Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Nitroglycerin, a critical pharmaceutical agent primarily utilized for treating angina pectoris and other cardiovascular conditions, has a storied history rooted in both medicinal applications and industrial origins. Its dual role as a vasodilator and an industrial explosive underscores its complex market dynamics. As regulatory landscapes evolve, alongside technological and clinical advancements, understanding nitroglycerin’s market trajectory offers valuable insights for stakeholders across pharma, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors.
Historical Context and Clinical Significance
Developed in the late 19th century, nitroglycerin's pharmacological utility revolutionized cardiovascular therapy. Its efficacy in rapid symptom relief for angina has established it as a standard treatment, supplemented by various formulations such as sublingual tablets, transdermal patches, and intravenous solutions [1]. Despite its age, nitroglycerin remains indispensable, owing to its rapid onset and reliable vasodilatory effects.
Market Size and Global Demand
The global demand for nitroglycerin persists driven by the endemic prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). According to the World Health Organization, CVDs account for approximately 17.9 million deaths annually, underpinning a continued need for effective therapies like nitroglycerin [2].
The pharmaceutical segment for angina management globally is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3-4% over the next five years, driven by aging populations and increased healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets [3]. The nitroglycerin market comprises both branded and generic formulations, with the latter dominating due to cost-effectiveness and widespread clinical adoption.
Key Market Players and Competitive Landscape
Major pharmaceutical players operating in licensed or generic manufacturing include Pfizer, Novartis, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Hikma Pharmaceuticals. Observations indicate a trend towards consolidations and licensing agreements aimed at optimizing supply chains and expanding geographic reach [4].
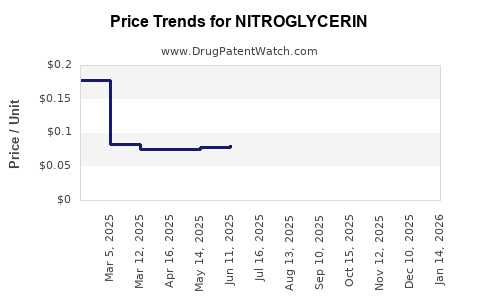
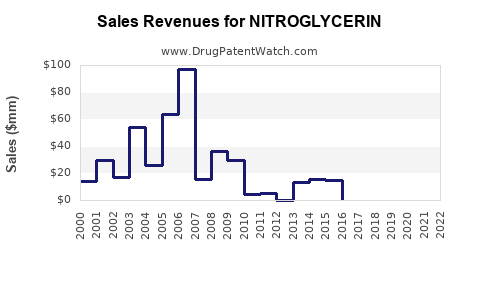
Generic manufacturers benefit from lower production costs, helping to sustain stable pricing despite patent expirations. For example, the expiration of several patents in the 2000s in North America and Europe led to a surge in generic production, significantly impacting market prices and profitability [5].
Regulatory Environment and Patent Dynamics
While original patents generally expired decades ago, regulatory oversight remains stringent. The FDA and EMA require comprehensive quality controls, especially considering nitroglycerin's sensitive nature due to its explosive properties. The regulatory landscape influences market entry barriers, with generic manufacturers investing heavily in compliance infrastructure.
Importantly, patents on certain formulations or delivery mechanisms can extend market exclusivity. Novel transdermal systems or combination therapies incorporating nitroglycerin have recently gained regulatory approval, potentially affecting market trajectories [6].
Manufacturing Challenges and Supply Chain Considerations
Manufacturing nitroglycerin poses unique challenges due to its explosive nature. Facilities must adhere to rigorous safety standards, increasing operational costs. Additionally, maintaining consistent quality and bioavailability across different formulations influences manufacturing investments.
Supply chain dynamics are also affected by raw material availability, geopolitical factors, and global health emergencies. Recent disruptions, like those caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, have highlighted vulnerabilities, prompting manufacturers to diversify sourcing and inventory management strategies [7].
Technological Innovations and Future Outlook
Innovations focusing on improved delivery systems—such as sustained-release transdermal patches and novel sublingual formulations—are expanding therapeutic options, potentially extending market longevity for nitroglycerin. Research into combination therapies aims to enhance efficacy and patient compliance.
