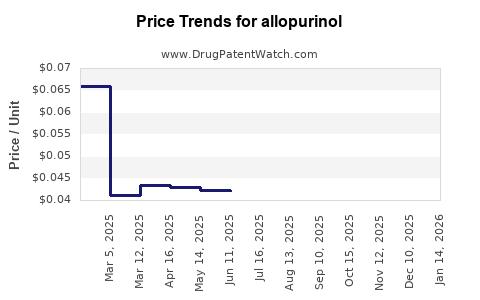
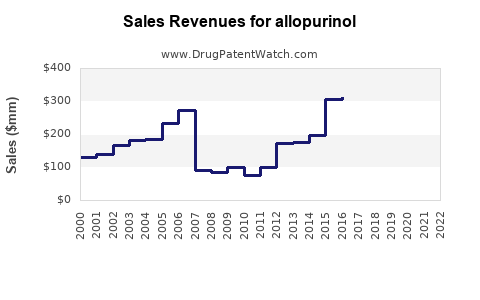
Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor primarily used to reduce uric acid levels in the treatment of gout and hyperuricemia, remains a cornerstone in the management of these conditions. Since its debut in the 1960s, allopurinol’s extensive clinical application has solidified its position within the pharmaceutical landscape. This analysis explores the current market dynamics and financial trajectory of allopurinol, driven by demographic trends, healthcare innovations, regulatory factors, and emerging competition.
Historical Context and Clinical Significance
Allopurinol was first introduced in 1966 by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and has since dominated the uric acid-lowering market due to its efficacy, safety profile, and affordability. It is prescribed predominantly for gout management, which affects approximately 4% of U.S. adults, with prevalence increasing among aging populations [1].
Its long-standing approval and generic availability position allopurinol as a low-cost, accessible medication globally. Despite newer agents like febuxostat and biologics targeting gout and hyperuricemia, allopurinol retains a significant market share owing to established clinical guidelines, extensive physician familiarity, and cost considerations.
Market Dynamics
Demand Drivers
-
Aging Population and Rising Gout Prevalence: The global increase in aging populations correlates with higher incidences of gout and hyperuricemia. The World Health Organization (WHO) expects the elderly segment (>60 years) to constitute over 20% of the population by 2050, propelling demand for uric acid-lowering therapies including allopurinol [2].
-
Chronic Disease Co-morbidities: Gout frequently coexists with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. As these comorbidities climb globally, so does the need for long-term management options like allopurinol.
-
Cost-effectiveness and Generic Status: Being off-patent, allopurinol's affordability ensures continued adoption, especially in developing nations where healthcare budgets are constrained.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing
Major players such as GSK, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Mylan manufacture allopurinol in generic forms, ensuring global supply stability. However, recent shortages arise from supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes, or manufacturing issues, impacting short-term availability.
Competitive Landscape
While allopurinol dominates, newer agents like febuxostat (approved in 2009) offer alternatives, especially for patients intolerant to allopurinol. However, febuxostat's higher cost and safety concerns—primarily cardiovascular risks highlighted in post-market studies—limit its widespread adoption [3].
Emerging therapies, such as uricases and monoclonal antibodies, are still under clinical evaluation, with limited impact on the immediate market. Yet, their development signals potential future shifts.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Allopurinol’s long history means a well-established safety profile; nonetheless, serious adverse reactions like allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome necessitate cautious prescribing. Regulatory agencies have issued recommendations to mitigate risks, but these do not significantly hamper market growth.
Financial Trajectory
Current Market Valuation
Estimates place the global allopurinol market at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2022, with steady growth projections of 3-5% annually. The Asia-Pacific region commands a sizable share, driven by large populations and increasing gout awareness.
Revenue Streams
- Generic Sales: Constitutes the bulk, due to low prices and widespread use.
- Brand Drugs: While original branded formulations like Zyloprim (GSK) still generate significant revenue, market share has diminished in favor of generics.
- Emerging Markets: Growth is accelerated in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, where affordable generics expand access.
Impact of Newer Agents
Despite competition, allopurinol’s financial trajectory remains positive. The cost advantage sustains its market presence, especially in price-sensitive markets. However, the potential market share loss to novel therapies with improved safety profiles could temper growth in the long term.
Future Outlook
- Market Expansion: Increasing clinical guidelines favoring uric acid control and expanding awareness suggest steady demand.
- Innovations and Formulation Improvements: Efforts to optimize bioavailability and reduce adverse events may enhance acceptance.
- Potential Disruption: Introduction of novel agents with superior efficacy and safety profiles could challenge market dominance, especially in high-income regions.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Safety concerns with certain formulations.
- Competition from newer, targeted therapies.
- Supply chain vulnerabilities affecting availability.
Opportunities:
- Expanding access in emerging markets.
- Developing combination therapies for enhanced efficacy.
- Leveraging digital health to optimize patient management.
Regulatory Landscape
Regulatory agencies maintain vigilant oversight to ensure safety. Recent guidelines aim to identify high-risk patients preemptively, not reducing allopurinol’s market but emphasizing safe prescribing practices.
Conclusion
Allopurinol’s market landscape is characterized by stability underscored by its proven efficacy, cost advantages, and entrenched clinical position. While innovative therapies threaten some market share, demand driven by demographic shifts and healthcare needs sustain its revenue. The future financial trajectory hinges on regulatory developments, safety management, and emerging therapies’ impact, with substantial growth potential in emerging economies.
Key Takeaways
- Allopurinol remains a dominant, cost-effective uric acid-lowering agent with a stable global market size (~USD 1.2 billion in 2022).
- Aging populations and increasing gout prevalence fuel demand, especially in Asia-Pacific and emerging markets.
- Competition from newer agents, safety concerns, and supply chain issues pose challenges but have limited immediate impact due to allopurinol’s affordability and clinician familiarity.
- Long-term growth prospects depend on expanding access, optimizing formulations, and monitoring developments in alternative therapies.
- Strategic focus on safety, manufacturing stability, and market penetration in developing nations will support sustained market presence.
FAQs
1. How does allopurinol compare economically to newer gout therapies?
Allopurinol's generic status renders it significantly more affordable—often costing a fraction of newer agents like febuxostat—making it the preferred option in cost-sensitive markets.
2. What safety concerns are associated with allopurinol?
Serious adverse reactions, including allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome, though rare, necessitate cautious prescribing and patient monitoring. Safety improvements focus on identifying at-risk populations.
3. What are the primary drivers of future demand for allopurinol?
Demographic aging, rising gout prevalence, and expanding healthcare access in developing regions will sustain demand, especially where cost-effective medications are prioritized.
4. How will emerging therapies influence allopurinol's market share?
While newer agents may attract specific patient subsets, allopurinol’s affordability and clinical familiarity ensure its continued prominence unless superior safety or efficacy profiles significantly shift prescribing patterns.
5. What regulatory trends could impact allopurinol’s market?
Ongoing safety evaluations and revised prescribing guidelines enhance patient safety but are unlikely to restrict access extensively; rather, they reinforce responsible use, maintaining market stability.
References
[1] Ryan, C. M. et al. (2015). Gout epidemiology and management: a review. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 16, 265.
[2] World Health Organization. (2018). Aging and health. WHO report.
[3] White, W. B. et al. (2018). Cardiovascular safety of febuxostat and allopurinol: a meta-analysis. Circulation, 138(13), 1339-1348.