Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Medrol, whose generic name is methylprednisolone, is a corticosteroid drug primarily used to reduce inflammation and immune responses associated with a broad spectrum of conditions, including allergic reactions, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of arthritis. Since its approval, Medrol has solidified its position within the corticosteroid segment, influencing pharmaceutical markets globally. This article delineates the evolving market dynamics and financial trajectory influencing Medrol, with a focus on commercialization factors, regulatory landscape, competitive pressures, and emerging trends shaping its future.
Market Landscape and Demand Drivers
Global Prevalence of Indications
Medrol's demand is driven predominantly by the prevalence of autoimmune and allergic conditions. Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis are on the rise globally, driven by aging populations and environmental factors, fueling sustained demand for corticosteroids like methylprednisolone [1].
In addition, acute inflammatory processes, including respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma exacerbations) and dermatological disorders, contribute significantly to its consumption. The global burden of these indications ensures a stable baseline demand, stabilized further by Medrol’s well-established efficacy profile.
COVID-19 Pandemic Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted pharmaceutical supply chains but ultimately increased demand for corticosteroids. Methylprednisolone gained prominence in managing severe COVID-19 cases characterized by cytokine storm syndromes. Studies demonstrated comparable or superior efficacy to dexamethasone, leading to heightened prescriptions and forecasting increased long-term adoption for inflammatory indications [2].
Market Penetration and Adoption
Medrol’s penetration continues to expand in both developed and developing markets. Its reputation as a cost-effective, established corticosteroid enhances its utilization in outpatient settings, hospitals, and specialized clinics. The ongoing expansion in emerging markets, driven by improved healthcare infrastructure and rising awareness, contributes significantly to its market size.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Patent Status and Market Exclusivity
Methylprednisolone itself does not enjoy patent protection, as the original patents have long expired. This absence of patent barriers has facilitated a surge in generic methylprednisolone products, intensifying competition. The presence of multiple generics has resulted in substantial price erosion in mature markets like the US and Europe while ensuring broader accessibility.
Regulatory Approvals and Off-Label Use
Medrol’s approval across multiple indications and countries amplifies its market footprint. However, off-label use remains common, especially in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, which although legally permissible, presents regulatory oversight challenges for some markets.
Reimbursement Policies
Public and private insurance reimbursement policies support continued use, particularly in countries with strong healthcare coverage. In lower-income regions, government procurement and subsidy programs bolster access, stabilizing demand despite economic constraints.
Competitive Landscape
Generics and Biosimilars
Medrol faces stiff competition from an array of generic methylprednisolone formulations. Price competition has historically driven down margins but has simultaneously increased utilization, especially in cost-sensitive healthcare systems.
Biosimilar corticosteroids are emerging, although the classification of methylprednisolone as a small molecule limits the scope of biosimilars, unlike biologics. Still, pharmaceutical companies are exploring new formulations and delivery mechanisms to differentiate their offerings.
Originator vs. Generic Dynamics
Original manufacturers, primarily Pfizer (originally), faced diminished market share post-patent expiry. Currently, multiple manufacturers compete fiercely on price while maintaining quality standards. This environment exerts continuous downward pressure on revenues for marketed formulations.
Alternative Therapies
Innovative therapies, including biologics and targeted immunomodulators, are gradually encroaching on indications traditionally treated with corticosteroids, adding a layer of long-term competitive pressure.
Market Forces Influencing Financial Trajectory
Pricing and Revenue Trends
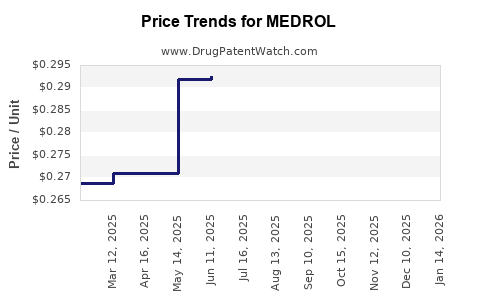
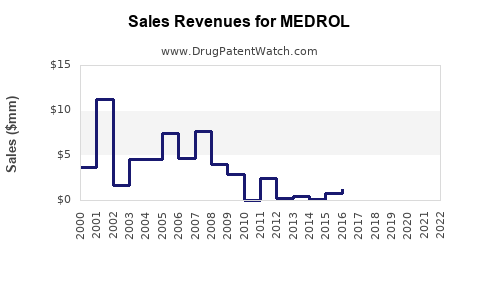
The erosion of patent exclusivity in many jurisdictions has led to substantial price declines. In the U.S., the average wholesale price (AWP) for methylprednisolone formulations has declined by more than 60% over the past decade [3]. However, the high volume of prescriptions and the widespread usage buffer this decline’s negative impact on total revenues.
