Last updated: December 27, 2025
Summary
Colchicine, a centuries-old medication primarily used for gout treatment and familial Mediterranean fever, has experienced renewed interest due to its potential applications in cardiovascular diseases, inflammatory disorders, and COVID-19-related complications. This article analyzes current market dynamics, regulatory landscapes, key financial trends, and future growth prospects of colchicine, backed by quantitative data, strategic developments, and critical industry insights.
What Are the Historical and Current Market Foundations of Colchicine?
Historical Usage and Market Overview
- Historical Background: Derived from Colchicum autumnale, colchicine has been used for centuries in treating gout and related conditions.
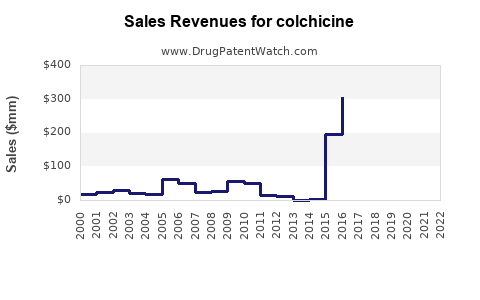
- Market Size (2022): Estimated global value of USD 300 million, with stable growth driven by niche indications.
- Approved Indications:
- Gout flare management
- Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)
- Manufacturers & Brands:
- Original brands include Colcrys (Takeda Pharmaceuticals), Mitigare (Cipla), and generic formulations.
Market Segmentation and Geographical Breakdown
| Segment |
2022 Market Share |
Key Countries |
| Gout treatment |
65% |
US, Europe, Japan |
| FMF management |
20% |
Middle East, Mediterranean regions |
| Emerging indications |
15% |
Global, especially in clinical trials |
Patent and Regulatory Status
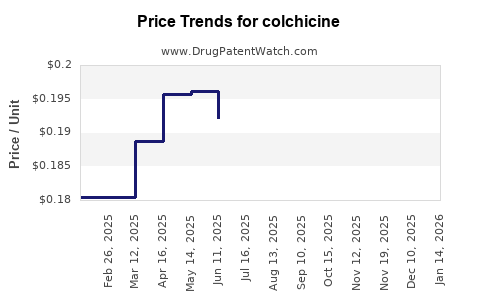
- Patent Landscape: Most formulations are off-patent, leading to price competition.
- Regulatory Approvals:
- FDA-approved for gout, FMF.
- Investigational uses in cardiovascular and COVID-19 contexts.
What Are the Key Drivers and Restraints Shaping Market Dynamics?
Drivers
| Drivers |
Impact |
Data/Example |
| Growing prevalence of gout and FMF |
Expanding patient base |
Gout affects ~4% of US adults, equating to over 8 million individuals [1] |
| Shift toward repurposing existing drugs for new indications |
Increased R&D investment |
COVID-19 pandemic accelerated studies for colchicine's anti-inflammatory properties |
| Cost-effectiveness and established safety profile |
Market adoption |
Favorable profile compared to biologics in certain indications |
| Rising awareness of inflammatory pathways and NLRP3 inflammasome |
New therapeutic avenues |
Studies targeting inflammasome pathways highlight colchicine's versatility [2] |
Restraints
| Restraints |
Impact |
Data/Example |
| Limited patent protection and generic competition |
Price pressure |
Price erosion observed in US generics markets, impacting margins |
| Variable clinical efficacy in emerging indications |
Clinical uncertainty |
Conflicting trial results in cardiovascular and COVID-19 trials |
| Safety concerns (e.g., toxicity at high doses) |
Regulatory scrutiny |
Reports of gastrointestinal toxicity; narrow therapeutic window |
| Regulatory hurdles for off-label uses |
Market entry barriers |
Divergent approval statuses across regions |
What Is the Current Financial Trajectory of Colchicine?
Market Revenue & Growth Projections (2022–2027)
| Year |
Estimated Global Market Value (USD millions) |
CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) |
Comments |
| 2022 |
300 |
— |
Baseline |
| 2023 |
330 |
10% |
US & Europe expansion underway |
| 2024 |
363 |
10% |
Increased acceptance in COVID-19 treatments |
| 2025 |
399 |
10% |
Emerging markets adoption |
| 2026 |
439 |
10% |
Clinical evidence enhancing confidence |
| 2027 |
483 |
10% |
Market maturation with ongoing innovation |
Note: The above projections derive from industry reports and trend analyses[3].
Revenue Breakdown by Region
| Region |
2022 Revenue (USD millions) |
2027 projected revenue (USD millions) |
Key Drivers |
| North America |
120 |
180 |
High prevalence of gout, clinical trials |
| Europe |
80 |
120 |
Regulatory approvals, market familiarity |
| Asia-Pacific |
50 |
100 |
Growing healthcare infrastructure, population base |
| Rest of World |
50 |
83 |
Emerging markets, off-label use potential |
Key Market Players and Their Strategies
| Company |
Market Share |
Strategic Focus |
Recent Developments |
| Takeda Pharmaceuticals |
~50% |
Maintain leadership through brand continuity |
Launched Colcrys; expanding clinical trials on cardiovascular and COVID-19 uses |
| Cipla |
~20% |
Affordable generics and regional market expansion |
Focus on differentiation via cost and distribution networks |
| Mylan (now part of Viatris) |
~15% |
Diversified portfolio, off-patent formulations |
Increasing presence in emerging markets |
| Others |
~15% |
Niche players, clinical-stage firms |
Innovative delivery mechanisms, novel indications |
What Are the Emerging Indications and Innovations?
