Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Gabapentin, a widely prescribed anticonvulsant and neuropathic pain agent, has experienced substantial market growth since its approval. Originally developed to treat epilepsy, gabapentin’s off-label uses—including neuropathic pain, restless leg syndrome, and anxiety disorders—have broadened its market scope. This analysis provides a comprehensive review of the current market landscape, future sales trajectories, and strategic factors influencing gabapentin's commercial performance.
Pharmacological Profile and Therapeutic Indications
Gabapentin operates by modulating calcium channels in the nervous system, thereby diminishing neuronal excitability. Its primary approved indications include:
- Epilepsy: Particularly as an adjunctive therapy.
- Neuropathic pain: Including diabetic peripheral neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia.
- Off-label uses: Anxiety, bipolar disorder, and sleep disorders, which contribute significantly to off-label sales.
The drug's safety profile, tolerability, and ease of administration have made it a preferred choice among neurologists and pain specialists worldwide.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Trends
The gabapentin market was valued at approximately $1.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% to 6% over the next five years. This growth is attributable to increasing prevalence of neuropathic pain and expanding off-label use, especially in regions with accessible healthcare infrastructure.
Regional Market Dynamics
- North America: Dominates the market (~$900 million, 56% in 2022). High prescribing rates, comprehensive healthcare coverage, and established guidelines support continued dominance.
- Europe: Significant market share (~$400 million), driven by aging populations and rising neuropathic conditions.
- Asia-Pacific: Fastest-growing segment (CAGR ~7%), due to expanding healthcare access, rising chronic disease burden, and increasing awareness of neuropathic pain management.
Market Drivers
- Rising prevalence of neuropathic pain: An estimated 7-10% of the global population suffers from neuropathic pain, a primary indication for gabapentin.
- Aging population: Older adults are more susceptible to chronic pain conditions.
- Off-label use proliferation: Growing acceptance of gabapentin for anxiety and mood disorders expands its user base.
- Generic availability: Patent expirations have led to widespread generic adoption, reducing costs and improving accessibility.
Market Challenges
- Regulatory scrutiny: Heightened concerns surrounding off-label use and abuse potential have prompted stricter prescribing guidelines in some jurisdictions.
- Competition: Other agents such as pregabalin (Lyrica) and newer neuromodulators are competing for market share.
- Safety concerns: Reports of misuse, dependency, and adverse events necessitate careful patient selection and monitoring.
Forecasting Sales Growth
Historical Sales Data
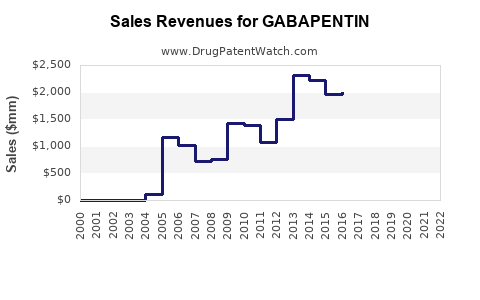
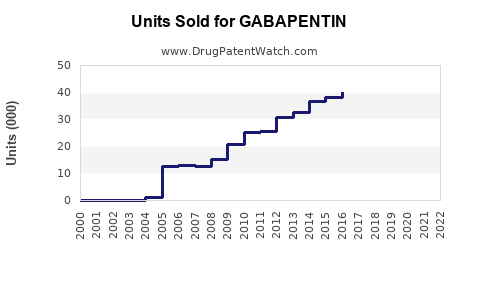
Analyzing recent trends, sales have increased consistently since the early 2000s. Post-2010, the growth has been particularly steady, with spikes linked to expanded indications and off-label prescriptions.
Future Projections (2023-2028)
- Baseline Scenario: Under current prescribing patterns and assuming steady growth, global sales are expected to reach $2.5 billion by 2028.
- Optimistic Scenario: Expanded off-label uses, increased awareness, and better access in emerging markets could push sales beyond $3 billion.
- Conservative Scenario: Regulatory restrictions and safety concerns could dampen growth, resulting in sales plateauing around $2 billion.
Key Factors Influencing Sales Projections
- FDA and EMA regulations: Stricter guidelines or withdrawal from certain indications may reduce off-label prescribing.
- Generic penetration: As patents expire (the original patent in the US expired in 2004), generics dominate the market, driving down prices but increasing volume.
- Emerging alternative therapies: Development of more targeted neuromodulators may cannibalize gabapentin sales.
- Healthcare policies: Insurance coverage plans influence prescription frequency.
Competitive Landscape
Major Market Participants
- Pfizer (Lyrica): A competitor with patent protection until recently, now facing generic erosion.
- Teva Pharmaceuticals: Major manufacturer of generic gabapentin formulations.
- Other Generic Manufacturers: Multiple companies supplying cost-effective options.
Market Entry Barriers
- Established manufacturing and distribution channels.
- Patent-based competitive advantages for branded formulations.
- Regulatory requirements for off-label promotional claims.
Strategic Opportunities
- Expanding indications: Clinical trials for new therapeutic areas could unlock additional revenue streams.
- Combination therapies: Developing fixed-dose combinations with other agents for neuropathic conditions.
- Emerging markets: Focused expansion into regions with rising chronic pain prevalence.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Recent FDA alerts about misuse and abuse have prompted manufacturers and healthcare providers to implement stricter controls. Strategies aligning with regulatory compliance and ethical prescribing are critical for sustained market access.
Key Market Drivers and Risks
| Drivers |
Risks |
| Rising neuropathic pain prevalence |
Regulatory restrictions on off-label use |
| Aging population demographic trends |
Competition from newer agents |
| Cost-effectiveness of generic formulations |
Safety concerns and potential litigation |
| Increasing awareness of neuropathic conditions |
Potential substitution by alternative therapies |
Key Takeaways
- Market potential remains strong due to increasing demand for neuropathic pain management and off-label uses.
- Generics dominate the landscape, offering affordability but limiting revenue growth for branded formulations.
- Regulatory environment will significantly influence future sales, particularly regarding off-label prescribing and safety concerns.
- Emerging markets present substantial growth opportunities, driven by rising healthcare infrastructure and chronic disease burdens.
- Innovation and clinical research are vital to expanding indications and maintaining competitive advantage amid patent expiries and market saturation.
FAQs
-
What is the main therapeutic use of gabapentin today?
Primarily, gabapentin is used for neurological conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain, with off-label prescriptions for anxiety and mood disorders.
-
How do patent expirations affect gabapentin sales?
The expiration of patent protection leads to the proliferation of lower-cost generics, which boosts volume but compresses margins for branded products.
-
Are there regulatory concerns impacting gabapentin's market?
Yes. Agencies have issued warnings about misuse and dependency, resulting in tighter prescribing guidelines and monitoring requirements.
-
What markets are expected to drive future growth?
North America and Europe continue to be mature markets, while Asia-Pacific and emerging economies are projected as high-growth regions.
-
What competitive strategies can manufacturers adopt?
Focusing on expanding clinical evidence, exploring new indications, and entering emerging markets can sustain and grow sales amid competitive pressures.
References
- Statista. (2022). Market size of gabapentin globally.
- MarketsandMarkets. (2022). Neuropathic pain treatment market analysis.
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). (2021). Safety Alerts for Gabapentin.
- IMS Health Data. (2022). Prescription trends for neuropathic pain medications.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). (2022). Regulatory updates on neuromodulators.