Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Alprazolam, a benzodiazepine classified under the Schedule IV controlled substances, is primarily recognized for its anxiolytic, sedative, and anticonvulsant properties. Since its launch by Pfizer in the mid-1980s under the brand name Xanax, alprazolam has established itself as one of the most prescribed medications globally. Its widespread use for anxiety and panic disorders, compounded by a complex regulatory environment and evolving market forces, warrants a detailed exploration of its market dynamics and financial trajectory.
Pharmacological Profile and Therapeutic Indications
Alprazolam acts on the central nervous system by enhancing the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), producing calming effects. Its rapid onset and high efficacy for short-term management of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic attacks have contributed to high prescription volumes.
The drug's primary indications include:
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Panic disorder with or without agoraphobia
- Short-term relief of anxiety symptoms
Off-label use, along with misuse and abuse potential, has influenced demand patterns and regulatory scrutiny.
Market Landscape and Key Players
Historically dominated by Pfizer (Xanax), the alprazolam market now encompasses generic manufacturers such as Mylan, Teva, and Sandoz, following patent expiration. The shift to generics has driven significant price reductions, profoundly impacting sales revenue.
Emerging pharmaceutical players and biosimilars are unlikely to challenge alprazolam's market dominance due to its low-cost generics and high regulatory barriers. Nonetheless, competition from newer anxiolytics and non-benzodiazepine agents—such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)—continues to influence market dynamics.
Regulatory Environment and Its Impact
Regulatory agencies, notably the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), impose rigorous controls. Given alprazolam's abuse potential, heightened regulatory oversight, scheduling, and prescribing restrictions—a consequence of the opioid crisis—have curtailed accessibility and expanded awareness of misuse.
In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) classifies alprazolam as a Schedule IV drug, implying strict regulatory control that limits refills and prescriber discretion. This regime influences market supply, pricing, and demand elasticity.
Market Dynamics: Trends and Influencers
1. Patent Expiration and Generic Competition
Pfizer’s patent on Xanax expired in the early 2010s, catalyzing a surge in generic formulations. The affordability of generics has expanded access but compressed profit margins for manufacturers. As a result, firms like Mylan and Teva have captured substantial market share, intensifying price competition.
2. Rising Prescription Volumes
Despite regulatory hurdles, prescription rates for alprazolam have fluctuated, driven by increasing prevalence of anxiety disorders globally. According to the CDC, anxiety disorders affect over 40 million adults in the U.S., contributing to steady demand [1].
3. Concerns Over Misuse and Abuse
The opioid epidemic has underscored the risks of benzodiazepines, prompting regulatory efforts and prescriber caution. This has led to decreased prescribing in some regions and increased demand for alternative treatments, influencing long-term sales trajectories.
4. Emergence of Alternative Therapies
Newer pharmacological options—like buspirone and hydroxyzine—and non-pharmacological approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) are increasingly replacing benzodiazepines for some patients, impacting market growth.
5. Geographical Market Variations
Developed markets, particularly North America and Europe, exhibit high prescription rates, but strict regulations and societal awareness of abuse are moderating growth. Conversely, developing countries show expanding demand driven by increasing mental health awareness, albeit with variable regulation and market penetration.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
Revenue Trends
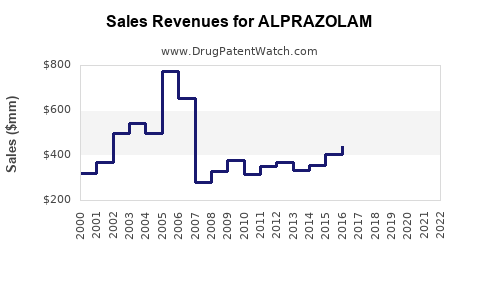
Pfizer's loss of exclusive rights led to a decline in brand-name sales, with generics capturing over 80% of the market share globally. Data indicates that in the U.S., alprazolam sales peaked around the early 2010s, with a subsequent decline due to regulatory measures and market saturation [2].
