Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Valsartan, a pivotal angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), is widely prescribed for hypertension and heart failure. Initially introduced in the late 1990s, valsartan rose to prominence due to its efficacy and favorable side-effect profile. However, its market landscape has undergone substantial transformation, molded by regulatory actions, patent expirations, litigation, and evolving healthcare demands. This analysis explores the intricate market dynamics and financial trajectory of valsartan, providing a comprehensive perspective vital for industry stakeholders.
Historical Context and Market Evolution
Early Adoption and Market Growth
Released commercially in 1996 by Novartis (later sold to generic manufacturers), valsartan initially gained rapid adoption owing to its targeted mechanism and clinical benefits over older therapies such as ACE inhibitors. During its peak, valsartan generated billions of dollars annually, reflecting robust global demand, especially in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific markets.
Patent Protection and Market Exclusivity
Valasartan's original patent, granted around 1994, extended exclusivity through several patents covering its composition, method of use, and formulation innovations. This provided Novartis and subsequent patent holders with market exclusivity, allowing premium pricing and significant revenue streams until patent expiry in key markets between 2012 and 2015.
Impact of Patent Expirations and Generic Entry
Patent Cliff and Market Penetration of Generics
The expiration of valsartan’s patents precipitated a sharp decline in branded sales. Generic manufacturers, including Teva, Sandoz, and others, rapidly entered the market, offering substantially lower-cost alternatives. As a result, the branded drug's market share plummeted, with generics capturing over 80% of the global valsartan prescriptions within a few years post-patent expiry.
Pricing Erosion and Revenue Decline
Generic competition led to intense price competition, reducing the average selling price (ASP) for valsartan by an estimated 70-80%. This erosion significantly impacted Novartis’s and other early patent holders' revenue, transforming the market from a high-margin business to a volume-driven segment.
Regulatory Challenges: The TEVA-Valsartan Contamination Incident
Sandoz’s Contamination Scandal
In 2018, global recalls were initiated after reports of nitrosamine impurities, particularly N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), appeared in valsartan products. Consumer safety concerns prompted authorities like the FDA and EMA to restrict sales, intensify quality control, and scrutinize manufacturing practices.
Legal and Market Ramifications
Companies such as Teva faced substantial legal liabilities and sales disruptions. The contamination incident also catalyzed stricter regulatory oversight, delaying product approvals and increasing compliance costs. The market experienced a temporary contraction, with some consumers switching to alternative therapies or branded versions perceived as safer.
Market Restructuring and Competition
Emergence of New ARBs and Combination Therapies
Advancements led to newer ARBs such as olmesartan, irbesartan, and losartan, offering similar or enhanced efficacy. Pharmaceutical firms began developing fixed-dose combination (FDC) products, integrating valsartan with diuretics (e.g., valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide), further fragmenting the market.
Global Market Access and Healthcare Cost Pressures
Governments and insurers increasingly emphasize cost-effectiveness, favoring generics over brand-name medications. Consequently, the volume of prescriptions for valsartan remains high, but margins have compressed, aligning with broader trends in pharmaceutical procurement.
Financial Trajectory and Future Outlook
Current Revenue Landscape
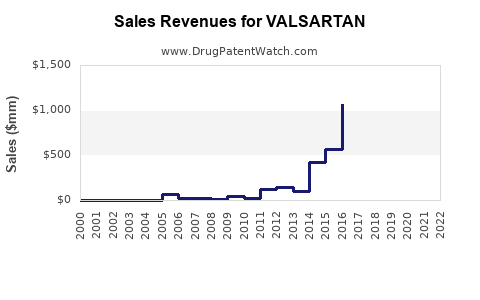
Today, valsartan’s global sales are predominantly driven by generic sales. Brands like Novartis's Diovan have scaled back or exited the market, focusing on undisputed innovators and specialty drugs. In 2022, global valsartan sales are estimated at approximately $250–$350 million, a stark decline from peak revenues exceeding $4 billion (circa 2012).
Emerging Factors Influencing Financial Prospects
- Regulatory stability is crucial; ongoing litigation and quality control concerns may dampen growth.
- Market saturation with generics limits upside potential; incremental growth relies on new formulations or combination therapies.
- Patent expiry of newer ARBs and the potential introduction of biosimilars or novel agents could further diminish valsartan’s market share.
- Emerging markets offer incremental growth prospects due to rising hypertension prevalence and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
Pharmaceutical Companies' Strategic Responses
Firms are increasingly focusing on niche therapeutic areas, orphan indications, and personalized medicine. Some companies explore reformulations with improved delivery mechanisms or combination products to sustain profitability.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Patent Extensions and Litigation
While the original patent expired in most jurisdictions, secondary patents and data exclusivities temporarily shield certain formulations or uses. However, patent challenges, especially in courts and patent offices, have reduced the duration of exclusivity.
Regulatory Approvals and Quality Assurance
Ongoing monitoring of nitrosamine impurities remains imperative. Regulatory bodies continue to tighten standards, complicating generic manufacturing but ensuring consumer safety—though at increased compliance costs.
Market Outlook and Strategic Considerations
Short- to Mid-term Outlook
The global valsartan market is expected to experience a gradual decline in revenue, with volume-driven sales maintaining stability despite pricing pressures. The overall trajectory suggests a maturity phase, aligned with pharmaceutical standard lifecycle models.
Long-term prospects hinge on healthcare policy shifts, technological innovations, and potential new indications. Investment in formulations that minimize impurities or provide improved therapeutic profiles could offer minor revenue streams.
Stakeholder Opportunities
- Generic manufacturers can capitalize on low-cost production in emerging markets.
- Pharmaceutical developers may explore innovative delivery methods or combination therapies to prolong product lifecycle.
- Investors should assess exposure in companies with diversified portfolios beyond valsartan.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expirations led to rapid generic penetration, causing significant revenue erosion for branded valsartan products.
- Regulatory incidents, notably nitrosamine contamination, temporarily disrupted supply and tarnished market confidence.
- Market competition has shifted toward newer ARBs and combination therapies, limiting valsartan's growth potential.
- Global sales now primarily derive from cost-sensitive generic markets, with revenues declining steadily.
- Future prospects for valsartan hinge on market saturation, regulatory environments, and the development of reformulated or combination products designed to address safety concerns.
FAQs
1. How did patent expirations affect valsartan’s market presence?
Patent expirations permitted generic manufacturers to enter rapidly, significantly reducing prices and branded sales, thereby shifting market share and shrinking margins for original patent holders.
2. What impact did the nitrosamine contamination crisis have on valsartan?
The contamination led to widespread recalls, regulatory scrutiny, and consumer concerns, disrupting supply chains and temporarily diminishing market confidence.
3. Are there ongoing lawsuits related to valsartan?
Yes. Numerous class-action and individual lawsuits allege contamination and related health issues, creating ongoing legal and financial risks for manufacturers.
4. What is the future trajectory of valsartan sales?
Sales are expected to decline gradually as generics dominate and newer therapies emerge, with limited recovery potential unless reformulations or new indications develop.
5. Can valsartan regain market share through innovation?
Potentially, but significant barriers exist, including regulatory hurdles and market competition from newer ARBs and combination formulations.
Sources
[1] IMS Health, "Global Pharmaceutical Market Data," 2022.
[2] FDA, "Valsartan Recall and Safety Notices," 2018.
[3] Novartis Annual Reports, 2012–2022.
[4] MarketWatch, "Generic Cardiovascular Drugs Market Analysis," 2023.
[5] European Medicines Agency, "Assessment Reports on ARBs," 2019.