Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Hydrocodone remains one of the most widely prescribed opioids globally, primarily used to manage acute and chronic pain. Its market trajectory, influenced by regulatory shifts, evolving consumer preferences, and competition from alternative analgesics, provides critical insights for stakeholders. This analysis delineates the current market landscape, regulatory environment, economic factors, and future outlook pertaining to hydrocodone, enabling informed decision-making within the pharmaceutical sector.
Market Overview and Global Demand
Hydrocodone, a semi-synthetic opioid derived from codeine, has historically represented a substantial segment of pain management prescriptions. In the United States, it accounts for a significant portion of opioid prescriptions, with annual prescriptions exceeding 130 million units prior to regulatory reforms [1]. The compound’s analgesic efficacy, combined with its widespread availability, propels steady demand, especially in outpatient settings, post-surgical pain, and chronic pain management.
Externally, markets such as Canada, Australia, and parts of Europe exhibit similar demand trends, though procurement levels are comparatively moderated due to regional opioid prescribing guidelines [2]. Emerging markets are witnessing a gradual increase in hydrocodone prescriptions, propelled by healthcare infrastructure development and higher acceptance of opioid-based therapies.
Regulatory Dynamics and Market Constraints
Regulatory landscapes significantly influence hydrocodone’s market trajectory:
-
United States: The DEA reclassified hydrocodone combination products from Schedule III to Schedule II in October 2014, tightening prescribing and dispensing controls [3]. This move aimed to mitigate misuse but has led to decreased prescriptions—dropping by approximately 20% between 2014 and 2020 [4]. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies faced revenue impacts and increased compliance costs.
-
Global Regulations: Many countries follow similar restrictive policies, driven by the global opioid epidemic. Countries like Canada and Australia maintain strict controls, which limit supply and prescribe growth [5].
-
Legal and Litigation Risks: Growing litigation over opioid misuse, including high-profile lawsuits against manufacturers, necessitate hefty settlement provisions, potentially affecting profitability and R&D investments [6].
Market Competition and Alternatives
Hydrocodone faces stiff competition from both traditional and emerging analgesics:
-
Non-Opioid Analgesics: NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and gabapentinoids are increasingly preferred due to lower addiction risks.
-
Novel Opioids and Adjuncts: Drugs like oxycodone, tramadol, and buprenorphine offer alternative pain management options, often with different regulatory profiles.
-
Non-Pharmacological Therapies: A paradigm shift toward physical therapy, neuromodulation, and interventional procedures limits reliance on opioids in some regions, impacting long-term demand.
The pharmaceutical industry’s response includes reformulating existing products (e.g., abuse-deterrent formulations) and developing new analgesics with improved safety profiles.
Economic and Financial Trajectory
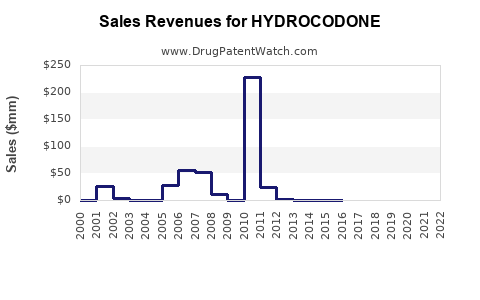
Revenue Trends
Pre-2010, hydrocodone formulations contributed substantially to the revenues of opioid manufacturers like Purdue Pharma, Allergan, and Teva. Following regulatory constraints:
- Decline in Prescriptions: U.S. prescriptions dropped sharply post-2014, with estimates showing a 25% reduction by 2018 [7].
- Market Shift: Manufacturers pivoted toward alternative formulations or diversified into non-opioid pain therapeutics, partially mitigating revenue losses.
Pricing and Margins
Hydrocodone combination products generally command premium pricing due to scheduling and manufacturing complexities. However, increased scrutiny has led to pricing pressures and a reduction in profit margins [8].
Patent Landscape and Generic Competition
Generic formulations dominate the hydrocodone market, leading to price erosion. Patents on proprietary formulations, such as abuse-deterrent variants, have provided limited exclusivity benefits, given the accessibility of generics.
