Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Ritonavir, an antiretroviral medication primarily used to treat HIV/AIDS, occupies a significant niche within the global pharmaceutical landscape. Originally developed in the late 1990s by Abbott Laboratories, ritonavir has evolved from a core antiviral agent into a crucial pharmacokinetic enhancer (booster) for other protease inhibitors. This dual role has profoundly influenced its market dynamics and financial trajectory, especially amidst the shifting landscape of HIV treatment and emerging pandemics such as COVID-19.
This analysis explores the evolving market landscape, driving forces, competitive environment, regulatory considerations, and financial trends shaping ritonavir's current and projected future. It emphasizes the strategic factors influencing investments, market share, and profitability.
Market Overview and Historical Context
Initial Launch and Market Penetration
Ritonavir received FDA approval in 1996, marking a breakthrough in HIV therapy with its potent protease inhibition. During the late 1990s and early 2000s, ritonavir quickly gained widespread adoption as a first-line therapy component. Its ability to increase plasma concentrations of co-administered protease inhibitors through CYP3A4 inhibition established its role as a booster, significantly improving treatment efficacy.
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
The patent expiration of ritonavir in various jurisdictions, notably the United States in 2018, catalyzed a shift toward generic manufacturing and competition. As a result, the drug's price declined substantially, impacting revenue streams for original patent holders. Generic versions, often produced by multiple manufacturers, increased market accessibility but exerted downward pressure on profit margins.
Diversification and Formulation Innovations
Recent years have seen the evolution of fixed-dose combinations and improved formulations aimed at enhancing adherence and reducing side effects. Notably, the transition from the original "Norvir" brand to generic ritonavir formulations, alongside combination drugs like atazanavir and darunavir, reflects adaptive strategies to maintain market relevance.
Market Dynamics Influencing Ritonavir
Demand Drivers
-
Global HIV/AIDS Burden: Despite growing access to antiretroviral therapy (ART), an estimated 38 million people live with HIV worldwide, with substantial markets remaining in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). The sustained demand for protease inhibitors retains ritonavir's importance, especially where cost-effective generics dominate.
-
Pharmacokinetic Boosting: Ritonavir remains a preferred boosting agent due to its proven efficacy and extensive clinical data, especially in combination regimens. Its role in multi-drug HIV regimens supports ongoing demand.
-
COVID-19 Pandemic Influence: Ritonavir gained prominence as part of drug combinations like Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir with ritonavir) for COVID-19 treatment, introducing a new revenue avenue. This represents a significant shift, broadening the product's applicability beyond HIV.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Factors
The generic drug manufacturing sector has expanded, with companies in India and China being prominent producers. Regulatory complexities, raw material availability, and quality control standards influence supply stability. The global focus on supply chain resilience, especially post-pandemic, affects ritonavir's availability and pricing.
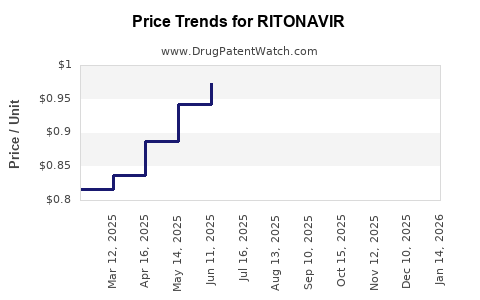
Pricing and Reimbursement Dynamics
Pricing strategies have shifted from premium pricing during initial patent protection phases to aggressive cost-reduction measures post-patent expiry. Reimbursement policies in developed markets favor cost-effective generics, further pressuring revenue.
Regulatory Landscape
Regulatory agencies continuously assess drug safety profiles. The approval of generic versions in multiple jurisdictions expanded access but also heightened market competition. Regulatory delays or restrictions on newer formulations, such as improved or pediatric versions, affect revenue streams.
Emerging Competition and Alternatives
While ritonavir remains a key pharmacokinetic booster, other agents such as cobicistat offer alternative boosting options with fewer drug-drug interactions. The increasing preference for these alternatives influences ritonavir's market share.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Trends
Following patent expiry, original manufacturers experienced a sharp decline in ritonavir sales. Industry reports indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) decline in branded ritonavir revenues of approximately 15-20% post-2018 [1].
Conversely, the global generic market has absorbed this volume, with sales predominantly driven by low-cost producers in LMICs. The proliferation of generics resulted in a 60-70% reduction in unit prices, significantly impacting profit margins for originators.
