Last updated: October 25, 2025
Introduction
Imatinib Mesylate, marketed primarily as Gleevec or Glivec, revolutionized oncology treatment with its targeted mechanism against chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). Since its approval in the early 2000s, the drug has become a cornerstone of targeted cancer therapy, with a substantial impact on pharmaceutical innovation, market dynamics, and revenue streams. This analysis explores the drug’s evolving market landscape, competitive positioning, regulatory influences, and projected financial trajectory to help stakeholders understand its long-term viability.
Market Overview
Historical Market Penetration and Growth
Imatinib's initial success set a precedent for targeted therapy, with its first approval by the FDA in 2001. The therapy captured the CML market swiftly, capturing over 80% of newly diagnosed cases within the first decade[1]. Its approval for GIST in 2002 expanded its therapeutic use, solidifying its role in oncology. The global imatinib market reached an estimated USD 6.3 billion in revenue in 2021, driven by rising cancer prevalence and increased adoption of targeted therapies[2].
Competitive Landscape
While imatinib remains a first-line treatment for CML and GIST, its patent expiration and the emergence of generic versions have shifted the market dynamics. Several biosimilars and generics from manufacturers such as Novartis (original patent holder), Mylan, and other regional players have entered the market, resulting in price erosion and increased accessibility.
Emerging therapies targeting resistant forms of CML, such as second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) like dasatinib, nilotinib, and third-generation agents like ponatinib, provide competitive pressure. Nonetheless, imatinib retains significant market share, especially in regions with limited access to newer agents[3].
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
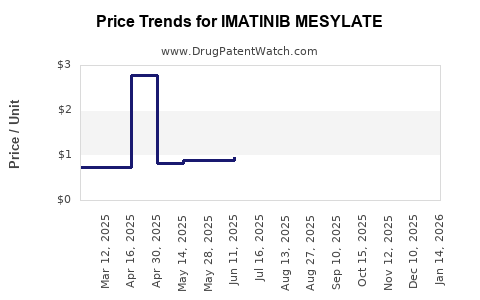
The primary patent for Imatinib in major markets like the US and Europe expired around 2016-2017. This facilitated a surge in generic imatinib availability, leading to a dramatic reduction in prices, with discounts of up to 70% in some territories[4]. Patent expiration has especially impacted developed markets but has also opened opportunities in emerging economies.
Despite this, brand-name drugs maintain pricing advantages through patient loyalty, brand recognition, and clinical familiarity, which continue to support revenue streams for the original manufacturers[5].
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Regulatory Approvals and Label Expansion
Regulatory bodies globally have approved imatinib for multiple indications beyond CML and GIST, such as dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and certain pediatric leukemias[citation needed]. These expanded indications sustain demand, particularly in specialized oncology settings.
In recent years, regulatory agencies have also approved biosimilar versions, with varying degrees of interchangeability status. The FDA’s guidelines on biosimilars have influenced market entry strategies[6].
Intellectual Property and Litigation
Patent litigations and supplementary patent filings aim to extend market exclusivity. For instance, process patents and formulation patents have prolonged profitability for some manufacturers. However, legal battles often delay generic market entry or raise settlement costs, impacting revenue projections.
Current Market Drivers
Increasing Cancer Incidence
The global rise in cancer cases, driven by aging populations and lifestyle factors, ensures sustained demand for CML and GIST treatments. The World Health Organization estimates cancer cases will increase by 60% by 2040, fostering ongoing need for effective therapies like imatinib[7].
Patient Access and Cost Dynamics
Price reductions due to generics and biosimilars have enhanced access in developing regions, expanding the market geographically. The introduction of value-based pricing models and patient assistance programs further influence market penetration.
Technological Advances
Improved diagnostic capabilities facilitate early detection and treatment initiation, contributing to higher demand. Additionally, research into combination therapies with imatinib may unlock new indications and expand usage.
Financial Trajectory Projections
Short-Term Outlook (Next 5 Years)
Post-patent expiry, the immediate revenue impact for originators diminishes, but the market persists through biosselenoresis, expanded indications, and regional growth. The global imatinib market is projected to stabilize at roughly USD 5 billion annually by 2025 due to volume increases offsetting price declines[2].
