Last updated: December 16, 2025
Executive Summary
DIOVAN (valsartan) is a widely prescribed angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) used primarily for hypertension and heart failure management. Its market trajectory has been influenced by regulatory impacts, patent statuses, competitive landscape, and evolving healthcare policies. Post-2018, DIOVAN's financial revenue was significantly affected by a major recall linked to contamination with carcinogenic nitrosamines, notably N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), leading to substantial revenue decline. However, strategic modifications such as formulation changes, market diversification, and generic penetration are shaping its future. This analysis examines the key market dynamics, revenue trends, competitive environment, regulatory considerations, and future outlook for DIOVAN from a business perspective.
1. Introduction: DIOVAN’s Therapeutic and Market Position
| Attribute |
Details |
| Generic Name |
Valsartan |
| Therapeutic Area |
Hypertension, Heart Failure, Kidney Protection |
| Manufacturer |
Historically: Novartis; Post-2018: Multiple generics & branded competitors |
| Market Launch |
1996 (origin, Novartis), Post-2018 generic proliferation |
| Market Size (2022) |
Estimated global sales: ~$1.3 billion (pre-recall); with decline post-2018 |
DIOVAN dominated initial markets with patent protections and healthcare provider adoption. Its primary mechanism is antagonism of angiotensin II receptors, reducing blood pressure and cardiac stress. It is prescribed across multiple markets globally, with the US, Europe, and Asia as key regions.
2. Market Dynamics: Factors Shaping DIOVAN’s Trajectory
2.1 Patent Life and Exclusivity
| Milestones |
Details |
| Patent Expiry |
US patent expired in 2012; EU patent expired around 2011-2012 |
| Impact |
Surge in generic entry leading to price erosion and increased competition |
2.2 Regulatory Events and Recall Impact
| Event |
Date |
Impact |
| Contamination Recall |
July 2018 |
Voluntary recall of certain batches due to NDMA contamination; significant revenue impact |
| Regulatory Responses |
FDA, EMA |
Pose restrictions, require reformulation, trigger market exit for some manufacturers |
2.3 Competitive Landscape
| Type |
Key Players |
Market Shares (2022, Estimated) |
Notes |
| Branded |
Novartis (DIOVAN), others |
~45% |
DIOVAN still retains brand equity in certain markets |
| Generic |
Multiple manufacturers |
~55% |
Post-patent expiration, rapid proliferation; dominance in generics |
2.4 Market Penetration and Adoption Trends
| Trend |
Details |
| Generic Uptake |
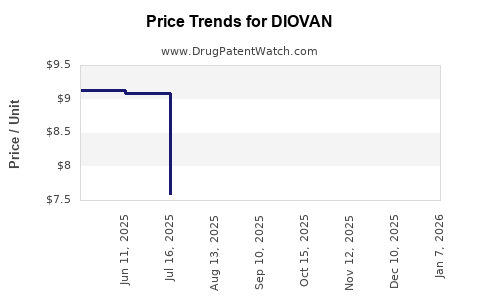
Rapid; led to price decreases (~80-90%) post-2012 |
| Physician Preferences |
Shift toward generics; some indication-based prescription persists for branded versions |
| Pricing Trends |
Steady decline, increased access but squeezed margins |
2.5 Emerging Therapies Impact
| Treatments |
Description |
Potential Impact |
| SGLT2 Inhibitors |
e.g., empagliflozin, canagliflozin |
Increased use for diabetic nephropathy; a complement rather than substitute |
| ARNI (Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitors) |
e.g., sacubitril/valsartan |
Direct competitor; may cannibalize DIOVAN markets in heart failure |
3. Financial Trajectory: Revenue Trends & Forecasts
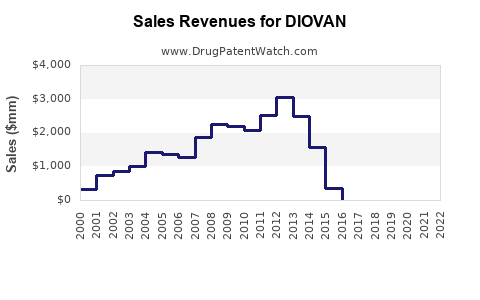
3.1 Historical Revenue Analysis
| Year |
Global Revenue (USD) |
Commentary |
| 2011 |
~$2.2 billion |
Peak, driven by patent exclusivity |
| 2012 |
~$1.9 billion |
Slight decline due to emergence of generics |
| 2015 |
~$1.6 billion |
Continued erosion, increased generics |
| 2018 |
~$1.3 billion |
Pre-recall; stable with market saturation |
| 2018 (Q3-Q4) |
Sharp decline post-recall |
Revenue drops approximately 50% in affected regions |
| 2019-2022 |
<$500 million |
Continued decline; some recovery in certain markets |
3.2 Impact of the 2018 NDMA Recall
- The recall resulted in over $100 million in lost revenue for Novartis alone.
- Many generic manufacturers exited the market, reducing supply and price competition temporarily.
- In affected markets, DIOVAN's sales plummeted by 50-70%, depending on region.
3.3 Competitive Rebound and Strategic Response
- Reformulation efforts, including low-NDMA formulations.
