaping demand patterns.
Sources
[1] IBISWorld. "Global ADHD Medications Market Analysis," 2023.