Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Levaquin, the brand name for Levofloxacin, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic belonging to the fluoroquinolone class. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1996, it has since become a vital component in treating various bacterial infections, including respiratory, urinary, skin, and soft tissue infections. With a complex interplay of market forces, regulatory landscapes, and evolving clinical guidelines, understanding the market dynamics and financial trajectory of Levaquin is critical for stakeholders, including pharmaceutical corporations, investors, and healthcare providers.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Growth Trends
The global demand for fluoroquinolones, including Levofloxacin, is driven by the increasing prevalence of bacterial infections, rising antibiotic resistance, and expanding healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets. According to IQVIA, the global antibiotic market was valued at approximately USD 54 billion in 2021, with fluoroquinolones representing a significant segment, anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3-4% over the next five years [1].
Levofloxacin’s position dominates the fluoroquinolone sector, especially in respiratory tract infections due to its favorable pharmacokinetics. Its broad spectrum, once-daily dosing, and oral bioavailability contribute to continued utilization across various healthcare settings.
Market Drivers
- Epidemiological Trends: Increased incidence of pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections sustains demand.
- Expanding Use in Emerging Markets: Growing access to healthcare and antibiotics in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa expand market reach.
- Shift in Treatment Paradigms: Preference for oral antibiotics reduces hospitalization costs, fueling outpatient use.
Market Challenges
- Antibiotic Resistance: Rising resistance levels diminish antibiotic efficacy, leading to reduced clinical utility and increased regulatory scrutiny.
- Adverse Events and Safety Concerns: Risks such as tendinopathy, QT prolongation, and potential neurotoxicity have led to warnings and restrictions.
- Regulatory Restraints: Agencies like the FDA and EMA have issued warnings emphasizing cautious prescribing, especially for certain populations.
Regulatory and Competitive Landscape
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies have issued black box warnings and restricted indications for fluoroquinolones, including Levaquin, emphasizing their appropriate use only when no alternative exists. The FDA’s 2016 safety communication highlighted risks associated with fluoroquinolones, leading to cautious prescribing practices and influencing sales trajectories [2].
Competitive Dynamics
Levofloxacin faces competition from other broad-spectrum antibiotics such as moxifloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and newer agents like delafloxacin. Generic manufacturers have further eroded brand name sales, with the market shifting toward cost-effective alternatives.
Innovation and Pipeline
Limited innovation exists in the fluoroquinolone class due to safety concerns and resistance issues. Nonetheless, some research endeavors are exploring modified fluoroquinolones with improved safety profiles, though these remain largely experimental.
Financial Trajectory
Historical Revenue Trends
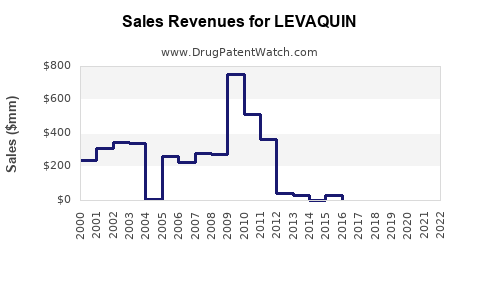
Levaquin experienced peak revenues globally in the early to mid-2000s, driven by widespread use and broad-spectrum indications. Johnson & Johnson, the original patent holder, reported substantial sales, with peak sales estimated at over USD 2 billion annually.
However, post-2010, sales declined markedly due to safety warnings, market saturation, and rising resistance. Patent expirations, beginning around 2012, accelerated generic competition, leading to significant price erosion.
Impact of Genericization
The entry of multiple generic manufacturers around 2012 caused a sharp decline in Levaquin's profit margins. Brand incentives diminished as the market shifted predominantly toward generics, which now account for the majority of Levofloxacin prescriptions.
Current Financial Outlook
Presently, Levaquin’s global sales are substantially lower, with estimates from IQVIA indicating annual revenues below USD 300 million. The drug’s utilization remains stable in specific niches—such as hospital-acquired infections—yet overall market penetration is limited by safety alerts and resistance concerns.
Future Revenue Projections
Projections suggest a continued decline for Levaquin absent significant innovation or new indications. Factors that could alter this trajectory include:
- Expansion into new geographic markets with unmet needs
- Development of formulations with improved safety profiles
- Strategic repositioning within combination therapies or alternative indications
Most industry analysts forecast a gradual decline in revenue over the next five years, compounded by the increasing prevalence of resistance and regulatory restrictions.
Market Dynamics and Influencing Factors
Antibiotic Stewardship and Prescribing Trends
Global antibiotic stewardship initiatives have prioritized reducing fluoroquinolone use to combat resistance. These campaigns influence prescription patterns, favoring narrow-spectrum or alternative agents, thereby constraining Levaquin’s growth.
Resistance and Efficacy
Rising resistance, notably in pathogens like Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, challenges the clinical utility of Levofloxacin. This resistance trend is a significant limiting factor in market expansion.
Safety Concerns and Regulatory Warnings
The dissemination of safety information has led clinicians to adopt more conservative prescribing behaviors, especially for vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and pregnant women, further impacting sales.
Emerging Alternatives and Innovation
The pharmaceutical pipeline for fluoroquinolones is limited, with minimal pipeline activity due to safety challenges. Newer antibiotics, including lipoglycopeptides and novel beta-lactams, have provided alternative treatment options, diminishing reliance on Levofloxacin.
Strategic Outlook for Stakeholders
Pharmaceutical companies seeking to extend Levaquin’s market viability must consider:
- Repositioning through new indications: Exploring additional therapeutic uses, including combination therapies.
- Safety profile improvements: Investing in formulations or derivatives with reduced adverse effects.
- Market segmentation: Focusing on regions with lower resistance or regulatory stringency.
Investors should recognize that without significant innovation or expansion into niche markets, Levaquin’s financial trajectory may continue its gradual decline.
Key Takeaways
- Market contraction is ongoing, driven by safety concerns, resistance, and regulatory constraints.
- Demand remains stable in specific niches, notably hospital settings managing resistant infections.
- Generic competition has eroded revenues, emphasizing cost-based prescribing over branded use.
- Innovation in the fluoroquinolone class is limited, constraining new growth avenues.
- Strategic repositioning is essential for brand sustainability amid evolving clinical and regulatory landscapes.
FAQs
1. What are the primary clinical indications for Levaquin?
Levaquin is mainly prescribed for bacterial respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, skin infections, and prostatitis, owing to its broad-spectrum activity.
2. How have safety concerns impacted Levaquin’s market?
FDA warnings about risks like tendinopathy, neurotoxicity, and cardiac arrhythmias have led to more cautious prescribing, impacting sales volumes and market share.
3. What is the current patent status of Levaquin?
Levaquin’s primary patents expired around 2012, leading to widespread generic manufacturing and a significant decline in brand name revenues.
4. Are there any ongoing efforts to develop safer fluoroquinolone derivatives?
Research is limited; most efforts focus on alternative antibiotics due to the intrinsic safety limitations of the fluoroquinolone class.
5. What is the future outlook for Levaquin in therapeutic use?
The outlook appears modest, with continued decline expected unless new indications are identified or significant safety improvements are achieved.
References
[1] IQVIA. (2022). Global Antibiotic Market Report.
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2016). Safety Announcement: FDA Advises Restricting Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics.