Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Levofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic developed by researchers at Hoechst AG (later acquired by Bayer AG), has gained widespread use in the treatment of bacterial infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and prostatitis. Its broad-spectrum efficacy, oral bioavailability, and once-daily dosing have established it as a pivotal asset within the antimicrobial pharmacopeia. This analysis examines the evolving market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory influences, and financial trajectory for Levofloxacin, providing essential insights for stakeholders and investors.
Market Overview and Epidemiological Drivers
The global demand for Levofloxacin is intrinsically linked to the epidemiology of bacterial infections. Increasing incidences of respiratory, urinary tract, and skin infections, especially in aging populations and immunocompromised patients, sustain the market’s foundational need. According to WHO estimates, bacterial infections remain among the top causes of morbidity worldwide, instigating ongoing demand for potent antibiotics like Levofloxacin [1].
Furthermore, rising urbanization and improved diagnostics have expanded the deployment of fluoroquinolones in primary care settings, especially in emerging markets. Fever and respiratory infection prevalence rates are heightened in regions with dense populations, underpinning regional variations in Levofloxacin usage.
Competitive Landscape and Market Share
Levofloxacin competes within the fluoroquinolone class against other agents such as ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin, and newer antimicrobial classes. The key differentiator remains its pharmacokinetic profile, providing convenient once-daily dosing and high tissue penetration, which contribute to its preferential positioning in clinical protocols.
Major pharmaceutical companies, notably Bayer (original patent holder), Teva, Sun Pharmaceutical, and Hikma, manufacture generic versions, intensifying price competition. Patent expirations in various jurisdictions (primarily post-2015) catalyzed a surge in generic availability, sharply affecting pricing and margins. Market share shifted as generics gained prominence, reducing branded revenues but expanding overall market access due to affordability.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. FDA and European Medicines Agency (EMA) have issued safety warnings regarding fluoroquinolone use, emphasizing risks like tendinitis, tendon rupture, neurotoxicity, and potential for serious cardiac adverse events [2]. These alerts precipitated restrictions, notably in cystic fibrosis and pediatric uses, and prompted prescriber caution.
Such safety concerns have dampened growth prospects, especially in developed markets, and could lead to increased litigation risks. The evolving regulatory landscape demands robust post-marketing surveillance and potential reformulation strategies to mitigate adverse effects, affecting the financial outlook.
Pricing Dynamics and Reimbursement Policies
Pricing for Levofloxacin varies globally, influenced by patent status, healthcare policies, and market competition. Originator products historically commanded higher prices, but the proliferation of generics post-patent expiry significantly lowered costs.
In developed markets, reimbursement policies favor generic utilization due to cost containment imperatives, pressuring margins for branded producers. Conversely, in emerging economies, fewer regulatory constraints and higher infection prevalences sustain steady demand at lower price points.
Technological Innovations and New Formulations
Advancements in formulation sciences have explored liposomal and sustained-release versions to enhance efficacy and reduce adverse effects. However, such innovations face high R&D costs and uncertain regulatory approval pathways, limiting near-term impact.
While new antimicrobial agents with novel mechanisms (e.g., omadacycline or gepotidacin) threaten to displace fluoroquinolones due to improved safety profiles, these are expensive and at early stages of market penetration.
Market Projections and Financial Trajectory
The global antibacterial agents market was valued at approximately USD 49.6 billion in 2021 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3-4% through 2028 [3]. Levofloxacin’s segment is expected to mirror this growth trajectory, moderated by safety restrictions and antibiotic stewardship initiatives.
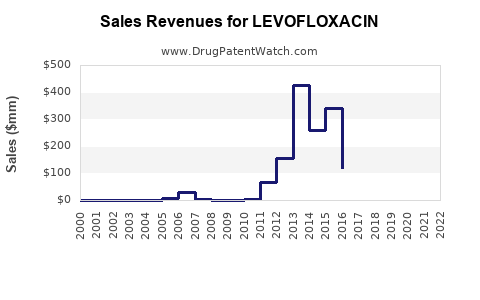
In developed markets, revenue is projected to decline modestly due to generic competition and safety-based prescribing restrictions but may be offset by increased demand in developing regions. Predicted revenues for Levofloxacin, considering global consumption patterns and pricing trends, could stabilize around USD 1.2-1.8 billion annually over the next 5 years.
