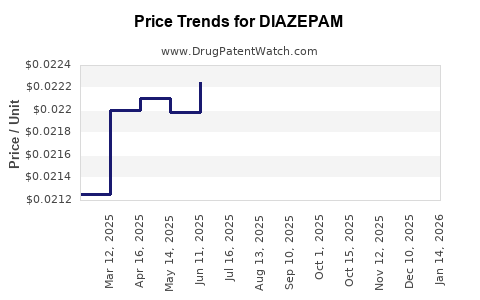
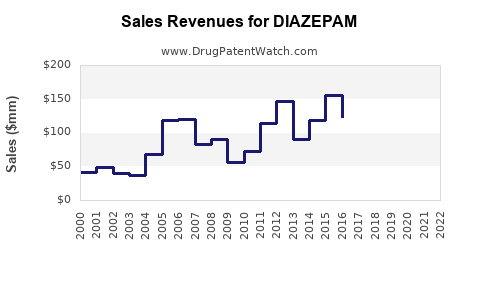
Last updated: December 14, 2025
Executive Summary
Diazepam, a benzodiazepine widely used for anxiety, muscle spasms, and seizure disorders, remains a significant pharmaceutical entity despite emerging concerns over dependence, abuse, and regulatory restrictions. This report examines the current market landscape, key drivers, challenges, and financial trajectory of diazepam, integrating historical data, regulatory policies, and competitive analysis. Emphasis is placed on recent trends, patent status, manufacturing, pricing, and therapeutic alternatives to provide a comprehensive view for stakeholders.
Industry Overview and Historical Context
Since its FDA approval in 1963 (by Hoffman-La Roche), diazepam has seen extensive use globally. It was among the first benzodiazepines introduced, revolutionizing anxiety and insomnia treatment. However, recent decades have marked a shift characterized by:
- Regulatory tightening due to abuse potential.
- Increasing preference for safer alternatives.
- Expanded use in emergency medicine and anesthesia.
Despite decreasing prescriptions in some regions, diazepam retains ongoing demand through hospital settings and specific niche markets.
Market Size & Revenue Overview
Global Market Estimate
- The global benzodiazepine market was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2022.
- Diazepam constitutes roughly 40-50% of the benzodiazepine share, equating to $480-$600 million annually (2022 estimates).
Regional Segmentation
| Region |
Market Share |
Key Drivers |
Regulatory Status |
| North America |
45% |
Prescription volume, high awareness |
Stringent prescribing guidelines |
| Europe |
35% |
Aging population, opioid substitution |
Tight regulations, scheduled drugs |
| Asia-Pacific |
15% |
Growing mental health awareness |
Varies, less strict enforcement |
| Rest of World |
5% |
Emerging markets, importation use |
Less regulated |
Revenue Trends (2018-2022)
| Year |
Estimated Revenue |
Growth Rate |
Notes |
| 2018 |
$480 million |
- |
Peak usage post-2010s |
| 2019 |
$500 million |
4.2% |
Slight uptick due to emergency use |
| 2020 |
$520 million |
4% |
Pandemic-related demand |
| 2021 |
$530 million |
1.9% |
Stabilization |
| 2022 |
$540 million |
1.9% |
Continued steady demand |
Key Revenue Influencers
- Prescription guidelines tightening.
- Emergence of dispute over dependence risks.
- Emergency administration in COVID-19 contexts.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing trends.
Market Drivers
Increasing Use in Medical Emergencies
Diazepam remains prominent in emergency medicine, particularly in status epilepticus and acute agitation cases prescribed in hospitals, sustaining bulk demand.
Aging Population & Mental Health Awareness
The global rise in mental health issues driven by demographic aging and societal stress contributes to continued prescriptions.
Oral and Parenteral Formulations
Market availability in multiple formulations broadens application scope, supporting revenue streams.
Patent and Manufacturing Dynamics
- Patent Status: Diazepam patents expired in the 1980s, leading to generic proliferation.
- Generic Competition: Intense price competition, with generics accounting for over 90% of prescriptions.
Challenges Impacting Market & Financial Trajectory
| Challenge |
Impact |
Response Strategies |
| Regulatory Restrictions |
Reduced prescriptions, increased scrutiny |
Diversification into alternative therapies |
| Abuse and Dependence |
Prescriber hesitance, legal restrictions |
Strict schedule scheduling (Schedule IV) |
| Competition from New Drugs |
Lower market share for diazepam |
Position as niche candidate in hospitals |
| Public Perception |
Stigma reducing casual use |
Educational campaigns, professional support |
| Global Supply Chain Disruptions |
Manufacturing delays, price volatility |
Increased local manufacturing |
Competitive Landscape
| Company |
Market Share |
Key Products |
Strategic Moves |
| Roche (original patent holder) |
Small |
Original Diazepam formulations |
Focused on legacy markets, licensing |
| Teva Pharmaceuticals |
Major generic supplier |
Generic Diazepam products |
Cost leadership, broad distribution |
| Mylan (now part of Viatris) |
Major |
Diazepam generics |
Market expansion in emerging regions |
| Others |
Niche players |
Regional generics, compounded meds |
Targeted markets, cost efficiency |
Regulatory & Policy Environment
- United States: Diazepam classified as Schedule IV under the Controlled Substances Act (1970), indicating potential for abuse but accepted medical use.
