Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Timolol, a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker developed in the 1970s, remains a cornerstone in ophthalmology and cardiology. Its widespread adoption and established efficacy have secured its place in the pharmaceutical landscape. This analysis explores the evolving market dynamics surrounding Timolol, dissecting its competitive positioning, regulatory environment, patent status, and financial trajectory. Insight into these factors provides a comprehensive understanding of its current and future market viability.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Indications
Initially launched for hypertension and angina management, Timolol's primary therapeutic segment shifted significantly after its integration into ophthalmology for glaucoma treatment. Its topical formulation effectively reduces intraocular pressure (IOP), making it one of the first-line treatments for open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension (OHT) [1].
Market Size and Growth
The global ophthalmic drug market, including glaucoma therapies, is projected to reach USD 13.4 billion by 2027, with beta-blockers like Timolol constituting a significant segment [2]. Despite newer agents emerging, Timolol's affordability and proven track record sustain demand, especially in emerging markets where cost sensitivity prevails.
Competitive Landscape
The primary competitors against Timolol include prostaglandin analogs (e.g., Latanoprost), carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., Dorzolamide), and combination therapies. These alternatives often offer improved compliance profiles or fewer side effects. However, Timolol's cost-effectiveness keeps it relevant, particularly in low-income regions.
Market Dynamics
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
Timolol's original patents expired decades ago, leading to the proliferation of generic versions. Generics dominate sales, dramatically reducing prices and margins for brand-name manufacturers. Regulatory approvals for generic formulations facilitate broad accessibility but constrict potential for brand-specific differentiation. The absence of patent protection intensifies price competition, compelling firms to seek new formulations or indications to sustain revenue.
Reimbursement and Pricing Pressures
Healthcare systems globally are increasingly enforcing cost containment measures. In regions like the EU and North America, insurance reimbursements favor generic drugs, further squeezing profit margins for branded timolol products. The rise of value-based care models promotes alternative therapies perceived as more efficacious or better tolerated, influencing prescriber preferences.
Emerging Market Opportunities
In developing economies, the price sensitivity and large population base contribute to sustained demand for Timolol. Manufacturers focus on expanding access through partnerships with government health programs and local distributors. Consequently, volume-driven growth offsets declining profitability per unit.
Innovations and Pipeline Developments
While Timolol itself remains a mature product, ongoing research aims to improve delivery mechanisms—such as sustained-release implants, combination formulations, and glaucoma devices—to enhance patient compliance and safety profiles. The potential introduction of Timolol-based combination drugs (e.g., Timolol with prostaglandins) could revitalize market interest by capturing broader therapeutic benefits.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Streams and Profitability
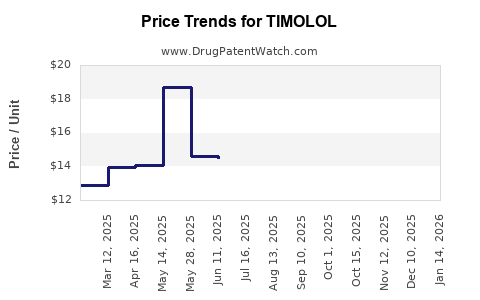
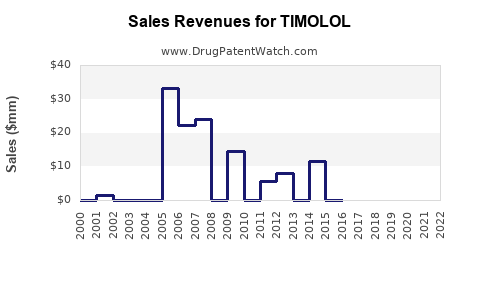
The generics' saturation significantly suppresses Timolol's pricing power. Market analyses indicate a decline in sales volumes of branded formulations, with global revenues falling from an estimated USD 500 million in the early 2000s to approximately USD 200 million in recent years [3].