Emerging markets, notably China and India, are poised for substantial growth owing to expanding healthcare infrastructure, increased bacterial infection prevalence, and broader generic acceptance. This regional shift could exert upward pressure on total Levofloxacin sales volume, although at lower price points.
Impact of Antibiotic Stewardship and Resistance
Antimicrobial stewardship programs aim to curtail misuse of antibiotics, directly impacting Levofloxacin sales. Resistance development, notably through mutations in the quinolone resistance-determining regions (QRDRs), diminishes clinical efficacy, prompting clinicians to favor alternative therapies.
The emergence of multi-drug resistant strains, such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producers and fluoroquinolone-resistant pathogens, limits Levofloxacin's applicability, further constraining revenue growth.
Intellectual Property and Patent Landscape
Patent landscapes, with key patents expiring between 2010 and 2020 in major jurisdictions, catalyzed a wave of generic entry. Brands like Levaquin, originally Bayer patent-protected, saw their exclusivity windows close, accelerating price erosion.
Continued patent filings for formulations or methods of use—such as combination therapies—may extend market exclusivity for certain formulations, influencing the financial pathways for select innovators.
Outlook: Strategic Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities lie in developing safer derivatives, novel delivery systems, and combination therapies that address resistance and safety concerns. Companies investing in such areas could restore market share and command premium pricing.
Conversely, adverse regulatory actions, declining prescription rates due to safety issues, and global antimicrobial resistance threaten revenue stability. Companies reliant on Levofloxacin revenues must diversify portfolios, invest in pipeline innovations, or focus on niche segments such as complicated infections.
Key Takeaways
-
Growing demand in emerging markets offsets stagnant or declining sales in developed countries due to safety restrictions and resistance.
-
Patent expirations and generics have drastically reduced profit margins, emphasizing the importance of innovation and new formulations.
-
Safety concerns and regulatory warnings impact prescribing patterns and revenue forecasts, necessitating continuous post-market vigilance and reformulation efforts.
-
Antimicrobial resistance presents a double-edged sword: hindering Levofloxacin's efficacy and offering opportunities for novel antibiotics, but also threatening overall fluoroquinolone utility.
-
Investing in pipeline diversity and addressing safety profiles are critical for companies seeking sustainable growth in the Levofloxacin segment.
Conclusion
Levofloxacin's market trajectory embodies the complexities of antimicrobial markets, characterized by evolving regulatory landscapes, resistance challenges, and competitive pressures. While current revenues face headwinds in mature markets, emerging economies and innovation avenues provide avenues for growth. Stakeholders must adapt strategy accordingly, balancing safety, efficacy, and economic considerations for sustainable profitability.
FAQs
1. What are the primary factors influencing Levofloxacin's declining sales in developed markets?
Regulatory safety warnings, increased antimicrobial resistance, stewardship initiatives, and patent expirations leading to generic competition have collectively driven down revenues in mature markets.
2. How does antimicrobial resistance impact the future of Levofloxacin?
Rising resistance diminishes Levofloxacin’s clinical efficacy, confining its use and prompting clinicians to seek alternative treatments, thereby constraining growth.
3. Are there ongoing innovations aimed at improving Levofloxacin’s safety profile?
Yes, research focuses on new formulations, delivery systems, and derivatives targeting reduced adverse effects, though clinical adoption remains limited.
4. Which regions offer the most significant growth opportunities for Levofloxacin?
Emerging markets like China, India, and across Southeast Asia present expansion opportunities due to rising infection rates and increasing access to generics.
5. What strategic moves should pharmaceutical companies consider to maintain profitability?
Investing in innovation, developing next-generation antibiotics, expanding in emerging markets, and exploring combination therapies will be critical to sustain revenues amidst declining patent protections.
Sources:
[1] World Health Organization. "Antimicrobial resistance." 2022.
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics: Boxed Warning and Contraindications." 2016.
[3] Grand View Research. "Antibiotics Market Size & Trends." 2022.