Furthermore, advances in manufacturing automation and process optimization are reducing costs and improving safety. These innovations can facilitate greater availability, especially in emerging markets, thus expanding the overall market size.
Financial Trajectory and Investment Opportunities
The stable demand profile combined with growth driven by demographic shifts suggests a steady financial underpinning for nitroglycerin. Established players witnessing patent expirations have experienced revenue declines initially, but growth potential exists through formulation innovations and market expansion.
Emerging markets present lucrative avenues, particularly where healthcare infrastructure upgrades boost cardiovascular treatment adoption. Conversely, increasing competition from alternative therapies—like calcium channel blockers and nitrates with longer duration—may pressure prices.
Investment opportunities revolve around generic manufacturers with scalable production capacities and innovative formulation developers. Additionally, companies engaged in manufacturing safer, non-explosive formulations could command premium valuations as safety regulations tighten [8].
Market Risks and Challenges
Key risks include regulatory hurdles related to safety protocols, particularly concerning handling and storage, which can stifle new entrants. Patent litigations and disputes over formulation claims could also impact market dynamics.
Substitutes and alternative therapies pose challenges, especially if new medications offer comparable efficacy with improved convenience or fewer side effects. Additionally, global supply chain disruptions and raw material shortages may impact production capacities and profitability.
Conclusion
The market for nitroglycerin remains resilient, underpinned by its essential role in cardiovascular therapy. While patent expiries and manufacturing challenges introduce volatility, technological advancements and expanding global healthcare access present opportunities for sustained growth. Stakeholders must navigate regulatory complexities and competitive pressures, leveraging innovations to optimize financial trajectories.
Key Takeaways
-
The global demand for nitroglycerin is driven by the high prevalence of cardiovascular conditions, ensuring steady market relevance.
-
Patent expirations have fostered a competitive generic landscape, stabilizing prices but encouraging innovation in formulations.
-
Manufacturing safety and quality standards significantly influence market dynamics and entry barriers.
-
Technological innovations in delivery systems and manufacturing processes can extend nitroglycerin’s market lifespan and profitability.
-
Emerging markets offer growth prospects, contingent upon improving healthcare infrastructure and regulatory environments.
FAQs
1. How does patent expiration affect nitroglycerin's market landscape?
Patent expiration allows generic manufacturers to produce cost-effective versions, increasing competition and reducing prices. While this drives accessibility, it pressures branded formulations' profitability, shifting focus toward formulation innovation and new delivery systems.
2. What are the main regulatory challenges for nitroglycerin manufacturers?
Regulations focus on safety standards due to its explosive nature, quality control for consistent dosing, and approval processes for new formulations. Stringent compliance can raise operational costs and pose barriers for new entrants.
3. Are there emerging alternatives to nitroglycerin in angina treatment?
Yes. Alternatives include calcium channel blockers, long-acting nitrates, and novel agents like ranolazine. These options may offer longer-lasting relief or fewer side effects, influencing nitroglycerin's market share.
4. How do technological innovations impact nitroglycerin’s global market?
Innovations in drug delivery, such as transdermal patches and sublingual formulations, improve efficacy and patient compliance. Manufacturing process improvements can lower costs and increase supply stability.
5. What is the outlook for investments in nitroglycerin manufacturing and formulations?
Stable demand and expansion in emerging markets suggest positive prospects. Investing in formulation innovation and scalable manufacturing capabilities offers growth opportunities, despite competitive and regulatory challenges.
References
[1] WHO. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). World Health Organization.
[2] WHO. Cardiovascular Diseases Fact Sheet. 2021.
[3] MarketsandMarkets. Cardiovascular Therapeutics Market Forecast. 2022.
[4] Global Data. Pharmaceutical Market Reports. 2022.
[5] U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. Patent Expirations in Cardiology. 2015–2020.
[6] EMA. Regulatory Approvals for Transdermal Cardiovascular Drugs. 2021.
[7] World Economic Forum. Supply Chain Disruptions in Pharmaceuticals. 2022.
[8] Fitch Ratings. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Safety Standards. 2022.