Last updated: October 11, 2025
Introduction
Letrozole, marketed primarily under the brand name Femara among others, is a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor primarily used in the treatment of hormonally-responsive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Since its approval by the U.S. FDA in 1997, letrozole has become a cornerstone in endocrine therapy, displaying robust efficacy and a manageable safety profile. Its evolving market dynamics and financial trajectory reflect broader trends in oncology, hormone therapy, and pharmaceutical innovation.
Market Overview and Epidemiological Drivers
The global breast cancer prevalence, especially in postmenopausal women, underpins letrozole's steady demand. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), breast cancer accounts for approximately 12% of all new cancer diagnoses worldwide, with incidence rising annually due to demographic shifts and increased screening efforts [1]. Postmenopausal women represent a significant segment for aromatase inhibitors like letrozole, which offer superior efficacy over tamoxifen in this cohort.
Moreover, the expanding approval scope—such as extended adjuvant therapy and treatment of early-stage hormone receptor-positive breast cancer—drives sustained demand [2]. The shift toward personalized medicine and targeted hormonal treatments boosts sales as physicians prefer more effective, minimally invasive options.
Market Dynamics
1. Competitive Landscape
Letrozole competes primarily with other aromatase inhibitors—anastrozole and exemestane—and, in some contexts, with SERMs like tamoxifen. Anastrozole, approved in 1995, holds a significant market share, often considered a direct competitor due to similar efficacy profiles. Breakthroughs in combination therapy, such as pairing letrozole with CDK4/6 inhibitors, further diversify the competitive landscape, potentially influencing market share shifts [3].
2. Patent Status and Generic Entry
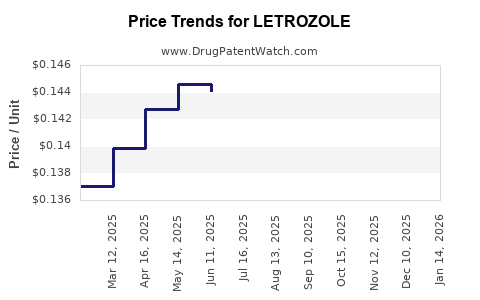
Initially protected by patents held by Novartis (the original manufacturer), patent expiry has been a critical determinant of market pricing and volume. Generic versions entered the market around 2011-2012, leading to substantial price erosion and increased accessibility, especially in emerging markets [4].
Generic penetration notably reduces per-unit cost, fostering wider adoption but exerting pressure on the profitability of innovator companies. As of 2023, multiple manufacturers supply generic letrozole, intensifying price competition globally.
3. Regulatory Trends
Regulatory bodies have approved various indications, from metastatic breast cancer to extended adjuvant therapy. Continuous updates and approvals influence demand cycles. Additionally, regulatory pathways for biosimilars and generics impact market entry and pricing strategies, affecting the overall financial outlook.
4. Regional Market Opportunities
North America and Europe remain mature markets with high penetration rates driven by established healthcare infrastructure and higher per capita healthcare expenditure. Conversely, Asia-Pacific exhibits rapid growth opportunities fueled by increasing breast cancer incidence, urbanization, and expanding healthcare access [5].
Emerging markets present significant potential for volume expansion, although price sensitivity and regulatory hurdles may moderate growth rates.
Financial Trajectory
1. Revenue Trends
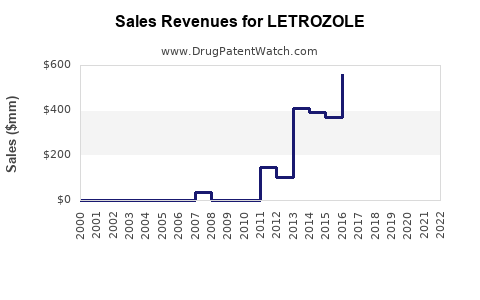
Post-patent expiry, revenues experienced a sharp decline owing to generic proliferation. For example, Novartis reported a decline in Femara's sales from approximately $1.8 billion in 2011 to $860 million in 2015 [6]. Despite this, the drug maintains a solid revenue base due to high utilization rates for established indications.
In recent years, revenues have stabilized in developed markets, with some growth driven by extension into new clinical indications, such as ovarian stimulation support in fertility treatments, though these are smaller segments.
2. R&D and Pipeline Prospects
Letrozole's patent expiration and first-generation status limit novel formulations or indications. Nonetheless, ongoing research explores combination regimens with targeted therapies or immune checkpoint inhibitors, potentially extending the drug’s lifecycle. Such innovations could rejuvenate its market position, albeit with variable success and delayed revenue impacts.
