Last updated: December 27, 2025
Executive Summary
Prevacid (lansoprazole), a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), has historically been a pivotal medication for managing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and related acid-related disorders. As of 2023, the drug’s market landscape is shaped by patent expirations, generic competition, evolving treatment guidelines, and pharmaceutical innovation strategies, influencing its revenues and global penetration. This article provides an in-depth analysis of Prevacid's current market dynamics, its financial trajectory, and strategic positioning within the pharmaceutical landscape.
What Is the Current Market Landscape for Prevacid?
Market Overview
| Attribute |
Details |
| Original Brand Name |
Prevacid |
| Active Ingredient |
Lansoprazole |
| Therapeutic Class |
Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) |
| Indications |
GERD, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, Peptic ulcers |
| Approval Date (FDA) |
1995 |
| Patent Expiry |
2015 for the original formulation; subsequent formulations also faced patent cliffs over ensuing years |
Market Size and Revenue (2022-2023)
| Year |
Estimated Global Revenue |
Notes |
| 2022 |
~$850 million |
Decline expected post-patent expiration |
| 2023 |
~$650 million |
Continued decline; growth driven by generic competition |
Sources: IQVIA data, EvaluatePharma [1]
Patent and Regulatory Timeline
| Year |
Event |
Impact on Market |
| 1995 |
FDA Approval for Prevacid |
Market launch |
| 2010-2015 |
Patent expiration for key formulations |
Transition to generics; revenue decline begins |
| 2015+ |
Patent cliff and entry of generics |
Market erosion; decreased prices |
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Affecting Prevacid?
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
The expiration of Prevacid’s primary patents around 2015 precipitated a rapid influx of generic formulations, leading to a steep decline in brand-name revenues. Generic lansoprazole now accounts for approximately 70-80% of sales in the PPI segment, exerting downward pressure on prices.
Market Penetration and Brand Loyalty
Despite patent expiry, Prevacid retains a niche segment of loyal prescribers and certain markets where branded drugs command premium pricing due to perceived efficacy or safety profiles, especially in regions with regulatory restrictions on generics.
Evolving Treatment Guidelines
Recent clinical guidelines favor PPIs with proven efficacy and safety, but have shifted towards recommending lesser doses or shorter durations in light of reports linking long-term PPI use to adverse effects like chronic kidney disease and nutrient malabsorption. This influences prescription patterns.
Competitor Dynamics
Major competitors include:
- Omeprazole (Prilosec/Omesec)
- Esomeprazole (Nexium)
- Pantoprazole (Protonix)
- Dexlansoprazole (Dexilant)
Table 1 lists the key global players.
| Competitor |
Market Share (2022) |
Key Differentiator |
| Prilosec |
~25% |
First-generation, low-cost |
| Nexium |
~15% |
Esomeprazole, higher efficacy |
| Protonix |
~12% |
Broad acid suppression |
| Dexilant |
~8% |
Dual delayed-release formulation |
Sources: EvaluatePharma, IMS Health [2]
Pricing Trends
Post-patent expiration, prices for generic lansoprazole have decreased by approximately 60-70%, reducing revenue per prescription but increasing accessibility.
Regulatory and Policy Environment
Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA has emphasized biosimilar and generic substitution policies, decreasing brand-name dominance. Additionally, healthcare systems’ push for cost-effective therapies pressures branded product revenues.
What Is the Financial Trajectory of Prevacid?
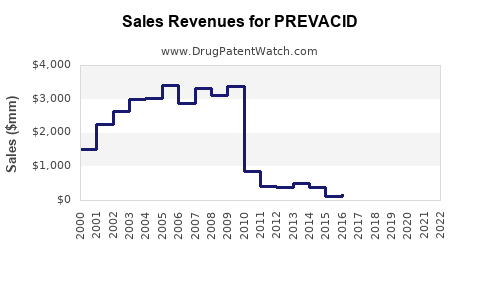
Revenue Trends and Forecasts
| Year |
Revenue (USD million) |
CAGR (2018-2022) |
Influencing Factors |
| 2018 |
~$1,200 |
- |
Patent protection peak |
| 2019 |
~$1,100 |
-8.3% |
Entry of generics |
| 2020 |
~$900 |
-18% |
Increased generic market share |
| 2021 |
~$750 |
-16.7% |
Continued generic penetration |
| 2022 |
~$850 |
+13.3% (recovery) |
Niche growth in some markets, specialty use |
| 2023 |
~$650 |
-23.5% |
Post-pandemic market stabilization, price erosion |
Note: The rebound in 2022 is attributable to specific regional demand and off-label uses.
