Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Gabapentin, initially synthesized in the 1970s, has evolved from a seizure medication to a pivotal drug for neuropathic pain management. Its broad therapeutic applications, regulatory landscape, and patent status significantly influence its market dynamics and financial trajectory. This report provides an in-depth analysis of these factors, elucidating the current market position, growth drivers, challenges, and future outlook for gabapentin.
Historical Background and Patent Landscape
Gabapentin, branded as Neurontin by Pfizer, received FDA approval in 1993 for the adjunctive treatment of partial seizures in epilepsy. Subsequently, it gained off-label popularity for neuropathic pain, anxiety, and other neurological conditions. The expiration dates of key patents have critical implications for market competition; Pfizer’s primary patent expired around 2004-2005, leading to the proliferation of generic formulations. This patent expiry substantially increased market accessibility and pricing pressures, fostering intense generic competition and precipitating a market shift from branded to generic versions.
The patent landscape remains complex: Pfizer and other patent holders faced patent litigations and challenges, with some patents invalidated, facilitating generic entry. Notably, the loss of patent exclusivity resulted in a significant decline in retail prices and reshaped the revenue streams for manufacturers.
Market Size and Growth Drivers
Epidemiological Factors
Neuropathic pain, a primary indication of gabapentin, affects a substantial global population. According to the World Health Organization, up to 7-10% of the population suffer from neuropathic pain globally. The growing prevalence of conditions such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia propels demand [1]. These underlying health trends bolster gabapentin’s usage for off-label and approved indications.
Off-Label Usage and Unapproved Prescriptions
Despite regulatory limitations, off-label prescribing of gabapentin has been prolific. Physicians increasingly prescribed it off-label for conditions like anxiety and restless leg syndrome, expanding its market reach. However, recent regulatory restrictions and media scrutiny regarding off-label overuse have influenced prescribing patterns, with some payers delisting gabapentin off-label indications to curtail spending.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Policies
In several countries, regulatory agencies and insurance providers have tightened controls on off-label use. For instance, Medicare in the US limited coverage for off-label use, which could dampen potential revenue growth. Conversely, increasing recognition of neuropathic pain as a significant public health concern sustains demand for gabapentin and similar drugs.
Competitive Landscape
Generic competition has eroded the profit margins of branded formulations. As of 2022, multiple pharmaceutical companies produce generic gabapentin, significantly reducing wholesale and retail prices. The rivalry affects revenue streams, although some firms leverage brand loyalty and formulation innovation to retain market share.
Market Penetration and Therapeutic Alternatives
Gabapentin faces competition from newer therapeutic agents such as pregabalin, duloxetine, and capsaicin patches, which target similar indications. Pregabalin, a successor to gabapentin, enjoys patent protection (padvalin) until 2030 in many jurisdictions, providing a protected revenue stream until then. The therapeutic switch to these alternatives may influence gabapentin’s market share, especially where efficacy, side-effect profile, and dosing convenience favor newer agents.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Trends
Pre-Patent Expiry Period
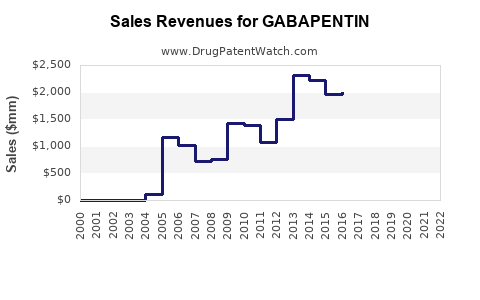
Before patent expiration, Pfizer’s gabapentin achieved peak revenues estimated at over $2 billion annually globally. The proprietary status enabled premium pricing and market control. The patent cliff around 2004-2005 precipitated a drastic revenue decline for branded formulations.
Post-Patent Era and Generics Impact
Post-expiry, prices plummeted—generics typically sell at 10-20% of patent-protected prices. The revenue share shifted predominantly to generic manufacturers, with Pfizer reporting a sharp decline in gabapentin-related revenues. However, total market volume remained robust due to ongoing demand, albeit with thinner margins.