Pricing Dynamics
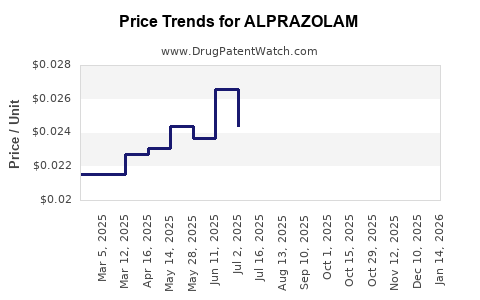
Generic competition has driven wholesale prices down by approximately 60-70% since patent expiry. For pharmaceutical companies, profit margins are increasingly reliant on high-volume, cost-efficient production and marketing.
Future Market Outlook
Analysts project a moderate decline in overall alprazolam sales over the next five years, driven by regulatory constraints, shifting prescriber preferences, and increased focus on abuse deterrence. However, the persistent global demand indicates a stable, albeit competitive, market environment.
Emerging Market Opportunities
Developing countries represent a growth vector, with rising healthcare infrastructure investment and mental health awareness. The low-cost nature of generics facilitates market entry, ensuring steady revenue streams for local and international producers.
Market Challenges
- Regulatory and Legal Risks: Stringent controls and evolving classification can restrict supply and increase compliance costs.
- Abuse and Misuse Concerns: Litigation risks, public health campaigns, and prescriber hesitancy may decrease demand.
- Competitive Pressure: Market saturation and alternative therapies erode market share.
- Reputational Risks: Media coverage around drug misuse and overdose potential impact prescribing behaviors.
Opportunities for Strategic Positioning
Pharmaceutical firms can leverage differentiation by:
- Developing abuse-deterrent formulations
- Investing in pharmacovigilance and risk mitigation strategies
- Expanding into emerging markets with tailored formulations
- Diversifying portfolio with non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics
Conclusion
Alprazolam's market remains resilient, grounded in its therapeutic efficacy and global demand for anxiety management. However, its financial trajectory faces headwinds from regulatory pressures, societal concerns over abuse, and market saturation. Strategic adaptations—such as introducing abuse-resistant formulations and expanding into emerging markets—are essential for maintaining profitability. Overall, while growth may moderate, alprazolam's entrenched position ensures its continued relevance within the anxiolytic landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expiration and generic proliferation have reduced costs and profit margins but expanded market access.
- Regulatory and societal scrutiny constrict prescribing practices, influencing sales volume.
- Demand persists due to high prevalence of anxiety disorders but is increasingly challenged by alternative treatments.
- Market potential lies in emerging economies and through innovation in abuse deterrence.
- Strategic focus areas include pharmacovigilance, reformulation, and regional expansion to sustain revenue trajectories.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected alprazolam's market revenue?
Patent expiration led to a surge in generic availability, drastically reducing prices and profit margins for brand manufacturers but expanding access and prescription volumes, stabilizing overall demand.
2. What regulatory challenges does alprazolam face?
As a Schedule IV controlled substance, alprazolam faces restrictions on prescribing and dispensing, with increased oversight aimed at curbing misuse, which can limit sales growth.
3. Are there any emerging formulations of alprazolam?
Yes, abuse-deterrent formulations and long-acting variants are under development to mitigate misuse risks and adapt to regulatory standards.
4. Which markets hold the most growth potential for alprazolam?
Emerging markets in Asia, Latin America, and Africa present significant growth opportunities due to rising mental health awareness and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
5. How do alternative therapies impact alprazolam's market share?
The rising preference for SSRIs, SNRIs, and non-pharmacological approaches reduces reliance on benzodiazepines, constraining market expansion but maintaining steady demand for short-term use cases.
References
[1] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). "Data and Statistics on Anxiety Disorders." CDC.gov.
[2] IQVIA. "Pharmaceutical Market Data Report, 2022."