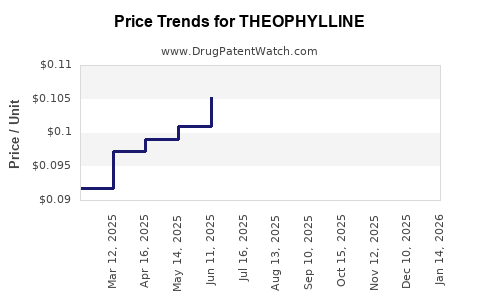
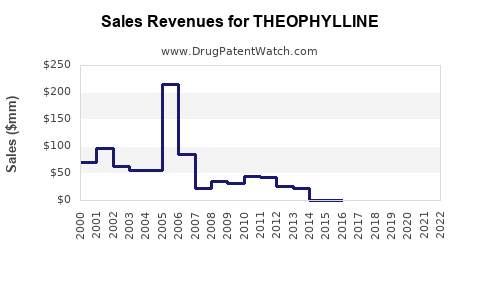
Last updated: January 14, 2026
Executive Summary
Theophylline, a methylxanthine derivative primarily used in respiratory diseases, remains a significant pharmaceutical agent despite declining global usage. Its market is driven by factors such as its longstanding efficacy in treating asthma and COPD, increasing prevalence of respiratory illnesses, and emerging niche applications. However, innovation, safety concerns, and competitive alternatives have impacted its growth trajectory. This analysis delves into the current market landscape, prospects, and financial forecast for Theophylline, providing crucial insights for industry stakeholders.
What Are the Pharmacological Profile and Current Usage of Theophylline?
Pharmacology and Therapeutic Uses
Theophylline acts primarily as a bronchodilator by inhibiting phosphodiesterase enzymes, leading to increased cyclic AMP and resulting in smooth muscle relaxation. It also exhibits anti-inflammatory and ventilatory stimulant effects.
- Primary indications:
- Asthma management (often as adjunct therapy)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Apnea in neonates (less common)
Dosage Forms and Formulations
| Formulation |
Description |
Typical Dose |
| Immediate-release tablets |
Oral, rapid onset |
300-600 mg/day |
| Sustained-release tablets |
Extended release for stable plasma levels |
300-900 mg/day |
| Intravenous infusion |
Acute management, ICU settings |
5-10 mg/kg/hr |
| Neonatal formulations |
Syrups or injections for apnea in infants |
Variable |
Market Penetration and Sectors
The use of Theophylline has declined in comparison to inhaled corticosteroids and β2-agonists, yet it retains niche applications, especially in regions with limited access to newer therapies.
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing Theophylline?
Drivers of Market Growth
- High Prevalence of Respiratory Diseases
- Global asthma cases: ~262 million (WHO, 2019)
- COPD prevalence: projected to surpass 250 million by 2025 (WHO)
- Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
- Low-cost alternative to newer biologics, especially in developing economies
- Established Clinical Efficacy
- Long history with well-documented safety and efficacy profiles
Restraints and Challenges
| Restraint |
Impact |
Description |
| Safety concerns |
Risk of toxicity at high serum levels |
Narrow therapeutic index; side effects include arrhythmias and seizures |
| Competition from newer agents |
Biologicals, LABAs, ICSs dominate current markets |
Better safety profiles, fewer monitoring requirements |
| Regulatory restrictions and shifts |
Stricter warnings; reduced prescribing guidelines |
Initiatives favoring inhaled therapies over systemic agents |
Emerging Trends
- Repurposing and Niche Uses: Use in neurodegenerative diseases; experimental applications
- Formulation Innovation: Development of controlled-release mechanisms to mitigate toxicity
- Regional Market Expansion: Increased use in emerging markets due to affordability issues
What Is the Financial Trajectory of Theophylline?
Market Size and Revenue Estimates
| Region |
2022 Market Size |
Expected CAGR (2023-2028) |
2028 Projections |
| North America |
~$150 million |
1.2% |
~$162 million |
| Europe |
~$130 million |
1.5% |
~$143 million |
| Asia-Pacific |
~$200 million |
4.8% |
~$245 million |
| Rest of World |
~$70 million |
2.0% |
~$77 million |
| Total Market |
~$550 million |
1.9% |
~$627 million |
Data Source: GlobalData Pharma Intelligence, 2022; projections based on regional growth trends
Key Financial Drivers
- Patent Status: No patent exclusivity, leading to generic market dominance
- Pricing Dynamics: Price erosion due to generic competition
- Off-Label and Niche Uses: Supplementary revenue streams
- Cost Structure: Low manufacturing costs favor profitability in high-volume markets
Revenue Generators and Losses
| Revenue Sources |
Contribution (%) |
Notes |
| Generic sales |
75% |
Dominant due to low-cost manufacturing |
| Niche clinical applications |
10% |
Neonatal apnea, experimental uses |
| Hospital/institutional sales |
10% |
Acute care, critical care settings |
| Formulation innovations |
5% |
Extended-release, combination drugs |
How Do Policy and Regulatory Trends Shape the Market?