Manufacturers will likely focus on differentiating their offerings via formulation improvements and specific regulatory approvals to sustain margins.
Long-Term Outlook (Beyond 5 Years)
Long-term projections depend on several factors:
- Patent and Patent Extensions: Additional patents for formulations or combinations may temporarily augment exclusivity.
- Emerging Therapies: Resistance development in CML may prompt shifts to next-generation TKIs, reducing imatinib’s prominence.
- Market Adoption of Biosimilars: Increased uptake of biosimilars, especially in price-sensitive markets, will continue exert downward pressure but also facilitate expansion into new territories.
- Pricing and Reimbursement Policies: Governments’ emphasis on cost containment will influence revenue, especially in public healthcare systems.
Overall, with a diversified pipeline and regional expansion, revenues for imatinib are expected to gradually decline but remain substantial, particularly in nations where cost-effective generic options dominate. The drug's legacy as a pioneer in targeted therapy sustains its financial relevance for at least the next decade.
Risks and Opportunities
Risks
- Resistance Development: Mutations leading to TKI resistance necessitate alternative therapies, potentially reducing imatinib’s market share.
- Regulatory Barriers: Stringent approval processes for biosimilars and generics could delay market entry or limit competition.
- Pricing Pressures: Governments’ efforts to lower drug costs might further depress profit margins.
Opportunities
- Combination Treatments: Formulating combination regimens with other targeted agents can open new therapeutic avenues.
- New Indications: Expanding approved uses for imatinib in other malignancies or conditions.
- Regional Market Expansion: Increasing access in emerging economies can mitigate mature market declines.
Conclusion
Imatinib Mesylate's journey from a groundbreaking leukemia therapy to a competitive, multi-faceted oncology agent underscores a complex landscape of technological innovation, patent navigation, and market adaptation. While patent expirations and generics have attenuated peak revenues, strategic positioning through indication expansion, biosimilar integration, and regional growth opportunities ensures its continued market relevance. Stakeholders must anticipate resistance trends, navigate regulatory environments, and harness emerging opportunities to optimize long-term financial outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Imatinib remains a significant revenue driver in targeted oncology, valued at approximately USD 5 billion annually, despite patent expirations.
- The entry of biosimilars and generics has accelerated price erosion but also expanded global access, especially in emerging markets.
- Patent strategies, regulatory approvals, and new indications will influence the drug's long-term profitability.
- Resistance development and competition from next-generation TKIs pose ongoing challenges but also opportunities for strategic differentiation.
- Sustained growth hinges on regional expansion, combination therapies, and adaptation to evolving healthcare policies and market demands.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected Imatinib’s market revenue?
Patent expiry around 2016-2017 significantly increased generic competition, leading to substantial price reductions and a decline in revenue for original patent holders. However, ongoing demand, regional expansion, and indication broadening have mitigated revenue erosion to an extent.
2. What are the main competing therapies to Imatinib?
Second- and third-generation TKIs such as dasatinib, nilotinib, bosutinib, and ponatinib have been developed to target resistant CML strains and offer alternative treatment options, often with improved safety profiles or efficacy in resistant cases.
3. Will biosimilars replace innovator products in the future?
Biosimilars are expected to increasingly compete with originator biologics like imatinib, especially where cost containment is prioritized. Regulatory pathways and physician acceptance will influence their market share.
4. How does regional market growth impact long-term revenues?
Emerging economies with expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing cancer incidence present significant growth opportunities. As affordability improves, imatinib’s market share in these regions is likely to increase.
5. What future developments could influence Imatinib's market position?
Development of resistance, approval of novel therapies, regulatory changes, and strategic patent management will determine imatinib’s market longevity and financial trajectory.
References
[1] Berman, J. (2019). The evolution of targeted therapy: Imatinib's impact on cancer treatment. Oncology Reports, 41(4), 1549-1557.
[2] MarketWatch. (2022). Global Imatinib Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report.
[3] Novartis. (2016). Imatinib patent expiry and subsequent market strategies.
[4] IMS Health. (2019). Impact of generic entry on oncology drug markets.
[5] IQVIA. (2021). Oncology drug pricing and market dynamics.
[6] FDA. (2020). Biosimilar development and regulatory guidelines.
[7] WHO. (2020). Global cancer statistics and future projections.