Ongoing Revenue Streams
Current revenues derive primarily from generic sales and formulations that may include novel delivery systems or combination therapies. Some pharmaceutical firms manufacture branded gabapentin with improved bioavailability or extended-release formulations to sustain premium pricing and improve patient compliance.
Emerging Markets
Growing healthcare infrastructure and investments in pain management in emerging markets like China, India, and Brazil present significant revenue opportunities. These markets display increasing adoption of generics, supporting the global gabapentin market expansion.
COVID-19 Pandemic Impact
The pandemic affected supply chains and prescribing behaviors. While demand for pain management drugs remained stable or increased due to chronic pain prevalence, supply disruptions and regulatory delays temporarily impacted revenue flows.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Regulatory and Legal Challenges
Growing concerns over gabapentin’s off-label use and associated risks, such as misuse or dependency, have prompted regulatory responses, including classifying gabapentin as a controlled substance in certain jurisdictions. These measures restrict prescribing freedom and impact sales trajectories.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Risks
Supply chain disruptions, especially in active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), could lead to shortages, affecting revenue and market stability. Strategic stockpiling and diversified sourcing are critical for sustaining supply.
Innovation and Formulation Development
Developing novel formulations, such as extended-release or combination products, offers avenues for revenue enhancement and differentiation. Patent filings related to these innovations can provide temporary market exclusivity.
Competitive Strategies
Active engagement in clinical research to demonstrate superior efficacy or safety profiles could support branded product differentiation. Strategic partnerships and licensing opportunities may also expand market reach.
Future Outlook
The gabapentin market is characterized by a declining trend in branded revenues due to patent expirations and burgeoning generic competition. Nonetheless, the core demand driven by neuropathic pain persists, projected to sustain the market over the next decade. Growth prospects reside in emerging markets, formulation innovations, and cautious regulation management. The transition toward newer agents like pregabalin and gabapentin enacarbil may further influence market share dynamics.
In conclusion, the market is mature with steady demand but faces downward pricing pressures. Companies that innovate, diversify indications, and navigate regulatory landscapes effectively will capitalize on residual opportunities.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expiration dramatically diminished gabapentin’s revenue potential for original developers; generic proliferation led to market saturation and significant pricing erosion.
- The global burden of neuropathic pain sustains demand, although off-label prescribing and regulatory restrictions influence market growth.
- Competitive landscape shifting towards alternative therapies like pregabalin and duloxetine constrains gabapentin’s market share but opens avenues for formulation advancements.
- Emerging markets present growth opportunities owing to increasing healthcare access and high prevalence of neuropathic conditions.
- Innovation in drug formulations and strategic market positioning remain vital for revenue retention amid ongoing generic competition.
FAQs
Q1: How has patent expiration impacted gabapentin’s market revenues?
A: Patent expiration around 2004-2005 resulted in a surge of generic formulations, drastically reducing prices and leading to a sharp decline in revenues for branded manufacturers like Pfizer.
Q2: What are the primary drivers for current demand for gabapentin?
A: The main drivers include the global prevalence of neuropathic pain conditions, ongoing off-label uses, and the drug’s established efficacy and safety profile in managing specific neurological disorders.
Q3: How does competition from newer drugs affect gabapentin’s market share?
A: Newer agents such as pregabalin and duloxetine, offering improved efficacy, dosing, or tolerability, are gradually capturing market share, especially where patent protections apply, limiting gabapentin’s growth potential.
Q4: What regulatory risks does gabapentin face?
A: Increasing classification as a controlled substance in certain jurisdictions and restrictions on off-label prescribing can reduce usage, influence market dynamics, and impact revenues.
Q5: Are there upcoming innovations that could revive gabapentin’s market?
A: Development of extended-release formulations, combination therapies, or novel delivery systems could enhance its market appeal and provide patentable advantages, potentially revitalizing revenues.
References
[1] World Health Organization. (2021). Neuropathic Pain Prevalence and Impact. World Health Stats.