Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Lansoprazole, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) primarily used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, has established itself as a significant entity within the global pharmaceutical landscape. Market forces, regulatory trajectories, patent statuses, and competitive landscapes jointly shape its commercial and financial trajectory. This article explores these dynamics, projecting future market prospects and delineating key factors influencing Lansoprazole's financial outlook.
Market Overview and Therapeutic Positioning
Lansoprazole, initially approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1995, commands a notable share in the PPI segment, which itself holds a dominant position in acid-related disorder therapies. The global demand for acid suppression drugs is driven by increasing prevalence rates of GERD and related conditions, as well as rising awareness of gastrointestinal health.
The therapeutic efficacy and safety profile of Lansoprazole have historically led to broad prescription acceptance, especially in developed markets. However, regulatory and patent landscapes impact the system's sustainability and competitive positioning.
Market Dynamics
1. Patent Expirations and Generics Entry
A pivotal factor influencing Lansoprazole's market valuation is patent expiration. Pfizer's original patent for Lansoprazole expired in multiple jurisdictions around 2010–2012, paving the way for generic competitors. This significantly eroded the drug’s branded pricing power, leading to a sharp decline in revenue from the original formulation.
The proliferation of generic versions has increased affordability and widened access, yet intensified price competition. Generic manufacturers typically price Lansoprazole at a substantial discount—often 20–40% less than branded counterparts—substantially impacting profit margins for originators.
Impact: Generic penetration has led to a decline in overall sales for branded Lansoprazole but broadened drug accessibility, boosting volume sales globally.
2. Market Penetration and Prescription Trends
Despite generic competition, Lansoprazole maintains a core market share, notably in regions with less extensive generic penetration or where physicians favor the original formulation due to perceived efficacy or safety. Prescription trends in emerging markets continue to evolve as healthcare infrastructure improves, creating additional avenues for growth.
Certain formulations and combination therapies with antibiotics or other agents sustain niche demand, particularly for Helicobacter pylori eradication protocols.
Impact: Volume-based sales remain a significant revenue component, even as per-unit prices decline.
3. Regulatory and Patent Strategies
Pharmaceutical companies employ patent strategies and market exclusivity to delay generic entry. Recent complex formulations, or new delivery mechanisms such as delayed-release formulations, can extend exclusivity periods artificially.
Regulatory hurdles—such as approval of biosimilars or over-the-counter (OTC) status—also influence market dynamics. Some markets increasingly reclassify PPIs for OTC availability, impacting prescription volumes and revenue.
Impact: Strategic patent management and regulatory pathways continue to influence Lansoprazole’s market trajectory, with potential for phased growth or decline depending on regional policies.
4. Competitive Landscape
Besides generics, PPIs like omeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, and rabeprazole vie for market share. The minor pharmacokinetic differences among these agents influence prescribing habits, especially when considering safety profiles or drug-drug interactions.
Developments in novel therapies, including potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs), threaten the traditional PPI market segment, potentially constraining future growth.
Impact: The competitive pressure constrains pricing power and necessitates differentiation strategies for stable revenues.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Projections
Historical Revenue Trends
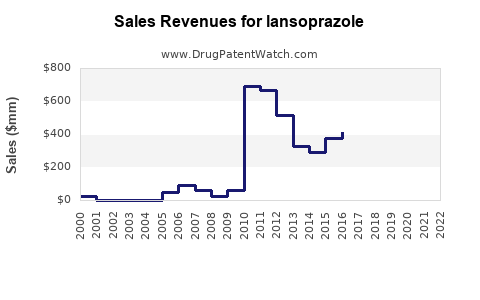
Pfizer’s Lansoprazole sales peaked in the early 2000s, prior to patent expiration, reaching hundreds of millions annually. Post-generic entry, revenues declined precipitously. Industry estimates suggest that the global Lansoprazole market was valued at approximately USD 1.5 billion in 2010, decreasing to below USD 300 million by 2020 for the original branded product.
Emerging markets have stabilized or even slightly increased demand, attributing to lower drug prices and expanding healthcare access.