Global Regulatory Landscape
- FDA (USA): Generally classified as a prescription drug with boxed warning for toxicity
- EMA (EU): Similar control measures; some countries recommend monitoring serum levels
- Developing Countries: Often less restrictive, leading to broader use
Impact on Market Dynamics
- Stricter safety regulations have limited off-label use and guided clinicians toward newer therapies
- Favorable policies in low- and middle-income countries sustain demand due to affordability
- Patent expirations facilitate generic entry, increasing accessibility but pressuring margins
Pharmacovigilance and Safety Standards
- Increased monitoring requirements reduce misuse
- Formation of global databases for adverse events influences prescribing behaviors
How Does Theophylline Compare with Alternatives?
| Attribute |
Theophylline |
Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS) |
Long-Acting β2-Agonists (LABAs) |
Biologicals (e.g., Omalizumab) |
| Administration |
Oral, IV |
Inhalation |
Inhalation |
Subcutaneous injection |
| Onset of action |
Rapid (oral), variable |
Rapid |
Slow |
Moderate |
| Efficacy |
Moderate |
High |
High |
Very high |
| Safety profile |
Narrow therapeutic index |
Better safety |
Better safety |
Best safety, costly |
| Cost |
Low |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Very high |
| Monitoring requirements |
Serum levels necessary |
Minimal |
Minimal |
Minimal |
What Are the Future Opportunities and Risks?
| Opportunities |
Risks |
| Drug repurposing (neurological) |
Toxicity and side-effects limit broader use |
| Formulation innovation (long-acting) |
Competition from newer drugs with wider safety margins |
| Market expansion in emerging economies |
Regulatory hurdles and safety reports impacting labeling |
| Integration into combination therapies |
Declining clinical relevance with advances in targeted biologics |
Key Takeaways
- The global Theophylline market is relatively modest (~$550 million in 2022) with low single-digit growth driven by regional demand and affordability.
- Despite declining prescription rates in developed nations, emerging markets maintain steady demand due to cost-effectiveness.
- Safety concerns and competition from newer therapies limit growth, but niche applications and formulation innovations represent growth avenues.
- Patent expiration and proliferation of generics have driven down prices, impacting revenue but expanding access.
- Regulatory trends favoring safety monitoring have constrained off-label and broad-spectrum use.
- The future market largely depends on innovation, regulatory environment, and acceptance in developing regions.
FAQs
1. What are the main factors influencing the decline of Theophylline in developed markets?
Answer: Safety concerns related to its narrow therapeutic index, availability of safer inhaled therapies, and regulatory restrictions have contributed to its decreased prevalence in developed markets.
2. Are there ongoing research efforts to repurpose Theophylline?
Answer: Yes. Investigations are underway exploring neuroprotective properties, potential benefits in neurodegenerative diseases, and combination therapies, though these are exploratory stages.
3. How does the cost structure of Theophylline influence its market presence?
Answer: Its low manufacturing cost and generic status make it an attractive option in price-sensitive markets, sustaining demand in regions with limited healthcare budgets.
4. What role do regulatory agencies play in shaping Theophylline's market dynamics?
Answer: Agencies like the FDA and EMA impose safety warnings and monitoring requirements, which influence prescribing practices and limit off-label use, thus affecting overall market traction.
5. What is the outlook for Theophylline in the next decade?
Answer: While mainstream use may decline further, niche applications and formulation innovations could sustain a modest market. Market expansion in developing nations offers growth potential, contingent on safety profile management.
References
- World Health Organization. (2019). Global Asthma Report.
- GlobalData Pharma Intelligence. (2022). Pharmaceutical Market Analysis: Theophylline.
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. (2022). Drug Safety and Availability.
- European Medicines Agency. (2022). Regulatory Policies for Respiratory Drugs.
- PubMed. Articles on Theophylline pharmacology and clinical trials.
This comprehensive analysis equips healthcare professionals, pharmaceutical companies, and investors with strategic insights to navigate the evolving Theophylline landscape.