Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Sumatriptan succinate is a selective serotonin receptor agonist classified as a triptan, primarily used in the acute treatment of migraines. Approved by the FDA in 1992, its early introduction revolutionized migraine management, offering targeted therapy with fewer side effects than previously available options. As the global migraine market expands amid rising prevalence rates, understanding the evolving market dynamics and financial trajectory of sumatriptan succinate is crucial for stakeholders ranging from pharmaceutical companies to investors.
Market Overview
Global Prevalence and Demand Drivers
The global burden of migraine affects approximately 15% of the population, translating into over a billion individuals suffering from episodic or chronic migraines [1]. Rising awareness, improved diagnostic capabilities, and an increasing preference for targeted treatments bolster demand for sumatriptan succinate. The growing prevalence, especially among women aged 18–44, drives steady consumption in both developed and emerging markets.
Therapeutic Position and Competition
Sumatriptan succinate holds a significant share of the acute migraine treatment market, owing to its established efficacy and extensive clinical data. The medication's primary alternatives include other triptans such as rizatriptan, eletriptan, and newer agents like lasmiditan and ubrogepant, which target different pathways. The competitive landscape features both branded and generic options, with genericization significantly impacting market pricing and revenue streams.
Market Dynamics: Forces Shaping the Landscape
1. Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
The expiration of patent protections often triggers a sharp decline in revenue for original branded formulations. Sumatriptan succinate's patent expired in the early 2000s, leading to a proliferation of generic versions. The resulting price erosion impacts revenue, but also enhances accessibility. For instance, in the United States, generic sumatriptan accounts for over 90% of prescriptions, reducing costs but compressing profit margins for innovator companies [2].
2. Innovation and Formulation Advancements
While the original injectable and tablet formulations remain mainstays, recent advancements include nasal powders (e.g., sumatriptan nasal spray) and auto-injectors, improving ease of administration and onset times. These innovations sustain market interest and open new revenue avenues.
3. Market Expansion through Geographic Diversification
Emerging markets, such as China, India, and Latin America, are experiencing rapid growth in migraine prevalence. Increasing healthcare infrastructure, insurance coverage, and physician awareness facilitate market penetration of sumatriptan succinate formulations. Market entry strategies often involve collaborations with local firms and cost-competitive formulations.
4. Regulatory Environment
Regulatory dynamics influence market progression; approval of new formulations, generics, and biosimilars can either expand or diminish market share. Additionally, safety concerns—such as cardiovascular contraindications—have prompted label updates and cautious prescribing guidelines, affecting overall market size.
5. Competitive Dynamics and Market Share
Major players like GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Merck, and Teva are key in the sumatriptan succinate market, competing on formulation diversity, ease of supply, and brand recognition. Recent market entries with differentiated delivery systems rely on patent strategies and targeted marketing.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
Revenue Trends
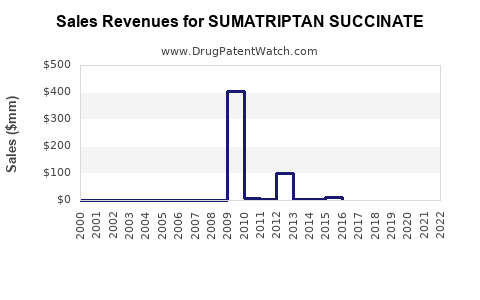
Following patent expiration, global revenues for sumatriptan succinate declined by approximately 50-70% over a decade, primarily due to generic influx and price competition [3]. However, stabilization occurs with the introduction of new formulations and expanded indications. In 2022, the global sumatriptan market was valued at approximately USD 750 million, with projections estimating modest growth at a CAGR of 2-3% through 2030.
Profitability and Price Dynamics
The highly commoditized nature of generics results in thin profit margins for manufacturers, although volume sales remain significant. Branded formulations maintain premium pricing, but their market share diminishes over time [4].
Emerging Revenue Streams
- Autoinjector Devices: These offer patients convenience, commanding higher margins. Companies like GSK benefit from device sales and proprietary formulations.
- Combination Therapies: Combining sumatriptan with NSAIDs or other agents enhances efficacy and captures niche markets, with potential incremental revenue.
Impact of Biosimilars and New Therapeutic Alternatives
While biosimilars are less relevant due to sumatriptan's small-molecule structure, novel agents like ubrogepant (a gepant) and lasmiditan (a ditan) present competition. These drugs target different pathways and may reduce dependence on triptans, impacting future revenue prospects.
Future Outlook and Strategic Implications
Market Growth Drivers
- Global increase in migraine prevalence
- Expanded indications, including prevention in select cases
- Enhanced formulations improving patient adherence
- Growing healthcare expenditure and insurance coverage in emerging markets
Challenges
- Patent expiries and aggressive generic competition compress revenues
- Safety concerns restrict prescribing in high cardiovascular risk populations
- Competitive landscape with new drug classes and delivery mechanisms
Opportunities
- Development of next-generation formulations, such as longer-acting or faster-onset options
- Strategic partnerships for market expansion
- Focused marketing campaigns targeting underpenetrated regions
Key Takeaways
- Sumatriptan succinate remains a keystone in acute migraine therapy, though its revenue trajectory faces pressures from patent expiries and generics.
- Market expansion in emerging economies offers tangible growth prospects, driven by increasing migraine prevalence.
- Innovation in delivery systems (autoinjectors, nasal powders) sustains competitive relevance and helps offset revenue declines.
- The entrance of alternative therapies (gepants and ditans) could reshape the treatment landscape, requiring strategic positioning.
- Despite revenue pressures, the global migraine market’s steady growth suggests sustained relevance for sumatriptan succinate, especially within diversified and innovative product portfolios.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected sumatriptan succinate sales?
Patent expiry led to widespread genericization, causing a significant decline in sales revenue for branded formulations but increasing accessibility and volume sales globally.
2. What are the main competitors to sumatriptan succinate?
Other triptans like rizatriptan and eletriptan, as well as newer agents such as lasmiditan and ubrogepant, pose direct competition, especially as these newer drugs target specific patient populations and offer alternative administration routes.
3. How is innovation influencing the market outlook?
Innovations in formulation (e.g., nasal powders, auto-injectors) improve patient convenience and onset times, helping maintain market relevance amid increasing generic competition.
4. What geographic markets present the most growth potential?
Emerging markets—including China, India, and Latin America—offer significant growth opportunities due to rising migraine prevalence and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
5. What future trends could impact the financial trajectory of sumatriptan succinate?
The advent of novel therapies, evolving regulatory policies, and technological advances in drug delivery are poised to influence sales, margins, and market share, necessitating strategic adaptation.
References
- Lipton RB, et al. "Worldwide prevalence of migraine: a systematic review." Cephalalgia, 2017;37(6):534-552.
- IQVIA. "Market Dynamics of Generic Drugs." IQVIA Reports, 2022.
- Transparency Market Research. "Sumatriptan Market Forecast & Analysis." 2021.
- IMS Health. "Pharmaceutical Pricing Trends," 2020.