Cost Dynamics
Manufacturing costs are relatively low for generic Timolol, but marketing and distribution expenses are vital for market penetration in competitive segments. R&D investments are minimal, primarily aimed at developing advanced delivery systems rather than new molecular entities.
Future Outlook and Revenue Forecasts
Projections suggest a continuing decline in global Timolol sales, driven by the competitive landscape and shifting prescriber preferences favoring newer therapies. However, stable demand persists in marginalized markets and for patients with established treatment regimens. The introduction of fixed-dose combinations may slow revenue erosion, with potential upside in niche segments.
Regulatory and Market Challenges
- Generic Competition: Intense price wars among generic manufacturers compress margins.
- Evolving Therapeutic Paradigms: Preference for prostaglandins with fewer systemic effects.
- Market Saturation: Limited scope for incremental revenue growth except through innovation.
- Reimbursement Policies: Cost containment measures restrict pricing strategies.
Opportunities for Strategic Growth
- Innovative Delivery Systems: Sustained-release formulations and ocular implants can command premium pricing.
- Fixed-Dose Combinations: Combining Timolol with agents like Latanoprost could capture unmet needs.
- Expanding Markets: Tailored strategies in emerging economies offer volume-based growth.
- Brand Differentiation: Focused marketing and clinical data could sustain brand loyalty amidst generic competition.
Key Takeaways
- Market Maturity: Timolol is a mature, commoditized product facing declining revenues due to patent expirations and competition from newer agents.
- Cost Advantage in Generics: Price competitiveness persists, especially in emerging markets, sustaining demand.
- Innovation as a Growth Driver: Delivery system enhancements and combination therapies offer avenues to revitalize the product’s market presence.
- Market Dynamics: Regulatory environments and reimbursement policies heavily influence profitability and strategic decisions.
- Long-term Outlook: While revenues are projected to decline, niche and emerging markets, alongside device-based formulations, could sustain a modest financial trajectory.
Conclusion
Timolol remains a vital component in glaucoma and cardiovascular treatments, yet its financial outlook is shaped by evolving market dynamics. Companies focusing on innovation, strategic market expansion, and product differentiation can mitigate revenue declines, ensuring continued relevance. Stakeholders must monitor regulatory shifts and technological advancements to adapt effectively. Ultimately, the role of Timolol in the therapeutic landscape will hinge on balancing its proven efficacy with the competitive pressures and economic realities shaping global healthcare.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration impacted Timolol’s market?
Patent expiration led to the proliferation of generic versions, resulting in significant price reductions and increased market penetration worldwide. While market share for branded versions declined, overall volume maintained demand, especially in cost-sensitive regions.
2. What are the main competitors to Timolol in glaucoma treatment?
Prostaglandin analogs, such as Latanoprost and Travoprost, are primary competitors due to their better compliance profiles and fewer systemic side effects. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and combination therapies also vie for market share.
3. Are there any innovations that could revitalize Timolol’s market?
Yes. Developing sustained-release implants, fixed-dose combination formulations, and ocular delivery devices can enhance compliance and efficacy, potentially generating new revenue streams.
4. How do reimbursement policies affect Timolol sales?
Reimbursement policies favoring cost-effective generics and strict cost-containment measures reduce net prices and profit margins, influencing manufacturers’ pricing strategies and market investments.
5. What is the future outlook for Timolol in the pharmaceutical industry?
While mature, Timolol retains enduring demand in certain markets. Its future depends on innovation, regulatory strategies, and market expansion initiatives. Niche applications and technological advancements will likely be central to its sustained presence.
Sources
[1] Wax, M. B. (2014). “Pharmacology and therapeutics of beta-adrenergic blockers in ophthalmology.” Current Opinion in Ophthalmology, 25(2), 119-124.
[2] Fortune Business Insights, “Global Ophthalmic Drugs Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, 2027,” 2021.
[3] IQVIA, “Global Ophthalmic Market Data,” 2022.