Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Theophylline, a methylxanthine derivative, has historically been a mainstay in the treatment of respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Despite its long-standing presence, shifts in clinical practice, regulatory standards, and emerging therapies have influenced its market positioning. This analysis explores the current market dynamics and financial trajectory of theophylline, providing strategic insights for stakeholders.
Historical Context and Therapeutic Profile
Theophylline’s therapeutic efficacy hinges on multiple mechanisms—bronchodilation through phosphodiesterase inhibition, anti-inflammatory effects, and respiratory muscle strength enhancement. Its oral delivery, established pharmacokinetics, and low cost facilitated widespread use, especially in resource-limited settings. However, its narrow therapeutic window and potential for adverse effects—such as cardiac arrhythmias and neurological toxicity—necessitated careful dosage regulation and monitoring.
Current Market Landscape
Market Size and Segmentation
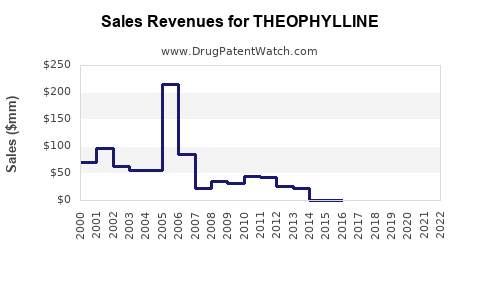
The global market for theophylline was valued at approximately USD 150 million in 2022, predominantly driven by low-cost formulations used in developing countries [1]. Mature markets, including North America and Europe, have observed declining utilization, replaced increasingly by inhaler therapies and biologics with superior safety profiles.
Key Regions
-
Developing Countries: Theophylline retains a significant presence owing to affordability and existing manufacturing infrastructure. Countries like India, Nigeria, and Indonesia report high usage rates.
-
Developed Markets: Adoption has waned, with prescribing guidelines discouraging routine use. Nonetheless, off-label applications and compounded formulations sustain niche demand.
Market Drivers
- Cost-Effectiveness: Its low price remains attractive amid rising healthcare costs.
- Existing Manufacturing Base: Widespread generic production facilitates access, especially in resource-constrained regions.
- Generic Availability: Theophylline’s patent expiry in the late 20th century led to a surge in generic options, suppressing prices and margins but ensuring broad availability.
Market Challenges
- Safety Concerns: The narrow therapeutic index complicates dosing, increases risk of toxicity, and limits utilization.
- Emergence of Alternative Therapies: Inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene receptor antagonists, and biologics offer improved safety and efficacy profiles.
- Regulatory Shifts: Guidelines increasingly recommend against routine use of theophylline in favor of newer agents, shrinking the market.
Pharmaceutical Industry Dynamics
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Generic producers dominate theophylline supply, with major players such as Sun Pharmaceutical, Mylan, and Teva. Market entry barriers are low due to straightforward synthesis and established quality standards. Regulatory compliance, however, remains vital, with both monographs and stringent standards imposed by agencies like the FDA and EMA.
Pricing and Margins
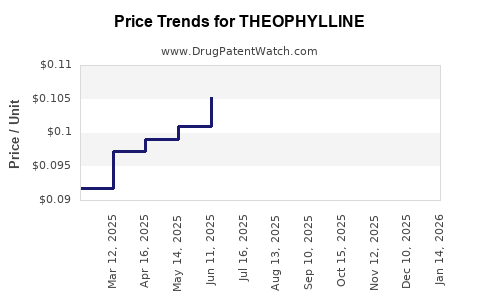
Price erosion persists, driven by generic competition and negotiation pressures. While inexpensive, the slow growth and declining demand threaten margins for manufacturers.
R&D and New Formulations
Limited R&D investment exists in developing new theophylline formulations or delivery methods. Most industry efforts focus on novel respiratory agents with better therapeutic profiles.
Future Financial Trajectory
Market Outlook (2023-2030)
The global theophylline market is expected to contract at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 2-3%, reflecting its diminishing role in mainstream respiratory care [2]. While markets in developing countries provide steady, albeit modest, revenues, advanced economies may witness further decline.
Growth Opportunities
- Niche Indications: Potential in specific patient populations requiring inexpensive therapy, such as in palliative settings.
- Combination Therapies: Incorporation into multi-drug inhalants, potentially expanding usage.
- New Formulations: Improved sustained-release formulations might mitigate toxicity risks, encouraging continued use.
Risks and Opportunities
- Risks: Stronger competition from modern therapies, regulatory restrictions, and safety concerns.
- Opportunities: Expanding access in underserved markets could ensure sustained sales; strategic formulations that enhance safety profiles may strengthen position.
Competitive Landscape
Major players leveraging large-scale manufacturing prevail. Market consolidation and patent expirations have increased price competitiveness but decreased profit margins. No significant pipeline innovations are currently projected, positioning theophylline primarily within a mature, declining market segment.
Regulatory and Epidemiological Influences
Recent guidelines such as the GINA report recommend against routine theophylline use due to safety risks [3]. Epidemiologically, the global burden of asthma and COPD continues to grow, but treatment paradigms favor inhaled therapies over systemic agents like theophylline.
Conclusion
Theophylline’s market dynamics are characterized by a shift from widespread use to niche applications. Its financial trajectory is expected to decline further, shaped by safety concerns, regulatory preferences, and the advent of superior therapies. Stakeholders must navigate a landscape marked by low margins, intense generic competition, and evolving clinical standards.
Key Takeaways
- The global theophylline market, valued at approximately USD 150 million in 2022, is experiencing a decline driven by safety concerns and evolving treatment guidelines.
- Its primary appeal remains in low-income regions where affordability and existing manufacturing infrastructure sustain demand.
- In developed markets, declining prescription rates and regulatory discouragement diminish theophylline’s market share.
- Future growth opportunities are limited. Strategic focus should be on niche indications, improved formulations, and leveraging its role where cost considerations outweigh safety concerns.
- Industry players must monitor regulatory changes and epidemiological trends to adapt product offerings and marketing strategies.
FAQs
1. Why has theophylline's clinical use declined in developed countries?
Advances in inhaled therapies, biologics, and stricter safety regulations have rendered theophylline less favorable due to its narrow therapeutic index and risk of toxicity.
2. What are the primary safety concerns associated with theophylline?
Adverse effects include cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, gastrointestinal disturbances, and neurological toxicity, often related to overdose or drug interactions.
3. Are there ongoing efforts to develop safer theophylline formulations?
Limited R&D exists; most efforts focus on alternative therapies. Some formulations aim at sustained-release delivery to reduce toxicity, but these are not widely marketed.
4. Which regions represent the greatest future revenue potential for theophylline?
Resource-limited markets in Africa, Asia, and Latin America continue to demand low-cost therapies, sustaining some demand despite global decline.
5. How do regulatory guidelines influence theophylline marketing strategies?
Guidelines that recommend against routine use restrict marketing claims and prescriptions, compelling companies to focus on niche markets or formulations with improved safety profiles.
References
[1] MarketWatch. "Global Theophylline Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report," 2022.
[2] Research and Markets. "Theophylline Market Forecast 2023-2030," 2023.
[3] Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). "Treatment Guidelines," 2022.