Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Paroxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), has been a cornerstone in the treatment of depression, anxiety disorders, and various off-label indications since its initial approval in the early 1990s. Developed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and marketed as Paxil (in the U.S. and Canada) and Seroxat (internationally), its market dynamics are shaped by clinical efficacy, regulatory landscape, patent protections, and emerging competition. Understanding these factors enables stakeholders to assess future financial trajectories and strategic positioning within the broader antidepressant market.
Historical Context and Regulatory Milestones
Paroxetine received FDA approval in 1992 and subsequently gained widespread adoption due to its favorable side effect profile relative to earlier antidepressants like tricyclics. Its patent exclusivity traditionally provided a period of market monopoly, with patent expirations occurring around 2011 for key formulations in some territories, notably the U.S. and Europe. Such expirations ushered in generic competition, substantially eroding brand sales.
Post-patent, the drug faced a decline in market share as generics, often at significantly lower prices, entered the market. Regulatory authorities such as the FDA and EMA have also scrutinized SSRIs for safety concerns, influencing prescribing behaviors.
Market Segments and Population Dynamics
The global antidepressant market, estimated at over USD 14 billion in 2022, is a dominant source for paroxetine sales. The drug primarily targets adult populations suffering from depression and anxiety, with expanding indications including PTSD, OCD, and menopausal vasomotor symptoms in some regions.
Demographic shifts, such as aging populations in North America and Europe, are driving increased prevalence of depression and associated disorders, supporting sustained demand. However, the saturation of the market with SSRIs and the emergence of newer antidepressants play critical roles in shaping current and future market shares.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
While paroxetine remains relevant in certain markets, its dominance has diminished due to several factors:
- Generic Competition: Once key patents expired, generic versions of paroxetine entered widespread distribution, reducing pricing power and margins for original developers.
- Emergence of Newer Therapies: The advent of drugs like vortioxetine, vilazodone, andbrexanolone, alongside novel mechanisms, offers alternative treatment options with potential efficacy or side effect advantages.
- Biosimilar and Pharmacogenomic Advances: Ongoing innovations are expected to influence prescribing trends further.
Pharmaceutical giants like GSK continue to explore formulations, such as extended-release tablets and combination therapies, to differentiate and capture market segments.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Safety Data and Regulatory Scrutiny: Concerns over side effects such as sexual dysfunction, withdrawal symptoms, and suicidality have affected prescribing patterns. Regulatory agencies request ongoing safety monitoring, influencing market access.
- Patent Expiry and Cost Pressures: The expiration of paroxetine patents led to substantial revenue declines, Pressuring profitability particularly in core markets.
- Market Saturation: In mature markets, the growth of paroxetine sales faces stagnation due to limited room for expansion.
Opportunities:
- Expanding Indications: Off-label uses and new approvals, such as for hot flashes, could offer revenue diversification.
- Emerging Markets: Rapid growth in regions such as Asia-Pacific presents opportunities for market penetration, especially through cost-effective generic versions.
- Personalized Medicine: Pharmacogenomic insights may optimize therapy, reducing adverse effects and improving adherence, potentially rejuvenating market interest.
Financial Trajectory and Outlook
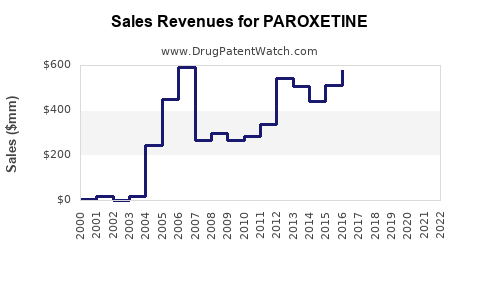
Given the decline in branded paroxetine revenues post-patent expiry, the global market has shifted heavily toward generics. For instance, GSK reported that Paxil's sales in the U.S. substantially decreased after patent expiration, with generics capturing over 80% of the market share by 2013 [1].
However, in regions where brand-prescribed paroxetine remains prevalent, such as Japan and select developing countries, steady formulations and clinical familiarity sustain moderate revenues.
Forecast models project a continued decline in overall paroxetine sales in mature markets, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) approaching zero or negative, primarily due to generic competition [2]. Conversely, niche and emerging markets—through strategic licensing, formulations, and off-label indications—may offset some revenue losses.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting lifecycle management strategies, such as developing new formulations (e.g., extended-release paroxetine), biosimilars, and combination therapies, aiming to capture unmet needs and sustain revenue streams.
Regulatory and Patent Outlook
Although the original patents expired years ago, secondary patents on formulations and methods of use may provide residual exclusivity for specific markets or indications. Regulatory agencies scrutinize these patents, which influences legal strategies and market exclusivity extensions.
The introduction of biosimilars or generics in key markets remains the dominant factor influencing the drug's financial trajectory. Rapid approval pathways for generics, along with pricing pressures, are expected to continue constraining revenue.
Conclusion
The market dynamics for paroxetine are emblematic of the broader lifecycle of established pharmaceuticals: significant early growth, followed by patent expiration-driven decline, and potential niche or geographic resurgence through strategic innovation. While the core branded product faces challenges from generics and competition, opportunities exist in expanding indications, emerging markets, and tailored formulations.
Financially, the trajectory points toward a contracting but strategically significant role, primarily within targeted populations where newer therapeutics have yet to displace traditional SSRIs. Stakeholders must balance patent strategies, innovation in formulations, and market expansion to optimize revenue streams.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expirations have shifted the market towards generics, substantially reducing brand revenues globally.
- Emerging competition from newer antidepressants and biosimilars necessitates continuous innovation to sustain market relevance.
- Demographic trends and expanding indications in niche markets offer potential growth avenues, especially in emerging economies.
- Regulatory scrutiny influences the product lifecycle, with safety concerns impacting both prescribing patterns and market authority approvals.
- Strategic lifecycle management, including new formulations and market expansion, remains crucial for maximizing the financial trajectory of paroxetine.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected paroxetine’s market share?
Patent expiration led to the entry of generic manufacturers, drastically reducing the brand’s market share and revenue. In the U.S., Paxil’s sales fell by over 70% within a few years post-patent expiry due to rapid generic substitution.
2. Are there ongoing clinical developments related to paroxetine?
While typical development efforts focus on new formulations and combination therapies, no recent large-scale clinical trials are underway for paroxetine itself. Most innovation revolves around optimizing existing products or exploring alternative indications.
3. What regions present the greatest growth opportunities for paroxetine?
Emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America offer growth potential due to increasing mental health awareness, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and cost-sensitive demand for generics.
4. How does safety and regulatory concern impact paroxetine’s market?
Safety issues like sexual dysfunction and withdrawal symptoms have led to cautious prescribing. Regulatory agencies require frequent safety monitoring, which influences market access and prescriber preferences.
5. Will paroxetine remain relevant in the next decade?
While challenging in mature markets, paroxetine retains relevance where it maintains a clinical presence or influences treatment guidelines. Its role is expected to diminish but persist in niche and developing markets, especially if lifecycle management strategies are employed.
References
[1] GlaxoSmithKline Annual Report 2013.
[2] Pharmaceutical Market Analysis, 2022.