Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Phenytoin, a longstanding antiepileptic drug, remains a mainstay in seizure management despite the advent of newer therapies. As a generic medication with widespread clinical use, its market dynamics are influenced heavily by patent expirations, manufacturing capacity, regulatory landscape, and competitive pressures. This report offers a comprehensive analysis of the current market status and provides price projections grounded in industry trends and influencing factors.
Market Overview
Phenytoin is primarily indicated for tonic-clonic and focal seizures. Its formulation exists in multiple forms: oral capsules, injectable solutions, and suspensions. The drug has remained largely on the market since its initial approval in the 1930s, with the original patent expiring decades ago. The current market is characterized by generic dominance, with few branded variants, notably Dilantin.
Global Demand and Usage Trends
The global epilepsy market is projected to reach $6.5 billion by 2027, with phenytoin accounting for approximately 15-20% of the antiepileptic medication market, especially in regions with limited access to newer drugs. The prevalence of epilepsy is stable, estimated at around 50 million cases worldwide, with a significant proportion of patients relying on phenytoin due to affordability and longstanding clinical familiarity.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Dynamics
Major pharmaceutical manufacturers such as Teva, Mylan (now part of Viatris), and Sandoz produce high-quality generics. Manufacturing capacity, raw material procurement, and regulatory compliance influence supply stability and, consequently, pricing. The supply chain is relatively mature, with few significant barriers, ensuring consistent availability in developed markets.
Regulatory Landscape
Phenytoin’s status as a generic diminishes the influence of patent protections. However, recent regulatory developments, including quality standards and biosimilar considerations, can impact market presence. International regulatory agencies continue to prioritize drug quality, affecting manufacturing costs and pricing.
Competitive Dynamics and Market Share
The market exhibits intense price competition among generic manufacturers, leading to historical price erosion. The proliferation of generic producers has driven prices downward, especially in North America and Europe. In emerging markets, pricing remains higher due to limited competition and less stringent regulatory environments.
Notably, the introduction of branded formulations, like Dilantin, maintains a premium segment for patients requiring specific formulations or brand trust.
Price Analysis and Historical Trends
Past Price Trends
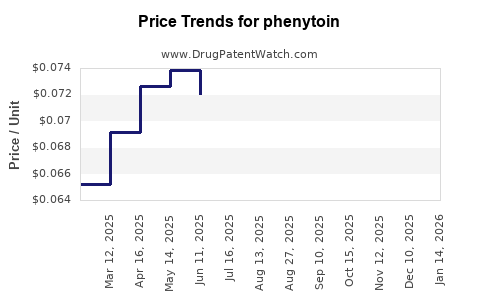
Historical data indicate a significant decline in phenytoin prices over the past decade. For example, in the United States, the average wholesale price (AWP) for phenytoin capsules decreased approximately 80% from 2010 to 2022, reflecting generic market saturation and increased competition.
Current Pricing
- United States: The retail price of a 100-count bottle of phenytoin capsules (initial dose: 100 mg) averages around $20-$30, down from over $150 a decade ago.
- Europe: Prices vary widely but generally follow similar downward trends, with pharmacy retail prices often below €20 per package.
- Emerging Markets: Prices remain higher, often between $10–$50 per bottle, depending on local regulations and market conditions.
Pricing Drivers
Key drivers include:
- Generic Competition: Multiple manufacturers reduce prices through competitive bidding.
- Regulatory Approvals: Faster approval pathways for generics facilitate market entry, intensifying price competition.
- Manufacturing Costs: Marginal for generic APIs, though quality standards influence compliance costs.
- Market Demand: Steady demand sustains revenues but limits pricing power due to external competition.
Price Projections to 2030
Short-term Outlook (2023–2025)
Given mature competition and a stable demand profile, prices are expected to stabilize at current levels within developed markets. Slight fluctuations may occur due to supply chain dynamics—e.g., raw material availability, geopolitical factors—and regulatory updates. Price erosion trends observed from 2010 to 2022 are unlikely to persist further in mature markets, though occasional price reductions may occur due to new entrants or manufacturing efficiencies.
Long-term Outlook (2026–2030)
- Price Stabilization: In major markets such as the US and EU, prices are projected to remain largely stable or experience marginal declines (1-3% annually).
- Emerging Markets: Price reductions could accelerate due to increased competition and regulatory harmonization, potentially declining 2-4% annually.
- Supply Chain Stability and Quality Standards: Maintaining high-quality manufacturing will be pivotal; new quality requirements could marginally increase costs, limiting downward price trends.
Influence of Biosimilar and Alternative Therapies
While biosimilar entry is not directly applicable (as phenytoin is a small-molecule drug), the introduction of novel antiseizure agents (e.g., brivaracetam, lacosamide) may influence demand dynamics, particularly in regions where newer drugs are preferred, potentially exerting downward pressure on phenytoin pricing.
Policy and Market Factors
- Pricing Regulations: Governments considering price controls or reimbursement policies may suppress prices further.
- Generic Market Entry Barriers: Patents/new formulations could temporarily raise prices but are unlikely to significantly disrupt the broader trend of price erosion.
Summarized Price Projection Table (USD)
| Year |
Developed Markets |
Emerging Markets |
| 2023 |
$20–$30 |
$10–$50 |
| 2025 |
$20–$30 |
$9–$45 |
| 2030 |
$19–$28 |
$8–$40 |
Based on current trends, with potential for minor deviations.