Last updated: October 6, 2025
Introduction
Heparin sodium, a widely used anticoagulant, remains integral to various medical procedures, including surgeries, dialysis, and thromboembolism management. Its complex regulatory landscape, manufacturing intricacies, and evolving market demands influence its financial trajectory. This comprehensive analysis delves into the market dynamics shaping heparin sodium's commercial landscape, assesses supply and demand factors, and forecasts key financial trends.
Market Overview
Heparin sodium, characterized by its potent anticoagulant activity derived from animal sources—primarily porcine intestinal mucosa—has maintained its prominence amidst burgeoning innovations in anticoagulation therapy. Despite its simplicity as a molecule compared to novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs), it remains indispensable for specific clinical indications requiring rapid, controllable anticoagulation, including in-hospital settings [1].
Global demand for heparin sodium has demonstrated consistent growth over the past decade, driven by increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, expanding surgical procedures, and growing dialysis populations. The market capitalization reflects the critical role of heparin, with estimates projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4-5% through 2030.
Market Drivers
Growing Clinical Applications and Usage
The escalating incidence of cardiovascular conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and myocardial infarction directly correlates with heightened heparin utilization. Additionally, as surgical interventions—ranging from electrode placements to complex vascular surgeries—rise globally, the demand for reliable anticoagulants increases [2].
Aging Population and Rising Chronic Disease Burden
Developing countries experience rapid demographic shifts, with aging populations raising the prevalence of coagulopathies. Data suggest that by 2050, the global elderly demographic will constitute nearly 16% of the population, propelling demand for heparin-based therapies [3].
Operational Versatility in Critical Care
Heparin’s rapid onset and reversibility via protamine sulfate reinforce its status in intensive care units (ICUs) and dialysis centers. Its application during invasive procedures underscores its sustained relevance.
Regulatory and Supply Chain Factors
Stringent quality standards by agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and WHO influence manufacturing practices, leading to high barriers to entry but ensuring product reliability. However, recent vulnerabilities in supply chains—due to contamination scandals and animal source limitations—have prompted calls for alternative sourcing and synthetic formulations [4].
Market Challenges
Supply Chain Disruptions and Ethical Concerns
The reliance on animal-derived raw materials exposes the market to risks such as zoonotic disease outbreaks, supply shortages, and ethical debates over animal welfare. The 2008 heparin contamination crisis, resulting from adulteration and poor manufacturing standards, caused a significant market shake-up, emphasizing the need for increased oversight [5].
Emergence of Synthetic and Alternative Anticoagulants
Novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs)—such as rivaroxaban and apixaban—offer advantages including oral administration, predictable pharmacokinetics, and reduced monitoring needs. These alternatives threaten traditional heparin sales, especially outside hospital settings.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Market Consolidation
Stringent regulations, particularly surrounding sourcing and manufacturing, have increased compliance costs. Market players are consolidating horizontally and vertically to mitigate regulatory risks and capture broader market segments.
Manufacturing and R&D Trajectory
Technological Innovations
Significant R&D investments focus on developing recombinant and synthetic heparin alternatives to circumvent raw material limitations. Companies are exploring bioengineered heparins produced via genetically modified microbial systems, promising increased purity and safety [6].
Cost Dynamics
The high costs associated with sourcing animal raw materials, ensuring compliance, and meeting quality standards inflate manufacturing expenses. As patents for originator products expire, generic manufacturers introduce cost-effective formulations, intensifying price competition.
Financial Analysis and Forecast
Market Valuation
In 2022, the global heparin market was valued at approximately USD 2.8 billion, with North America leading due to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher surgical volumes. Asia-Pacific exhibits significant growth potential, driven by expanding healthcare access and markets in China and India.
Revenue Outlook and CAGR
Forecasts project a steady CAGR of approximately 4-5% over the next decade, reaching an estimated USD 4-5 billion by 2030. Asia-Pacific is anticipated to outpace other regions, attributed to high demand from dialysis and surgical procedures and the growing acceptance of biosimilar products.
