Last updated: October 14, 2025
Introduction
Atorvastatin calcium, marketed globally as Lipitor among other brand names, is a leading pharmaceutical agent in the cholesterol-lowering category. As a statin, it suppresses hepatic enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, reducing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and consequently lowering cardiovascular risk. Its broad therapeutic use, patent status, and market competition define its evolving financial landscape. This report examines the current market dynamics and financial trajectory of atorvastatin calcium, providing insights into factors influencing its growth, challenges, and future prospects.
Market Overview and Historical Context
Introduced in 1997 by Pfizer, Lipitor became the world's top-selling drug within a decade, achieving peak annual sales exceeding $12 billion globally (1). Its initial patent protection, expiring in various jurisdictions between 2011 and 2012, facilitated a significant generic market influx, leading to substantial price declines. Despite this patent expiration, atorvastatin remains prevalent due to its established efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness.
The global statin market is projected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5–7% until 2028, driven by increasing cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevalence, aging populations, and a rise in hyperlipidemia awareness (2). While generic versions account for a large market share due to lower prices, branded formulations continue to retain premium positioning in specific segments.
Market Dynamics
1. Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
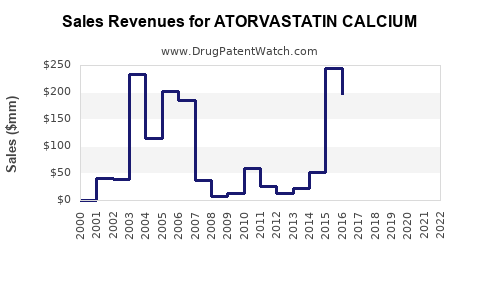
The expiry of Pfizer's patent significantly shifted the market landscape. Generic atorvastatin gained rapid market acceptance, leading to price erosion—some estimates suggest reductions of up to 80% compared to brand-name versions (3). The decline in revenue from Lipitor for Pfizer was profound. However, the widespread adoption of generics set the stage for increased accessibility, expanding treatment adherence among diverse populations.
2. Patent Litigation and Regulatory Strategies
To extend market dominance, Pfizer pursued patent litigation and market-specific regulatory strategies, which delayed generic entry in certain territories. The company also introduced fixed-dose combinations and formulations with improved bioavailability, aiming to retain some market share amidst generic competition (4).
3. Growing Cardiovascular Disease Burden
Globally, CVD remains the leading cause of death, accounting for approximately 32% of all deaths (5). As the prevalence surges—particularly in developing economies—demand for lipid-lowering agents, including atorvastatin, rises correspondingly. Increased awareness of hyperlipidemia management and preventative cardiology contributes positively to ongoing market relevance.
4. Emergence of Novel Lipid-Modifying Agents
The competitive landscape is now more sophisticated, with newer agents such as PCSK9 inhibitors (e.g., evolocumab, alirocumab) offering potent LDL reduction for high-risk populations. Although more expensive, these biologics impact atorvastatin’s market share among specific patient groups. Nonetheless, cost-effectiveness of generic atorvastatin sustains its role as first-line therapy.
5. Regulatory and Policy Influences
Healthcare policies favoring generic substitution, price controls, and value-based care influence market dynamics. Many governments promote generic prescribing, which diminishes revenue streams for branded formulations. Conversely, initiatives emphasizing comprehensive cardiovascular screening increase overall statin utilization.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
1. Revenue Patterns Post-Patent Expiry
Pfizer’s revenues from Lipitor experienced a sharp decline post-2011, with the company's global statin revenues dropping by over 70%. Despite this, the drug's global sales persisted in the form of generics, with global markets generating billions annually from combined generic sales—estimates place the generic atorvastatin market at around $3–4 billion in 2022 (6).
2. Key Market Segments
-
Developed Markets: The U.S. and Europe exhibit high statin penetration, with generics constituting over 80% of prescriptions. Price pressures persist, but high-volume usage sustains profitability.
