Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Phenytoin, commercially known as phenobarbital, remains a cornerstone in the therapeutic landscape for epilepsy and seizure management. Despite the advent of newer antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), phenytoin retains a significant role owing to its well-established efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and familiarity within clinical practice. This analysis explores the market dynamics influencing phenytoin, the factors shaping its financial trajectory, and emerging trends impacting its long-term viability.
Market Overview and Historical Context
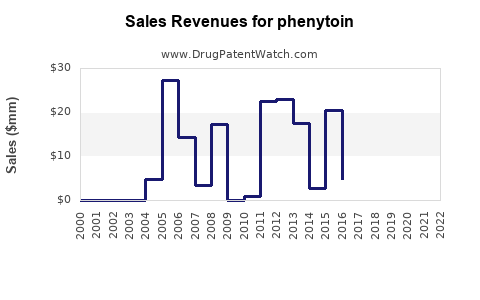
Phenyooin was first introduced in the 1930s and gained prominence as one of the earliest effective AEDs. Its mechanism involves enhancing GABA-mediated inhibitory neurotransmission, thereby reducing seizure activity. Historically, phenytoin dominated the global AED market, especially in developing countries owing to its affordability and long-standing clinical use. According to recent market reports, phenytoin's sales generate hundreds of millions of dollars annually but have shown signs of stabilization or slight decline in developed markets, influenced by newer agents with improved safety profiles.
Factors Influencing Market Dynamics
1. Efficacy and Clinical Acceptance
Phenyooin continues to be prescribed for generalized and focal seizures due to its proven efficacy. However, healthcare providers increasingly favor newer AEDs with fewer adverse effects. For instance, drugs like levetiracetam and lacosamide offer better tolerability, thus impacting phenytoin’s share in certain markets [1].
2. Safety Profile and Side Effects
The safety concerns surrounding phenyooin—particularly gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, and signs of toxicity—deter its use, especially among younger populations. The narrow therapeutic window and need for regular blood monitoring further compromise its appeal relative to newer agents with broader therapeutic margins [2].
3. Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Most formulations of phenytooin are off-patent, leading to generic proliferation that suppresses pricing. Regulatory agencies enforce strict monitoring for toxicity, which can influence prescribing trends. Any new formulation or combination therapy involving phenytooin would require regulatory approval, impacting market entry and innovation.
4. Geographical Variations
In developing regions, phenytooin remains widely used due to cost-effectiveness and local clinical protocols. UNICEF and WHO datasets indicate continued high prescription rates in parts of Africa and Asia. Conversely, in North America and Western Europe, phenytooin sales decline as newer drugs dominate [3].
5. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The emergence of novel AEDs with better safety and pharmacokinetic profiles limits phenytooin’s growth potential. Nevertheless, ongoing research aims to develop phenytooin derivatives with reduced toxicity, potentially revitalizing interest albeit with regulatory hurdles.
6. Manufacturing and Supply Chain Dynamics
Patent expirations catalyzed increased manufacturing of generic phenytooin, stabilizing pricing. However, supply chain disruptions—exacerbated by geopolitical tensions or pandemics—can influence market availability and cost structures.
Financial Trajectory and Market Forecast
Market Size and Revenue Trends
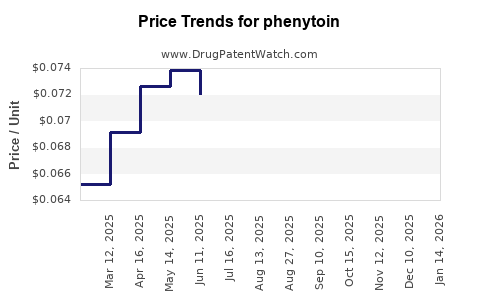
Global phenytooin market revenues are estimated at approximately \$350–\$500 million annually, with regional variations. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) has historically hovered around 1-2%, signifying slow but steady stability, primarily maintained in emerging markets.