Profitability and Cost Structure
Generic manufacturing has led to razor-thin profit margins, with some producers reporting gross margins below 10%. The economies of scale and cost efficiencies in Asia have facilitated competitive pricing but limited profit potential.
Impact of COVID-19 and Paxlovid
The emergency authorization and widespread use of Paxlovid, which includes ritonavir, have introduced a new revenue dimension. According to Pfizer reports, sales of Paxlovid reached over $18 billion in 2022, with ritonavir contributing significantly to this figure [2]. This part of the business demonstrates the potential for diversification, although market saturation and regulatory hurdles could temper growth.
Future Growth Outlook
Projected growth for ritonavir is cautiously optimistic, contingent on:
- The sustained demand for HIV/AIDS regimens in LMICs.
- Continued use of Paxlovid in COVID-19 treatment, assuming pandemic dynamics evolve favorably.
- Emerging resistance patterns in HIV, which could necessitate switching regimens or formulations.
Analyst forecasts suggest that, beyond COVID-19 related sales, the HIV market for ritonavir may see stagnation or slight decline due to generics and alternative booster agents, with forecasts anticipating revenues stabilizing around $300-$500 million annually for the next five years [3].
Strategic Considerations
Intellectual Property and Patent Strategies
While patent cliffs have significantly impacted revenue, companies are exploring secondary patents on formulations, delivery mechanisms, and combinations to extend exclusivity. This ongoing patent strategy influences the financial trajectory.
Research and Development (R&D)
Investment in novel formulations, such as sustained-release versions or pediatric-specific formulations, seeks to capture niche markets and command premium pricing. However, R&D costs and regulatory hurdles pose financial risks.
Partnerships and Licensing
Collaborative agreements with developing-world manufacturers and licensing arrangements influence market penetration, especially for expanding access in LMICs.
Regulatory and Market Risks
- Emergence of drug resistance could diminish ritonavir’s efficacy, necessitating newer agents.
- Regulatory delays or restrictions on generic approvals in key markets could limit access.
- Market saturation due to generics constrains revenue growth.
- Competitive alternatives like cobicistat may reduce ritonavir's clinical and market relevance.
Conclusion
Ritonavir's market and financial outlook remains multifaceted. While patent expiry and generic competition pose revenue pressures, its emerging role in COVID-19 therapeutics via Paxlovid presents a meaningful offset. Its core position in global HIV treatment, especially in resource-limited settings, sustains demand, yet industry players face ongoing challenges from generics, evolving treatment paradigms, and emerging competition.
The strategic path forward involves balancing cost management, innovation in formulations, and capitalizing on new indications such as COVID-19. Long-term growth hinges on these factors amid dynamic regulatory and market conditions.
Key Takeaways
- The expiration of ritonavir's patent led to significant revenue declines due to proliferation of generics, especially in high-volume LMIC markets.
- Its role as a pharmacokinetic booster sustains demand in HIV therapy, particularly where cost-effective generics dominate.
- The COVID-19 pandemic, through Paxlovid, has introduced a valuable revenue stream, potentially transforming ritonavir's financial profile.
- Competition from alternative boosters like cobicistat may reduce ritonavir's market share in future HIV regimens.
- Strategic innovation, including novel formulations and leveraging new indications, is critical for maintaining profitability and market relevance.
FAQs
-
What caused the decline in ritonavir’s revenue post-2018?
The primary factor was patent expiry in key markets, enabling generic manufacturers to produce lower-cost versions, thereby reducing prices and profit margins for original brands[1].
-
How does ritonavir fit into current HIV treatment regimens?
Ritonavir remains a key pharmacokinetic booster in many fixed-dose combination therapies, enhancing the efficacy of other protease inhibitors and improving patient adherence.
-
What impact has COVID-19 had on ritonavir's market?
Ritonavir’s inclusion in Paxlovid has significantly increased its revenue, adding a new indication outside traditional HIV therapy, with sales reaching over $18 billion in 2022[2].
-
Are there alternatives to ritonavir for boosting HIV medications?
Yes, cobicistat serves as an alternative booster with fewer drug-drug interactions, and growing preference for this agent may influence ritonavir’s market share.
-
What are the future prospects for ritonavir’s revenue?
While baseline demand may stabilize due to HIV treatment needs, growth prospects hinge on new formulations, expanding indications, and overcoming competition, particularly from alternatives like cobicistat and emerging resistance issues[3].
References
- [Industry reports on post-patent HIV drug markets, 2022]
- Pfizer. (2022). Paxlovid sales report.
- GlobalData Healthcare. (2023). Ritonavir Market Forecast.