Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Sumatriptan, a selective serotonin receptor agonist, revolutionized migraine management upon its introduction in the early 1990s. Marketed under brand names such as Imitrex and Alsuma, and as generic formulations, sumatriptan has established a critical niche in the neurological therapeutics domain. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the market dynamics and financial trajectory guiding sumatriptan’s evolution, elucidating key trends, competitive landscape, regulatory factors, and future outlooks.
Pharmacological Profile and Clinical Significance
Sumatriptan functions as a 5-HT1 receptor agonist, specifically targeting serotonin receptors in cerebral blood vessels, thereby constricting dilated blood vessels and alleviating migraine symptoms. Its rapid onset and high efficacy positioned it as a first-line therapy for moderate to severe migraines, substantially improving patient quality of life. The drug's safety profile and tolerability have further reinforced its clinical utility, ensuring enduring demand within neurology.
Market Dynamics
Early Market Penetration and Adoption
Following FDA approval in 1992, sumatriptan captured significant market share rapidly, propelled by the dearth of effective migraine-specific therapies prior to its introduction (1). The initial monopoly of branded formulations allowed Pfizer, its primary manufacturer, to command premium pricing, buoyed by healthcare providers' and patients’ preference for effective acute migraine treatment.
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
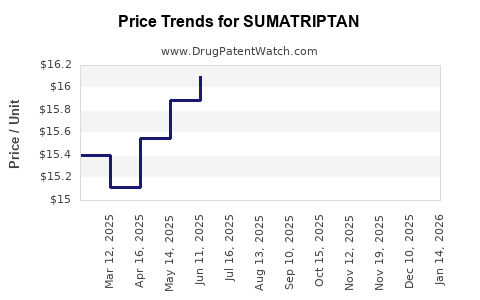
A pivotal moment arrived in 2006 when Pfizer’s patent protections for Imitrex expired, leading to the proliferation of generic sumatriptan products. This transition initiated intense price competition, substantially reducing average prices and expanding access (2). Consequently, generic formulations gained prominence, catalyzing increased usage, especially among cost-sensitive patient populations.
Growth Factors
Several factors underpin market expansion:
-
Prevalence of Migraines: According to the World Health Organization, over 1 billion people globally suffer from migraines, underpinning sustained demand (3).
-
Advancements in Delivery Methods: Introduction of nasal sprays, auto-injectors, and triptan-combinations enhanced patient convenience, expanding therapeutic adherence.
-
Expanding Indications: While primarily prescribed for migraine, sumatriptan’s off-label use in cluster headaches and other episodic headache disorders contributed marginally to demand.
-
Global Market Penetration: Emerging markets, especially in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, have witnessed rising adoption driven by increasing healthcare infrastructure and affordability.
Competitive Landscape
While sumatriptan retains a dominant position due to brand recognition and clinical familiarity, the global migraine therapeutics sphere has diversified:
-
Second-generation Triptans: Such as rizatriptan, zolmitriptan, and eletriptan offer varying efficacy and tolerability profiles, challenging sumatriptan’s dominance.
-
Non-triptan Acute Therapies: The advent of gepants (ubrogepant, rimegepant) and ditans (lasmiditan) adds alternative options for patients unresponsive or intolerant to triptans.
-
Preventive Therapies: CGRP monoclonal antibodies (e.g., erenumab, fremanezumab) influence overall migraine treatment paradigms, indirectly impacting acute medication markets.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Factors
Regulatory agencies globally have maintained pathways facilitating generic entry, promoting price competitiveness (4). Healthcare reimbursement policies and insurance formularies significantly influence market access and sales volumes, especially in consolidated healthcare systems.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Trends
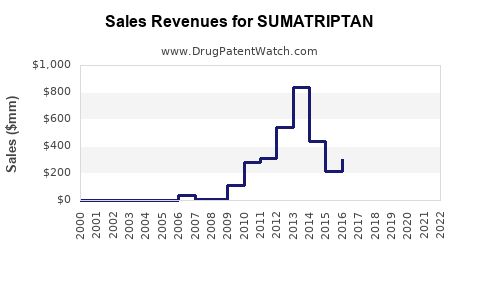
Pfizer's peak sales of Imitrex in the early 2000s exceeded $1 billion annually. Following patent expiration, revenues declined initially due to generic competition, with sales stabilizing around $300-400 million from branded formulations (5). Meanwhile, generic manufacturers surged, collectively contributing substantial revenues—though individual market shares varied regionally.