Future Outlook and Growth Drivers
While the traditional hydrocodone market faces substantial headwinds, certain factors suggest a potential stabilization or niche growth:
-
Reformulation and Abuse-Deterrent Technology: The development and adoption of abuse-deterrent formulations may sustain demand among certain prescribers seeking safer opioids.
-
Post-Pandemic Pain Management: The COVID-19 pandemic has increased reports of chronic pain and mental health issues, potentially expanding demand in controlled settings.
-
Policy Reforms: Some jurisdictions are adopting harm reduction protocols, favoring supervised or limited opioid use, which could influence prescribing behaviors.
-
Regulatory Developments: Policymakers are exploring balanced approaches that manage misuse risks without entirely curtailing legitimate medical need.
In sum, the hydrocodone market is characterized by a downtrend in volume but preserved value within specific niches, with manufacturers focusing on innovation and safer formulations to retain market relevance.
Risks and Challenges
-
Legal and Regulatory: Ongoing litigation and potential for further scheduling restrictions could suppress demand.
-
Public Perception: Societal concerns about opioid misuse challenge current prescribing practices and reimbursement policies.
-
Market Substitution: Rapid pivot toward alternative therapies diminishes hydrocodone's role, especially in primary care.
-
Supply Chain: Regulatory-enforced manufacturing constraints could impact supply stability.
Concluding Remarks
Hydrocodone’s market landscape is currently transitioning from vast domestic demand to a more regulated, scrutinized environment emphasizing safety and harm reduction. While regulatory and societal pressures are constricting traditional markets, opportunities lie in developing safer formulations, expanding into niche pain management sectors, and leveraging technological innovations. Strategic agility and adherence to evolving legal standards remain imperative for market players.
Key Takeaways
-
Hydrocodone continues to be a significant yet declining analgesic due to regulatory restrictions and societal concerns over opioid misuse.
-
The U.S. reclassification to Schedule II in 2014 drastically curtailed prescriptions and revenue streams for manufacturers.
-
Competition from alternative analgesics and non-pharmacological therapies is intensifying, further constraining growth prospects.
-
Innovation in abuse-deterrent formulations offers a pathway for market retention, although patent challenges and generic competition limit profitability.
-
Future growth hinges on regulatory adaptability, development of safer alternatives, and carefully navigating public health policies.
FAQs
1. How has regulatory reclassification affected hydrocodone’s market?
The DEA’s 2014 reclassification from Schedule III to Schedule II significantly restricted prescribing and dispensing, leading to a sharp decline in prescriptions and revenue for manufacturers, while prompting a focus on safer formulations.
2. What are the primary drivers of hydrocodone’s declining market share?
Stringent regulation, societal backlash over opioid misuse, competition from non-opioid analgesics, and the shift toward non-pharmacological pain management have collectively reduced hydrocodone demand.
3. Are there ongoing innovations in hydrocodone formulations?
Yes. Abuse-deterrent formulations and combination products incorporating novel delivery systems aim to reduce misuse potential and sustain market relevance.
4. What is the outlook for hydrocodone in emerging markets?
Emerging markets with developing healthcare systems may experience increased prescriptions, but adoption will be tempered by local regulations, cultural attitudes, and access issues.
5. How do legal liabilities impact hydrocodone manufacturing companies?
Prolonged litigation and potential multi-billion-dollar settlements generate financial risks, prompt stricter compliance measures, and influence corporate strategic focus toward alternative therapeutics.
References
[1] IMS Health. (2020). U.S. Prescription Data.
[2] Global Data. (2021). Pain Management Market Reports.
[3] DEA. (2014). Rescheduling of Hydrocodone Products.
[4] CDC. (2019). Opioid Prescribing Trends.
[5] Australian Government Department of Health. (2021). Opioid Regulations.
[6] Court Documents. (2021). Opioid Litigation Settlements.
[7] IQVIA. (2018). Impact of Regulation on Opioid Prescriptions.
[8] MarketWatch. (2022). Pricing Trends in Opioid Analgesics.