Last updated: October 15, 2025
Introduction
Gilead Sciences Inc. stands as a prominent player within the biopharmaceutical industry, renowned for its pioneering antiviral therapies and extensive R&D pipeline. As the industry evolves with rapid technological advancements, shifting regulatory landscapes, and emerging competitive threats, understanding Gilead's market position, strengths, and strategic approach becomes essential for stakeholders aiming to navigate its future trajectory.
Market Position in the Global Pharmaceutical Arena
Gilead’s core competencies center around the antiviral market, with leading treatments for HIV, hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C (HCV), and, more recently, COVID-19. The company's strategic investments in these areas have cemented its dominant market share, particularly in HIV and HCV spaces.
According to recent industry reports, Gilead commands approximately 80% of the global HIV therapeutic market, reflecting its longstanding leadership with drugs like Truvada, Descovy, and Biktarvy [1]. In HCV, Gilead’s portfolio, including Harvoni and Epclusa, remains influential, though competitive pressures from newer agents and generic formulations have slightly eroded its dominance [2].
Its recent foray into COVID-19 therapeutics with Veklury (remdesivir) positioned Gilead as a key player during the pandemic. While Veklury gained emergency use authorization, its long-term market position remains influenced by emerging antiviral treatments and evolving treatment protocols [3].
Despite its stronghold in antiviral therapies, Gilead exhibits comparatively limited presence in specialty areas like oncology or autoimmune diseases, contrasting with rivals such as Pfizer and Roche, who have diversified portfolios across therapeutic domains.
Strengths Driving Gilead’s Market Position
1. Robust R&D Pipeline and Innovation Capabilities
Gilead’s commitment to innovation underpins its market resilience. The company has invested heavily in research and development, with an annual R&D expenditure exceeding $4 billion [4]. Its focus on next-generation antivirals, long-acting formulations, and combination regimens fosters sustainable growth and addresses resistance issues.
2. Established Brand Portfolio in HIV and HCV
Gilead’s HIV treatments benefit from decades-long market presence, with drugs like Biktarvy leading the market with significant sales (approximate sales of $6 billion in 2022). Its comprehensive portfolio offers high barriers to entry for competitors, leveraging patient loyalty and regulatory approvals [5].
In HCV, although newer agents have entered the market, Gilead's formulations, notably Harvoni, retain a strong foothold due to proven efficacy and safety profiles.
3. Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
Gilead's strategic acquisitions, such as Arcus Biosciences and partnership negotiations with biotech firms, bolster its pipeline and expand its technological capabilities [6]. These collaborations enable Gilead to tap into innovative modalities, including immuno-oncology and gene editing, diversifying its future revenue streams.
4. Early and Proactive COVID-19 Response
The rapid development and deployment of remdesivir during the pandemic showcased Gilead’s agility. Its positioning as an early treatment option in COVID-19 enhanced the company's visibility and reinforced its reputation as an antiviral innovator.
5. Focused Market Segmentation and Geographic Expansion
Gilead maintains a strong presence in the U.S., Europe, and emerging markets. Expansion into Africa and Asia—areas with high HIV prevalence—supports sustained growth and broadens its global footprint [7].
Strategic Challenges and Threats
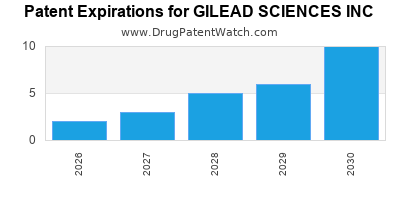
1. Patent Expirations and Generic Competition
The impending patent expirations pose significant threats. Generics and biosimilars are eroding revenue from key products, notably in HCV, where Harvoni's patent protection is nearing its end. This intensifies price competition and compresses margins.
2. Growing Competition in Antiviral Market
Competitors like AbbVie, Merck, and BMS are investing heavily in antiviral therapies, especially in HIV and HCV. The emergence of novel agents with improved efficacy or dosing regimens threatens Gilead's market share.