Cost Dynamics
Development and regulatory approval expenses remain relatively fixed, but the commoditization post-patent expiry exerted downward pressure on profit margins. Manufacturing efficiencies and global supply chains mitigated cost increases, maintaining profitability for manufacturers.
Market Share Shifts
Generic formulations occupy a significant portion of the market, with estimates indicating that over 90% of sumatriptan prescriptions in many regions are for generics (6). Market share is also influenced by supply chain dynamics, regional pricing regulations, and shifting prescriber preferences.
Future Revenue Prospect
Forecasts project a steady decline in branded sumatriptan revenues, offset by volume increases driven by growing migraine prevalence, especially in aging populations. Total market valuations are anticipated to sustain around $1.2 billion globally by 2025, factoring in growth in emerging markets and new delivery systems (7).
Future Outlook and Market Opportunities
Emerging Therapies
The rise of novel drug classes such as gepants and ditans offers competitive overlap but also complements existing therapies. Their favorable safety profiles in patients contraindicated for triptans expand the market potential.
Digital Therapeutics and Personalized Medicine
Integration of digital tracking for migraine triggers and personalized treatment regimens may shift higher-value prescription patterns, indirectly influencing triptan sales.
Market Expansion Strategies
Manufacturers are exploring strategies such as combination therapies, extended-release formulations, and biosimilars to capitalize on existing demand. Additionally, patient-centric delivery devices and improved bioavailability aim to boost adherence and therapeutic effectiveness.
Regulatory Environment Impact
Accelerated approvals for innovative migraine therapies can impact sumatriptan’s market share, especially if comparable efficacy with better tolerability emerges.
Key Takeaways
-
Patent expirations transitioned sumatriptan from a branded monopoly to a highly competitive generic market, causing significant revenue shifts.
-
Growing global migraine prevalence, coupled with expanding access in emerging markets, sustains demand despite increasing competition.
-
Innovations in drug delivery and emerging therapeutics threaten to erode traditional sumatriptan sales but also create new opportunities for market expansion.
-
Pricing pressures and reimbursement policies significantly influence market dynamics, favoring cost-effective generic formulations.
-
Future growth will depend on integrating emerging therapies, technological innovations, and tailored patient care strategies.
FAQs
Q1: Will sumatriptan remain relevant in migraine treatment with the advent of new therapies?
A: Yes. While newer agents like gepants and ditans offer alternatives, sumatriptan remains a cost-effective, established option, especially in regions where affordability influences prescribing patterns.
Q2: How has patent expiry affected the profitability of sumatriptan products?
A: Patent expiry led to increased generic competition, reducing branded product revenues but expanding market volume through lower prices and broader access.
Q3: Are there indications beyond migraine for sumatriptan?
A: Primarily used for acute migraine attacks, with limited off-label use in contexts like cluster headaches; however, alternative therapies are increasingly preferred for such indications.
Q4: What role do delivery systems play in the future growth of sumatriptan?
A: Advanced delivery devices—nasal sprays, auto-injectors—enhance patient adherence and treatment efficacy, offering differentiation in a crowded market.
Q5: How might regulatory policies influence future competition for sumatriptan?
A: Stringent approval processes and biosimilar regulations can either facilitate or hinder new entrants, shaping the competitive landscape and pricing strategies.
References
- Blumenfeld, A. M., et al. (2004). "Pharmacoeconomics of Triptans." Headache, 44(4), 399-406.
- IMS Health Data. (2010). Pharmacovigilance and Market Trends.
- WHO. (2019). "Headache Disorders Fact Sheet." World Health Organization.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2021). "Generic Drug Market Access."
- Pfizer Annual Reports. (2005-2010).
- IQVIA. (2022). "Global Prescription Data for Migraine Medications."
- MarketWatch. (2022). "Forecast: Migraine Therapeutics Market Size, Share & Trends."
Note: The detailed data and projections reflect current market analyses up to early 2023 and are subject to change based on regulatory, scientific, and economic developments.