Future Market Outlook
Forecasting the future entails analyzing several variables:
- Generic Penetration and Competition: Continued dominance of generics is expected unless branded reformulations re-enter the market with superior benefits or patents are reinstated.
- Regional Market Dynamics: Growth in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, driven by healthcare expansion, could offset declines in mature markets.
- Pipeline and Reformulations: Innovations such as vacated patent pathways for novel formulations or combination therapies could revive revenues.
- Regulatory Changes: Transition of Lansoprazole to OTC in developed markets might reduce prescription revenues but increase OTC sales volumes, potentially stabilizing total revenue streams.
Projected Revenue Range: Based on current industry analyses, the global market for Lansoprazole and its equivalents is projected to stabilize or experience modest growth at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1–3% over the next five years, primarily driven by emerging markets.
Implications for Stakeholders
Pharmaceutical companies need strategic patent management, formulation innovation, and market segmentation to sustain profitability. Market entrants should focus on low-cost manufacturing, especially in regions with high demand for generic PPIs. Healthcare policy shifts toward OTC availability can redefine revenue models, emphasizing volume over premium pricing.
Regulatory and Competitive Risks
Increasing regulatory scrutiny over PPIs concerning long-term safety issues—such as potential risks for renal disease and fractures—may influence prescribing habits and reimbursement policies, potentially tempering sales growth. Moreover, the advent of P-CABs, which offer faster and potentially more durable acid suppression, poses a competitive threat.
Key Market Drivers and Restraints
| Drivers |
Restraints |
| Rising prevalence of acid-related gastrointestinal conditions |
Patent expiries and aggressive generic pricing |
| Increased healthcare access in emerging markets |
Market saturation and narrow profit margins |
| Technological innovations extending patent life |
Safety concerns impacting prescribing patterns |
| Development of alternative therapies (P-CABs) |
Regulatory hurdles and OTC reclassification trends |
Key Takeaways
- Lansoprazole’s commercial landscape has been profoundly shaped by patent expirations, leading to a shift from branded revenues to volume-driven generic sales.
- The global Lansoprazole market is experiencing a transitional phase characterized by intense price competition but sustained demand in emerging markets.
- Strategic formulations, patent management, and regional market expansion remain critical for stakeholders seeking financial resilience.
- Innovation, including formulations with enhanced efficacy or safety profiles, presents potential avenues for revenue stabilization.
- Regulatory shifts and the emergence of novel acid-suppressive therapies will continue to influence competitive positioning and profitability.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiry impacted Lansoprazole’s market share?
Patent expiry led to widespread generic entry, significantly reducing the original product's market share and pricing power, transitioning revenues from branded to generic sales predominantly.
2. What are the primary regions driving future demand for Lansoprazole?
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to sustain or increase demand due to expanding healthcare infrastructure and affordability.
3. Are there potential alternatives threatening Lansoprazole's market?
Yes. P-CABs like Vonoprazan offer faster, more durable acid suppression, posing competitive threats to traditional PPIs including Lansoprazole.
4. What strategies can pharmaceutical companies employ to maintain revenues?
Innovative formulations, extending patent exclusivity through new delivery systems, expanding OTC availability, and market diversification are key strategies.
5. How might regulatory developments affect Lansoprazole’s future?
Regulatory restrictions based on safety concerns and shifts toward OTC status could reduce prescription revenues but may expand overall market volume.
Conclusion
Lansoprazole's market and financial trajectory reveal a complex interplay between patent climates, generic competition, regional healthcare dynamics, and therapeutic innovations. While revenue pressures have intensified post-expiry of patent exclusivity, strategic adaptation through formulation innovation and market expansion can sustain its relevance. Stakeholders must remain vigilant to regulatory developments and emerging therapies to optimize their positioning in this evolving landscape.
References
[1] GlobalData. "Proton Pump Inhibitors Market Analysis," 2022.
[2] IQVIA. "Pharmaceutical Market Report," 2022.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "Lansoprazole Approval History," 1995.
[4] Statista. "Pharmacoeconomic Trends in Acid Suppressants," 2022.
[5] MarketWatch. "Generic Drug Market Dynamics," 2022.