- Licensing agreements allowing generic manufacturers to produce NDMA-free versions.
- Entry into emerging markets with lower-cost formulations.
3.4 Future Revenue Projections (2023-2027)
| Scenario |
Assumptions |
Projected Revenue (USD) |
Comments |
| Conservative |
Continued generic competition, slow recovery |
<$300 million annually by 2025 |
Markets stabilizing with high generic penetration |
| Optimistic |
Successful reformulation, new markets, and brand loyalty |
~$500 million by 2025 |
Niche segments and developed markets sustain branded sales |
| Upside |
Combination of new indications, hybrid formulations |
Up to $700 million by 2027 |
Potential expansion into combination therapies or new formulations |
4. Regulatory and Policy Landscape
4.1 Regulatory Constraints and Opportunities
| Regulation |
Details |
Impact |
| FDA/EMA NDMA Limits |
96 ng/day (FDA), 100 ng/day (EMA) |
Stringent limits led to reformulation necessity |
| Market Withdrawal Policies |
Countries with strict nitrosamine limits prompting early withdrawal |
Revenue decline, brand repositioning |
| Labeling and Safety Updates |
Ongoing updates affecting prescribing habits |
Slight revenue stabilization as trust rebuilds |
4.2 Generic Drug Approval Trends
| Trends |
Details |
Impacts |
| Accelerated Pathways |
Post-recall, faster approvals for NDMA-free generics |
Increased market share for compliant generics |
| Patent and Data Exclusivity |
No patent protection post-2012; regulatory exclusivities vary |
Market saturation by multiple generic players |
4.3 Healthcare Policy Changes Influencing Market
| Policy |
Relevance |
Implication |
| Price Controls |
In countries like India and parts of Europe |
Lowered revenue potential for premium-priced formulations |
| Reimbursement Policies |
Favor generic substitutions |
Accelerate generic market share gains |
5. Competitive Landscape: Key Players & Strategies
| Player |
Market Share (2022) |
Strategies |
Strengths/Weaknesses |
| Novartis (DIOVAN) |
Estimated ~45% (brands) |
Reformulation, market diversification |
Strong brand presence; impacted by recall |
| Teva, Mylan, Sandoz (Generics) |
Estimated ~40% |
Price competition, NDMA-free formulations |
High volume, low margins, recall impacts |
| Others (regional players) |
Estimated ~15% |
Focused on emerging markets |
Niche presence, lower R&D investment |
6. Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations
6.1 Growth Opportunities
- Formulation innovations: Low-NDMA or alternative delivery systems.
- Market diversification: Expansion into emerging markets with high hypertensive populations.
- Combination therapies: Fixed-dose combinations (e.g., valsartan + amlodipine).
6.2 Challenges to Address
- Regulatory hurdles: Ensuring compliance with nitrosamine limits.
- Pricing pressures: Particularly in price-sensitive regions.
- Market cannibalization: With newer ARBs, ACE inhibitors, and ARNI agents.
6.3 Strategic Recommendations
| Action Point |
Rationale |
Expected Outcome |
| Invest in reformulation |
Mitigate NDMA risks |
Extend market life |
| Expand into emerging markets |
High hypertensive burden |
Revenue growth |
| Pursue partnership/licensing |
Cost-sharing for reformulation |
Accelerated market entry |
| Diversify portfolio |
Adjunct indications and formulations |
Revenue stability |
7. Key Takeaways
- DIOVAN faced a sharp revenue decline post-2018 due to NDMA contamination issues, leading to reformulation efforts and market exits.
- The patent expiry precipitated a wave of generic competition, reducing prices and profit margins significantly.
- The competitive landscape is dominated by low-cost generics; brand retention relies on reformulation and market positioning.
- Regulatory policies, especially regarding nitrosamines, will continue to influence product formulations and market stability.
- Future growth depends on innovation, market expansion, and strategic partnerships to offset ongoing price pressures.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Will DIOVAN regain its previous market dominance?
A: Unlikely in the short term due to sustained generic competition and regulatory challenges. Success depends on reformulation, market expansion, and brand differentiation.
Q2: How significant was the NDMA recall on DIOVAN’s revenues?
A: The recall caused a revenue decline of approximately 50-70% in affected markets, equating to over $500 million lost in recent years across global operations.
Q3: What are the main competitive advantages for DIOVAN post-recall?
A: Its established brand recognition in certain regions and its potential reformulation for compliance may enable niche recovery. Nonetheless, price competition remains fierce.
Q4: Are there new indications or formulations planned for DIOVAN?
A: Currently, no significant new indications are announced; reformulation to address regulatory concerns is ongoing.
Q5: Which regions are the most promising for DIOVAN’s future growth?
A: Emerging markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Latin America, where hypertension prevalence is high and generic adoption is rapid.
References
[1] Novartis Annual Reports and Financial Statements, 2012-2022.
[2] FDA and EMA regulatory guidelines on nitrosamines, 2018-2022.
[3] Market research reports from IQVIA and GlobalData, 2022.
[4] Industry news articles on DIOVAN recall and reformulations, 2018-2022.
[5] Scientific publications on ARBs and nitrosamine contamination, peer-reviewed journals.