3. Limited Diversification Beyond Antivirals
Gilead's narrow focus on antivirals exposes it to sector-specific risks. The absence of a robust oncology or autoimmune pipeline limits its resilience against downturns in the antiviral segment.
4. Pricing and Reimbursement Pressures
Healthcare systems worldwide are increasingly emphasizing cost-effectiveness, leading to downward pressure on drug prices. Gilead's high-cost therapies could face reimbursement hurdles, affecting profitability.
5. Regulatory and Political Risks
Global regulatory environments are tightening, especially concerning patents and drug pricing policies. Political pressures in key markets could impact Gilead’s market access strategies.
Strategic Insights
1. Diversification into New Therapeutic Areas
To mitigate over-reliance on antivirals, Gilead should accelerate diversification into oncology, inflammation, and rare diseases through internal R&D and acquisitions. Its recent investments in cell therapy and immuno-oncology signify a move toward this strategy.
2. Emphasis on Biosimilars and Price Competitiveness
Developing biosimilars for established products can counteract patent expirations and tap into cost-sensitive markets. Gilead’s ability to leverage its manufacturing capabilities can facilitate this transition.
3. Accelerating Innovation in Long-Acting Therapies
Investment in long-acting formulations for HIV and HCV enhances patient adherence and provides a competitive edge. Clinical development programs focusing on monthly or quarterly dosing can redefine treatment paradigms.
4. Strategic Collaborations and Licensing Agreements
Partnering with biotech firms for cutting-edge technologies, such as gene editing, can expand Gilead’s pipeline. Licensing agreements with academia or smaller biotechs expedite access to novel modalities.
5. Market Expansion and Equity in Emerging Economies
Enhanced focus on emerging markets through tailored pricing models, local manufacturing, and patient education initiatives will foster long-term growth, especially in regions with high disease burden.
Key Takeaways
- Gilead’s leadership in antiviral therapies remains robust but faces increasing patent expirations and generic competition.
- Strategic diversification beyond antivirals is critical for sustaining growth; recent efforts in oncology and gene therapies are promising.
- The company’s innovation in long-acting formulations and biosimilar development can serve as future growth pillars.
- Collaborations and acquisitions are key drivers of pipeline expansion; maintaining active partnerships is essential.
- Geographical expansion, particularly in emerging markets, offers a resilient growth trajectory amid domestic pricing pressures.
FAQs
1. How does Gilead’s patent portfolio impact its competitive positioning?
Gilead’s extensive patent portfolio provides significant market exclusivity for flagship antiviral products, securing high-profit margins. However, approaching patent cliffs for key drugs like Harvoni exposes it to generic competition, necessitating pipeline diversification.
2. What are Gilead’s main growth opportunities outside antiviral therapies?
Emerging opportunities include oncology, immuno-oncology, rare diseases, and gene editing. Recent acquisitions and collaborations signal a strategic pivot to diversify beyond antivirals.
3. How does Gilead plan to address pricing pressures?
Gilead is investing in biosimilars, long-acting formulations, and value-based agreements with payers to improve cost competitiveness while maintaining profitability.
4. What role do emerging markets play in Gilead’s growth strategy?
Emerging markets, especially in Africa and Asia, present substantial opportunities due to high disease burden and unmet needs. Local manufacturing, tailored pricing, and education initiatives are central to its expansion plans.
5. What are the risks associated with Gilead’s reliance on antiviral therapies?
Dependence on a narrow product portfolio makes Gilead vulnerable to market shifts, generic competition, and regulatory changes. Broadening the pipeline mitigates these risks.
References
[1] IQVIA. (2022). Global HIV market analysis.
[2] EvaluatePharma. (2022). Hepatitis C drug market report.
[3] FDA. (2021). Emergency Use Authorization summary for Veklury.
[4] Gilead Sciences Annual Report. (2022).
[5] MarketWatch. (2022). Gilead’s HIV treatment revenues overview.
[6] Gilead Sciences Press Release. (2022). Strategic acquisitions and partnerships update.
[7] World Health Organization. (2022). Global HIV and hepatitis B and C epidemiology reports.