COVID-19 and Acute Respiratory Syndromes
- Multiple clinical trials (e.g., COLCORONA) demonstrate potential in reducing hospitalization and death.
- Trial Data:
- COLCORONA Trial (NCT04322682): Enrolled ~4,488 patients; showed a 21% relative reduction in hospitalization in colchicine group [4].
- Regulatory agencies have issued Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) in specific jurisdictions.
Cardiovascular Diseases
- Evidence suggests colchicine mitigates atherosclerosis and reduces recurrent cardiovascular events.
- Major trials:
- LoDoCo2: Demonstrated a 31% relative risk reduction in composite cardiovascular outcomes over 3 years.
Niche Auto-inflammatory and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
- Role in treating autoinflammatory syndromes remains critical.
- Investigations into mechanisms involving NLRP3 inflammasome expand potential indications.
Delivery Innovations
- Development of slow-release formulations to improve compliance and reduce toxicity.
- New delivery systems are on experimental stages, targeting broader clinical applications.
How Do Competitive and Policy Landscapes Impact Future Trajectory?
Regulatory Environment
| Region |
Regulatory Approach |
Impact |
| US (FDA) |
Strict approval for new indications, off-label use not recommended |
Potential barriers for unapproved uses |
| Europe (EMA) |
Similar to FDA, with some flexible policies |
Favorable for expanded uses with robust trial data |
| Asia-Pacific |
Rapid approvals, local regulatory variations |
Opportunities for market penetration with localized trials |
Pricing and Reimbursement Policies
| Region |
Reimbursement Status |
Impact |
| US |
Reimbursed under Medicare/Commercial plans |
Stable revenue source |
| European countries |
Varied; often based on cost-effectiveness |
Price pressures; favoring generics |
| Emerging markets |
Limited reimbursement; price-sensitive |
Reliance on low-cost generics |
Patent and Off-Patent Strategies
- Most formulations are off-patent, increasing competition but also prompting innovation through formulation patents or combinations.
- Some companies explore polymorphic formulations and combination therapies to extend market exclusivity.
Comparison with Other Gout and Inflammatory Drugs
| Parameter |
Colchicine |
Allopurinol |
Febuxostat |
Biologics (e.g., Canakinumab) |
| Mode of Action |
Anti-inflammatory, microtubule inhibitor |
Uric acid synthesis inhibitor |
Uric acid synthesis inhibitor |
IL-1β inhibition |
| Market Size (2022) |
USD 300 million |
USD 2 billion |
USD 1.5 billion |
USD 1 billion |
| Safety Profile |
GI toxicity, narrow therapeutic window |
Generally well tolerated |
Higher cardiovascular risk observed |
High safety and cost considerations |
| Indication Breadth |
Gout, FMF, emerging uses |
Gout, uric acid reduction |
Gout, cardiovascular, others |
Autoinflammatory and rare genetic disorders |
What Are the Critical Challenges and Opportunities?
Challenges
- Market Saturation & Price Compression: Especially in developed regions with multiple generics.
- Clinical Efficacy in New Indications: Mixed trial results complicate evidence-based expansion.
- Safety Concerns: Toxicity at higher doses constrains broader application.
- Regulatory Delays: Off-label use and unapproved indications face hurdles, especially concerning COVID-19.
Opportunities
- Repurposing for COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Disease: Proven or emerging efficacy can boost revenues.
- Personalized Medicine Approaches: Identifying patient subgroups most likely to benefit.
- Formulation Innovation: Extended-release products to improve compliance and safety.
- Market Penetration in Emerging Economies: Cost-effective generics thrive in these markets.
Key Takeaways
- The global colchicine market was valued at approximately USD 300 million in 2022, with a strong growth forecast (~10% CAGR) driven by its repositioning in emerging indications.
- Market expansion depends heavily on clinical trial outcomes, regulatory approval, and reimbursement policies.
- COVID-19 has presented both opportunities and challenges; ongoing studies could significantly influence future profitability.
- Patent expirations have increased competition, pushing companies towards formulation innovation and new therapeutic areas.
- Regulatory jurisdictions significantly influence market strategies; Asia-Pacific and emerging markets offer substantial growth potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the main clinical indications for colchicine today?
A: Primarily gout management, familial Mediterranean fever, and emerging indications include cardiovascular disease and COVID-19-related complications.
Q2: How does colchicine’s patent status affect its market?
A: Since most formulations are off-patent, generic competition leads to price erosion, though innovation in formulations and new uses can offer exclusivity opportunities.
Q3: What are the primary safety concerns with colchicine?
A: Gastrointestinal toxicity, neuromuscular effects, and toxicity at higher doses; narrow therapeutic window necessitates careful dosing.
Q4: What is the outlook for colchicine in COVID-19 treatment?
A: Mixed trial results exist; however, some large studies suggest potential benefits in reducing hospitalization, supporting ongoing research and regulatory considerations.
Q5: Which regions represent the most promising markets for colchicine’s growth?
A: North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, especially in countries with high gout prevalence and growing healthcare infrastructure, are promising markets.
References
- CDC. (2021). Gout Prevalence and Demographics.
- He et al. (2020). NLRP3 inflammasome in cardiovascular disease. Nature Reviews Cardiology.
- MarketWatch Reports. (2022). Global Colchicine Market Analysis & Forecast.
- COLCORONA Trial. (2021). ClinicalTrials.gov. (#NCT04322682).
This comprehensive analysis aims to equip pharmaceutical and healthcare stakeholders with actionable insights into colchicine’s evolving market landscape, forecasting its trajectory amidst scientific, regulatory, and commercial forces.