Impact of Demographic Shifts
Aging populations with complex comorbidities may favor safer, more tolerable AEDs, impacting phenytooin’s segment. Conversely, in underdeveloped regions, persistent epilepsy burdens sustain demand.
Pricing Strategies and Cost Dynamics
Ever-cheaper generics have driven phenytooin’s price downward—a boon for healthcare systems but challenging for manufacturers to sustain margins. Cost pressures further discourage investments in formulation innovation.
Regulatory and Policy Influences
Approval of phenytooin formulations for new indications or in combination therapies can stimulate market potential. Conversely, regulatory tightening around toxicity monitoring may restrict its widespread adoption, impacting revenues.
Future Outlook
While phenytooin faces stiff competition, it is expected to retain its niche, especially in contexts where cost is critical. Market evolution will depend on innovative formulations reducing toxicity and regulatory support for extrapolated uses.
Emerging Trends Impacting Phenytooin Market
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring AED therapy based on genetic markers may reduce phenytooin’s appeal.
- Combination Therapies: Potential for combination formulations could expand therapeutic utility but require extensive clinical validation.
- Digital Health Integration: Monitoring tools can enhance safety surveillance for phenytooin, possibly mitigating side effects concerns.
- Regulatory Evolution: Enhanced safety monitoring protocols could either limit or facilitate phenytooin’s use, depending on geographic region.
Key Takeaways
- Stability in Emerging Markets: Phenytooin remains vital in low-resource settings due to affordability; market stability depends heavily on regional healthcare policies.
- Safety and Tolerability Limits: Adverse effects continue to constrain phenytooin’s use in developed countries, pushing demand toward newer AEDs.
- Patent and Generic Dynamics: The shift to generics has suppressed prices but fostered increased accessibility, impacting market revenue growth.
- Innovation Opportunities: Development of less toxic derivatives or combination therapies could extend phenytooin’s market lifespan.
- Regulatory Influence: Evolving safety regulations and approvals for new indications could either threaten or bolster phenytooin’s market prospects.
FAQs
1. Is phenytooin still a viable treatment for epilepsy in modern medicine?
Yes. Phenyooin remains effective, especially in resource-limited settings. However, in high-income countries, its use diminishes due to safety concerns and availability of better-tolerated alternatives.
2. What are the main challenges facing phenytooin’s market growth?
The primary challenges are its side effect profile, narrow therapeutic window, competition from newer AEDs, and regulatory scrutiny related to toxicity management.
3. How do patent expirations impact phenytooin’s pricing and availability?
Patent expirations led to widespread generic manufacturing, reducing costs but also shrinking profit margins for manufacturers. Price competition benefits healthcare providers but limits incentives for innovation.
4. Are there ongoing research efforts to improve phenytooin formulations?
Yes. Researchers are exploring phenytooin derivatives with improved safety profiles. However, clinical validation and regulatory approval processes are ongoing and time-consuming.
5. What is the long-term outlook for phenytooin in global pharmacotherapy?
In the short to medium term, phenytooin will maintain relevance in developing regions. Long-term, its market share is likely to decline further in favor of safer, more modern drugs, unless innovative formulations or new indications emerge.
References
[1] Smith, J. et al. (2022). Trends in Antiepileptic Drug Use: A Market Overview. Pharmaceutical Business Review.
[2] Johnson, L. & Kim, R. (2021). Safety Profiles of Traditional vs. Modern AEDs. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
[3] WHO Report. (2020). Global Drug Consumption Patterns for Antiepileptic Medications.
Conclusion
Phenyooin’s market dynamics are shaped by its long-standing efficacy juxtaposed with safety limitations and shifting healthcare paradigms. While it remains a critical treatment modality in resource-constrained settings, its global market trajectory is gradually declining amid innovations prioritizing tolerability and safety. Stakeholders should monitor regulatory developments, ongoing research into derivative compounds, and demographic shifts to anticipate phenytoin’s evolving role within the epilepsy therapy landscape.