-
Emerging Markets: Rapid urbanization, increased health awareness, and growing CVD prevalence boost atorvastatin demand. Price sensitivity is high, favoring generics.
3. Future Growth Opportunities
Despite intense competition, the market for atorvastatin remains viable, driven by:
-
Expanded Indications: Use in primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular events sustains increased demand.
-
Formulation Innovations: Fixed-dose combinations with antihypertensives and novel delivery methods can command premium pricing.
-
Partnerships and Licensing: Strategic alliances with local manufacturing and distribution entities facilitate market penetration in developing regions.
4. Financial Outlook (Next Decade)
Market forecasts project modest growth (CAGR of 3–4%), compounded by generics’ price erosion but offset by volume increases. The sustained global burden of CVD, coupled with drug affordability and new formulations, supports a steady revenue stream. Pfizer and other manufacturers are diversifying portfolios through development of lipid-modifying agents to complement or replace atorvastatin in specific niches.
Challenges and Risks
-
Market Saturation: Extensive generic penetration limits premium pricing.
-
Emergence of Alternatives: Costlier biologics and novel oral agents threaten market share in high-risk segments.
-
Regulatory Hurdles: Stringent approval processes for biosimilars and generics influence market access timelines and profitability.
-
Pricing and Reimbursement Policies: Public and private payers crystallize drug reimbursement strategies, influencing pricing and sales volumes.
-
Patent Litigation and Market Exclusivity: Shifts toward patent challenges threaten future proprietary advantages.
Conclusion
Atorvastatin calcium's market is characterized by significant post-patent competition, declining brand revenues, and expanding volume-driven sales in emerging markets. Its pivotal role in cardiovascular risk management sustains steady demand, despite competitive pressures from newer agents and biosimilars. The pharmaceutical industry will need to innovate formulationally, strategically align with healthcare policies, and expand into new therapeutic niches to optimize financial outcomes over the next decade.
Key Takeaways
- The patent expiration of atorvastatin led to a substantial decline in branded sales but expanded access through generics, enabling sustained global volume growth.
- The ongoing rise in cardiovascular disease prevalence, especially in emerging markets, underpins the drug's long-term demand.
- Generics account for the majority of atorvastatin sales, with price erosion remaining a significant financial challenge.
- The emergence of novel lipid-lowering drugs introduces competition, particularly for high-risk patient segments.
- Strategic portfolio diversification and formulation innovation are critical for maximizing future financial returns.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiry affected atorvastatin’s revenue?
Patent loss caused a sharp decline in Pfizer’s Lipitor revenues, with generic competition reducing prices by up to 80%. However, global demand persists through generics, maintaining steady sales volumes.
2. What are the primary factors driving atorvastatin’s market growth?
Increasing global prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors, expanding use in primary prevention, and rising health awareness are key drivers, especially in emerging markets.
3. How do biosimilars and new lipid drugs impact atorvastatin’s market?
While biosimilars pertain mainly to biologics, newer oral agents like PCSK9 inhibitors target high-risk populations. They compete mainly in niche segments but do not significantly displace atorvastatin as a first-line therapy due to cost considerations.
4. What opportunities exist for pharmaceutical companies regarding atorvastatin?
Formulation enhancements, combination therapies, and strategic expansion into underserved markets offer avenues for revenue growth.
5. What is the outlook for atorvastatin’s financial performance over the next decade?
Steady volume growth in developing regions, coupled with intense price competition, will likely result in modest revenue increases. Innovation and strategic market positioning are essential to sustain profitability.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Lipitor (atorvastatin calcium) Prescribing Information. 2022.
- MarketsandMarkets. Statin Market by Type, Application, and Region – Global Forecast to 2028. 2022.
- IMS Health. Global Pharmaceutical Market Data. 2022.
- Pfizer Annual Reports. 2011-2021.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Cardiovascular Diseases Fact Sheet. 2022.
- EvaluatePharma. World Review of Drugs for Lipid Management. 2022.