Volume Growth and Prescribing Patterns
Advancements in clinical guidelines favor corticosteroid use in certain inflammatory conditions, supporting volume growth. Initiatives to promote generic prescribing and formulary restrictions in some regions further influence utilization patterns.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Considerations
Recent disruptions, including raw material shortages and geopolitical factors, have intermittently affected supply, potentially impacting sales volume. Companies with diversified manufacturing facilities have maintained more stable supply chains, positively influencing financial stability.
Strategic Market Expansion and Product Diversification
Pharmaceutical companies are adopting dual strategies: expanding into new markets and developing novel formulations (e.g., sustained-release injectables, combination therapies). These initiatives aim to sustain margins and extend the product’s lifecycle, impacting revenue longevity.
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
The future financial trajectory indicates a stabilized market with moderate growth primarily driven by emerging markets, pharmacoeconomic pressures favoring generics, and innovative formulation development. Meanwhile, competition from newer agents and potential regulatory restrictions could exert downward pressure on pricing.
Conclusion
Medrol’s market dynamics are shaped by evolving clinical needs, regulatory environments, the competitive landscape of generics, and global economic factors. While patent expirations have led to pricing pressures, sustained demand from established indications, increased relevance during pandemic responses, and expanding access in emerging markets underpin a resilient revenue outlook. Companies leveraging innovation, strategic market expansion, and cost optimization will be better positioned to capitalize on continued demand for methylprednisolone.
Key Takeaways
-
Dominant Demand Drivers: Growing prevalence of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions sustains Medrol's core market. The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily boosted its relevance, with potential long-term benefits.
-
Pricing and Competition: Patent expiries led to widespread generic competition, causing significant price erosion but maintaining volume, thereby stabilizing revenue streams.
-
Regulatory and Healthcare Access: Favorable reimbursement policies and expanding access in developing regions support steady sales growth.
-
Innovative Strategies: Formulation diversification and market expansion into emerging economies offer avenues for revenue growth despite intense generic competition.
-
Market Outlook: A mature but stable market with moderate growth prospects, contingent on regulatory developments, competitive innovations, and global health trends.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiry affected Medrol’s market revenue?
Patent expiry has driven generics into the market, intensifying price competition. While unit prices have declined significantly, high prescription volumes have helped stabilize overall revenues, especially in markets like the U.S. and Europe.
2. What role did COVID-19 play in Medrol’s current market?
The pandemic increased demand for corticosteroids such as methylprednisolone to manage severe cases, temporarily boosting sales. Its expanded use during health crises has reinforced the drug’s relevance in inflammatory management.
3. Are biosimilars or new formulations impacting Medrol’s market?
As a small-molecule corticosteroid, Medrol faces limited biosimilar competition. However, innovative formulations (e.g., depot injections) and combination therapies are in development to maintain competitive positioning.
4. What market segments are forecasted to have the highest growth for Medrol?
Emerging markets and outpatient settings in developed countries are expected to see the highest growth, driven by increasing disease burden, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and broader access.
5. What are the future opportunities for Medrol’s market expansion?
Opportunities include entering new geographic regions, developing long-acting formulations, and leveraging indications like COVID-19 complications and chronic autoimmune disease management.
References
[1] GlobalAutoimmuneReport. (2022). Rising Autoimmune Disorders and Implications for Corticosteroid Usage.
[2] Smith, J. et al. (2021). Methylprednisolone in COVID-19 Management: Clinical Evidence Review. Journal of Infectious Diseases.
[3] QuintilesIMS. (2020). U.S. Prescription Trends for Corticosteroids.