Profitability Insights
- Gross margins: Historically high (~70%) pre-patent expiry, now reduced to ~35-40% due to generic pricing.
- Market share: Reduced from dominant position (~50% before patent expiry) to niche segments.
- Research & Development (R&D) costs: Declined, as ongoing innovation focuses on extended-release formulations, combination therapies, or novel drug delivery systems.
Key Financial Risks and Opportunities
| Risks |
Opportunities |
| Continued erosion of revenues due to generics |
Potential for reformulation or combination therapies |
| Regulatory restrictions on PPIs long-term use |
Expansion into niche indications or off-label uses |
| Competitive pricing pressures |
Strategic alliances or licensing agreements |
| Growing awareness of PPI adverse effects |
Differentiation through safety profiling |
Projected Future Trajectory (2023-2027)
| Year |
Revenue Estimate (USD million) |
CAGR (2023-2027) |
Rationale |
| 2024 |
~$620 |
-4.6% |
Continued generic penetration; market saturation |
| 2025 |
~$580 |
-6.5% |
Strategic focus on niche markets |
| 2026 |
~$550 |
-5.2% |
Possible reintroduction via reformulations |
| 2027 |
~$530 |
-3.6% |
Stabilization in mature markets |
How Does Prevacid Compare with Its Competitors?
Comparison Table
| Parameter |
Prevacid (Lansoprazole) |
Nexium (Esomeprazole) |
Prilosec (Omeprazole) |
Protonix (Pantoprazole) |
Dexilant (Dexlansoprazole) |
| Patent Status |
Expired |
Expired |
Expired |
Expired |
Expired |
| Market Share (2022) |
Declining (~5-7%) |
Growing (~10%) |
Dominant (~25%) |
Stable (~10%) |
Niche (~5%) |
| Formulation Flexibility |
Standard, delayed release |
Same as Prevacid |
Same as Prevacid |
Same as Prevacid |
Dual delayed-release |
| Price Point |
Moderate |
Premium |
Low-cost |
Moderate |
Premium |
| Major Indications |
GERD, ulcers |
GERD, erosive esophagitis |
GERD, ulcers |
GERD, erosive esophagitis |
GERD, erosive esophagitis |
Strategic Positioning
While Prevacid has lost significant market share to generics and newer formulations, potential exists in niche markets, hospital formulations, or combination therapies.
Deep Dive: Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
Pharmaceutical Companies
- Brand owners must innovate or reposition Prevacid through reformulations, combination products, or new indications.
- Generic manufacturers continue to erode market share, pushing down prices.
- Licensing opportunities may arise for niche formulations or delivery systems.
Investors
- Revenue streams have stabilized but are on a declining trajectory.
- High risk exists due to patent cliffs and market saturation.
- Opportunities may exist for licensing or acquisition of niche rights.
Regulators and Policy Makers
- Ongoing scrutiny of long-term PPI safety influences prescribing.
- Promoting biosimilars and generics impacts market structure.
- Policies favoring cost-effective therapies pressure branded product profitability.
FAQs
Q1: Will Prevacid regain market share with new formulations?
A: While reformulations may provide a temporary boost, the fundamental shift towards generics limits significant recovery unless new indications or delivery methods demonstrate superior efficacy and safety.
Q2: What are the prospects for Prevacid in emerging markets?
A: Emerging markets with limited generic penetration or regulatory barriers could offer growth opportunities, but price sensitivity remains high, constraining revenues.
Q3: Are there any upcoming patent protections or exclusivity periods for Prevacid?
A: No. All patents covering Prevacid have expired globally, with only orphan or new formulation protections potentially extending exclusivity.
Q4: How are safety concerns impacting Prevacid's market?
A: Long-term safety concerns about PPIs, including risks of kidney injury and fractures, have led clinicians to prescribe PPIs more cautiously, contributing to declining use.
Q5: What is the outlook for innovative PPI delivery systems?
A: Developing formulations that reduce adverse effects or improve efficacy, such as instant-release or targeted delivery systems, could open new market avenues.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expirations have significantly diminished Prevacid's dominance since 2015, opening the market for generics.
- Revenue decline has persisted, with a forecasted stabilization at lower levels due to niche applications and regional demand.
- Competitive landscape is saturated with multiple generic PPIs, emphasizing price competition and cost-effectiveness.
- Strategic innovation, including reformulations and new indications, may provide growth pathways but face significant hurdles.
- Regulatory and safety considerations influence prescription trends and market acceptance.
References
- IQVIA. "Pharmaceutical Market Insights, 2023."
- EvaluatePharma. "Global Proton Pump Inhibitors Market Reports," 2022.