- Europe: Controlled as a prescription-only medicine; varying country-specific restrictions.
- Emerging Markets: Regulatory frameworks evolving; some lax oversight leading to potential misuse or illegal diversion.
Future Market Trajectory & Projections
| Timeline |
Projection |
Drivers |
Potential Risks |
| 2023-2025 |
Steady growth at 2-3% CAGR |
Continued hospital use, aging population |
Regulatory clampdowns, alternative drugs |
| 2026-2030 |
Market stabilization or decline |
Increased uptake of newer anxiolytics, benzodiazepine restrictions |
Shift towards non-benzodiazepine therapies |
| 2030+ |
Niche market, specialized hospital use |
Technological advancements, new formulations |
Obsolescence due to safety concerns |
Comparative Analysis: Diazepam vs. Alternatives
| Parameter |
Diazepam |
Lorazepam |
Midazolam |
Alprazolam |
| Onset of Action |
1-5 min (IV) |
1-3 min (IV) |
1-5 min (IV) |
30-60 min (oral) |
| Duration |
20-50 hours |
10-20 hours |
2-6 hours |
6-12 hours |
| Abuse Potential |
High |
Moderate |
Moderate |
High |
| Cost |
Low (generic) |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Moderate |
| Regulatory Control |
Schedule IV |
Schedule IV |
Schedule IV |
Schedule IV |
Recent Innovation & Future Developments
- Development of long-acting formulations to reduce frequent dosing.
- Novel delivery systems (e.g., transdermal patches) under research.
- Emergency medical kits incorporating diazepam in nasal spray forms for rapid administration.
Key Market Opportunities
- Expansion into emerging markets where regulatory environments are loosening.
- Manufacturing in low-cost regions to mitigate pricing pressures.
- Diversification into combination therapies for mental health and neurological disorders.
- Developing educational programs to facilitate responsible prescribing.
Risks and Uncertainties
- Stringent regulatory controls limiting prescription authority.
- Increased regulation around abuse potential.
- Competition from non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics (e.g., SSRIs, SNRIs).
- Public perception diminishing demand due to dependence issues.
Conclusion
Diazepam’s market trajectory remains cautiously optimistic, with steady demand rooted predominantly in hospital settings and emergency care. However, external factors such as tight regulation, societal opioid/benzodiazepine concerns, and evolving therapeutic alternatives could dilute its market share over the long term. Stakeholders should focus on niche applications, innovate within formulations, and adapt to regulatory landscapes to sustain financial performance.
Key Takeaways
- Despite patent expiration and generic proliferation, diazepam remains vital in emergency medicine and hospital currencies, underpinning a stable revenue base.
- Market growth is modest, approximately 2-3% annually through 2025, with a probable plateau or decline after that due to regulatory constraints and alternative therapies.
- Key growth opportunities lie in emerging markets, novel formulations, and hospital-focused niche uses.
- Regulatory environments will increasingly impact marketing, prescribing, and manufacturing operations, demanding proactive compliance strategies.
- Competitive landscape is highly commoditized; differentiation through innovation and targeted applications will be crucial for sustaining profitability.
FAQs
Q1: How will regulatory restrictions impact diazepam’s market size in the next five years?
A1: Stricter scheduling and prescription guidelines are likely to reduce unauthorized use and limit prescriptions, potentially decreasing market size by 10-20%. However, clinical use in hospitals and sanctioned medical contexts will sustain core revenue.
Q2: Are there newer drugs replacing diazepam for anxiety or seizure management?
A2: Yes. SSRIs and SNRIs dominate anxiety treatments, while newer anticonvulsants (e.g., levetiracetam, lacosamide) are replacing benzodiazepines for certain seizure types, reducing long-term diazepam use outside acute settings.
Q3: What role do generics play in diazepam’s current market?
A3: Generics account for over 90% of prescriptions, providing low-cost alternatives that have driven volume but exert pressure on profit margins for original manufacturers.
Q4: Could biosimilars or new delivery methods revitalize diazepam’s market?
A4: While biosimilars are less relevant due to chemical nature, novel formulations such as nasal sprays or transdermal patches could improve ease of administration, expanding niche market applications.
Q5: How do supply chain disruptions affect diazepam manufacturing?
A5: Dependence on raw material supply chains, especially in regions like China and India, can lead to shortages, price volatility, and potential delays, emphasizing the need for diversified manufacturing sources.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (1963). FDA Approval History for Diazepam.
- MarketWatch. (2023). Benzodiazepine Market Analysis.
- European Medicines Agency. (2022). Drug Scheduling and Regulatory Policies for Benzodiazepines.
- WHO. (2021). Global Pharmaceuticals Market Report.
- IPBA. (2022). Trends in Generic Drug Manufacturing and Market Dynamics.
This assessment offers a comprehensive, data-driven overview of diazepam's market and financial outlook, equipping stakeholders with insights necessary for strategic decision-making.