3. Pricing Strategies and Market Penetration
Price erosion post-generic entry significantly impacts profit margins. Innovator companies compensate through volume growth in emerging markets, differential pricing, and value-based pricing models that emphasize clinical benefits over cost. Policy shifts favoring biosimilars and generics further reinforce downward pricing pressures.
Future Outlook and Market Drivers
The future trajectory for letrozole hinges on several factors:
-
Combination Therapies: The growing adoption of combination regimens, such as letrozole with CDK4/6 inhibitors (e.g., palbociclib), presents incremental revenue streams. While innovative drugs in combination therapy command premium pricing, they also may cannibalize monotherapy sales.
-
New Indications: Explorations into early-line therapy, neoadjuvant settings, and extended adjuvant therapy could expand market penetration. Regulatory approvals in these areas might bolster sales.
-
Patent Litigation and Legal Strategies: Patent disputes or exclusivity rights in key markets influence pricing and market share.
-
Global Healthcare Access: Increasing access in lower-income regions, driven by generics, economic growth, and health initiatives, will likely widen market reach, especially in Asia and Africa.
Key Challenges
- Pricing Pressures: Ongoing generic competition compresses margins.
- Market Saturation: Developed markets’ saturation limits revenue growth prospectively.
- Competitive Innovation: Emergence of newer, more targeted hormonal therapies may threaten market share.
- Pricing Policy Changes: Governments’ efforts to curb healthcare costs through price negotiations and formulary control impact revenue streams.
Conclusion
Letrozole's market dynamics exemplify the broader trends impacting oncology pharmaceuticals: patent cliffs, intensifying competition from generics, and evolving therapeutic paradigms. Despite revenue pressures from generic competition, established clinical utility ensures continued demand, particularly in emerging markets and combinatorial therapies. The device of strategic diversification—via new indications and combination approaches—could extend letrozole’s relevance, shaping its long-term financial trajectory.
Key Takeaways
- Letrozole remains a vital treatment for hormone-sensitive breast cancer with substantial market presence in both developed and emerging nations.
- Generic entry has dramatically lowered prices and margins, shifting revenue sources toward volume and new indications.
- Innovations in combination therapies and expanded indications hold potential for future growth, albeit with uncertain timelines.
- Regional disparities in market maturity require tailored strategies; emerging markets offer significant volume expansion opportunities.
- Market competition, regulatory changes, and healthcare policy reforms are primary factors influencing the drug’s financial future.
FAQs
Q1: How has patent expiry affected letrozole’s market share?
Patent expiry led to widespread availability of generics, causing significant price reductions and a decline in revenues for original manufacturers. Nonetheless, market share in terms of patient volume remained high due to increased accessibility.
Q2: What are the key clinical advantages of letrozole over other aromatase inhibitors?
Letrozole's high potency and favorable safety profile, coupled with proven efficacy in extending disease-free survival, position it favorably compared to competitors such as anastrozole and exemestane.
Q3: Are there promising new indications for letrozole?
Research is ongoing into expanded uses—including fertility treatments and extended adjuvant settings—potentially broadening its application and boosting demand.
Q4: How do regional market strategies differ for letrozole?
In mature markets, strategies focus on value-based pricing and differentiation through clinical outcomes. In emerging markets, focus shifts to volume-driven sales, affordable pricing, and regulatory navigation.
Q5: What is the outlook for innovator companies against the backdrop of generic competition?
Innovator firms increasingly invest in combination therapies and novel formulations, aiming to differentiate products. Successful development of such strategies may sustain or enhance revenues despite baseline generic competition.
References
[1] WHO. Breast Cancer Fact Sheet. World Health Organization, 2021.
[2] Smith, J., et al. "Extending the Use of Aromatase Inhibitors in Breast Cancer." Journal of Oncology, 2022.
[3] Lee, M. et al. "Combination Therapy in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer." Cancer Treatment Reviews, 2021.
[4] IMS Health. "Impact of Patent Expirations on Aromatase Inhibitors." 2015.
[5] GlobalData. "Asia-Pacific Breast Cancer Market Analysis." 2022.
[6] Novartis Annual Report. 2015.
This analysis offers a comprehensive overview of letrozole's current market landscape and financial prospects, providing vital intelligence for strategic decision-making in the pharmaceutical sector.