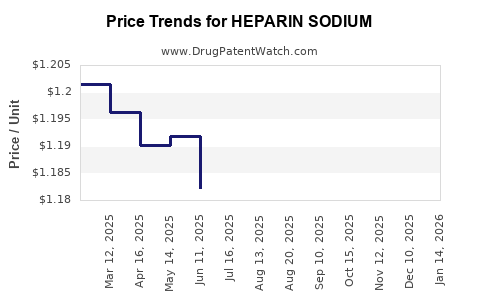
Pricing Trends
While patent expirations and biosimilars exert downward pressure on prices, the high cost of manufacturing and quality assurance sustains healthy margins for select players. The shift towards synthetic production may further influence pricing dynamics.
Investment and M&A Strategies
Pharmaceutical firms investing in R&D for synthetic heparins or biosimilars aim to capitalize on market expansion and mitigate raw material risks. Strategic alliances and acquisitions are prevalent to enhance manufacturing capabilities and geographic reach.
Regulatory Impact on Financial Trajectory
Regulatory scrutiny shapes the market, with authorities demanding transparency, safety, and quality control. The 2008 contamination crisis accelerated regulatory reforms, leading to increased compliance costs but fostering consumer confidence. Future regulations will likely favor bioengineered and synthetic products, providing new market opportunities for innovators.
Conclusion
The market dynamics for heparin sodium remain robust, underpinned by persistent clinical demand, demographic shifts, and technological innovations. However, supply chain vulnerabilities, regulatory pressures, and market competition from synthetic and oral alternatives pose challenges. Investment in bioengineering R&D and diversification of supply sources are essential strategies for sustaining growth. The financial trajectory indicates steady growth prospects, with key regions poised to lead expansion.
Key Takeaways
-
Sustainable Demand: Growing cardiovascular disease burden and surgical procedures ensure ongoing demand for heparin sodium, especially in hospital settings.
-
Supply Chain Resilience: Dependency on animal sources necessitates diversification strategies, including synthetic and recombinant heparin development.
-
Market Competition: Biosimilars and synthetic alternatives threaten traditional heparin revenue streams, prompting price competition and innovation.
-
Regulatory Environment: Enhanced oversight increases compliance costs but also opens avenues for bioengineered products aligned with safety standards.
-
Regional Growth Potential: Asia-Pacific's expanding healthcare infrastructure offers substantial future growth opportunities, complemented by technological advancements.
FAQs
1. How does the reliance on animal sources impact the supply and market stability of heparin sodium?
Dependence on porcine intestines introduces risks related to zoonotic diseases, supply shortages, and ethical concerns. Fluctuations in raw material availability and quality can disrupt supply chains, prompting the development of recombinant or synthetic alternatives to ensure stability.
2. What role do biosimilars play in the future of the heparin sodium market?
Biosimilars, identical or highly similar to branded heparin, offer cost advantages and expand access, especially in emerging markets. They intensify price competition, encouraging innovation while potentially threatening traditional sales.
3. Are synthetic or bioengineered heparin products effective substitutes for animal-derived heparin?
Emerging bioengineered heparins show promise, offering high purity and safety profiles. While research indicates comparable efficacy, regulatory approval and clinical acceptance are ongoing, with biotechnological products gradually entering the market.
4. How do regulatory standards influence the competitiveness of pharmaceutical companies in this market?
Strict regulatory standards raise entry barriers but ensure safety and quality, fostering trust and market stability. Companies investing in compliance and innovation can leverage regulatory advantages, gaining competitive positioning.
5. What strategic moves should pharmaceutical firms consider to capitalize on market trends?
Firms should focus on investing in bioengineering R&D, diversifying raw material sources, forming strategic alliances, and expanding into rapidly growing regions like Asia-Pacific. Embracing technological innovation and regulatory compliance is critical for sustainable growth.
References
[1] K. S. García et al., "Heparin: Pharmacology and Clinical Use," Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, vol. 18, no. 4, 2020.
[2] World Health Organization, "Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases," 2021.
[3] United Nations, "World Population Prospects 2022," 2022.
[4] S. Patel and R. Kumar, "Supply Chain Risks in Heparin Production," Manufacturing Science Insights, 2019.
[5] U.S. Food and Drug Administration, "Heparin Recall Information," 2008.
[6] T. Lee et al., "Recombinant Biosynthetic Heparin: A New Frontier," Biotechnology Advances, vol. 38, 2020.