Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Loteprednol etabonate (LE) is a corticosteroid employed primarily in ophthalmology to treat posterior segment and anterior segment eye inflammatory conditions. Since its FDA approval in 1998, LE has carved a niche due to its targeted potency and reduced systemic side effects compared to traditional corticosteroids. As the ophthalmic anti-inflammatory segment evolves with technological advances and competitive pressures, understanding its market dynamics and financial trajectory is essential for stakeholders—including pharmaceutical companies, investors, and healthcare practitioners. This article examines key market drivers, competitive landscape, regulatory influences, and financial prospects shaping LE's future.
Market Overview
The global ophthalmic corticosteroid market, estimated to reach USD 2.4 billion by 2028 (CAGR ~4.2%), encompasses a broad range of therapies, with LE playing a significant role [1]. Its unique structure, designed for targeted delivery with minimal systemic absorption, positions it advantageously within a crowded therapeutic landscape. The drug's primary indications include post-operative ocular inflammation, allergic conjunctivitis, and keratitis.
During recent years, increased prevalence of ophthalmic inflammatory conditions—stemming from aging populations, rising diabetes incidence, and UV exposure—has fueled demand for effective corticosteroids like LE. Concurrently, innovations in drug delivery systems, such as preservative-free formulations and sustained-release implants, bolster LE's market potential.
Market Dynamics
1. Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety Profile
LE's design minimizes intraocular pressure elevation and other corticosteroid side effects, a common concern with traditional steroids. This safety profile enhances its acceptance among clinicians and patients, especially for long-term use or in populations vulnerable to steroid-induced complications [2].
2. Competitive Landscape
Despite being a well-established drug, LE faces increasing competition from newer agents:
- Biologic and non-steroidal alternatives: Such as cyclosporine and lifitegrast for dry eye, which may indirectly influence inflammation management.
- Other corticosteroids: Dexamethasone and prednisolone formulations, often more potent or with different delivery modalities.
- Emerging drug delivery technologies: Sustained-release implants like dexamethasone intraocular devices threaten oral or topical corticosteroids' dominance.
The patent landscape significantly influences market stability. Patent expirations have led to generic entries, reducing prices, and increasing accessibility [3].
3. Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies continually evaluate corticosteroid safety, impacting prescribing patterns. Recent guidelines emphasize tailored dosing to minimize adverse effects, which may influence market size positively by encouraging the development of formulations with improved safety profiles.
Post-approval, market expansion can be hindered or facilitated depending on regulatory hurdles associated with new indications or formulations. For example, approval for pediatric use broadens the market scope, whereas restrictions on off-label uses may limit growth.
4. Formation of Strategic Alliances and M&A Activity
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly engaging in mergers and acquisitions to expand ophthalmic portfolios. For example, Alcon’s acquisition of Novartis’ ophthalmology division, including LE-related assets, bolstered their market presence [4]. Strategic licensing agreements for LE formulations and combination therapies further influence market expansion and innovation.
5. Geographic Expansion
The majority of LE sales originate from North America and Europe. Emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East show promising growth due to expanding healthcare infrastructure, rising ophthalmic disease prevalence, and improving drug affordability. Local regulatory approvals and manufacturing partnerships are pivotal for market penetration.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Projections
Historical Performance
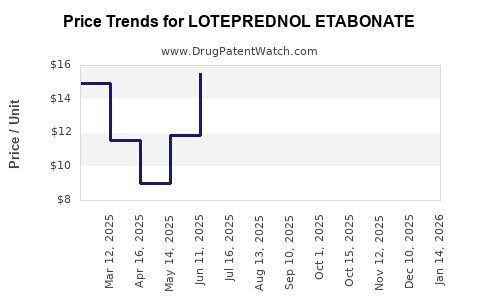
LE's revenue peaked shortly after its launch, driven by its clinical efficacy and favorable safety profile. However, revenue growth has plateaued due to patent expirations and the entry of generics in key markets, which significantly reduce per-unit prices.
Forecasted Growth
Analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 3-5% over the next five years, considering:
- Emerging market expansion: Anticipated 6-8% CAGR, driven by increased ophthalmic healthcare access.
- Product innovation: Development of novel delivery systems and formulations could stimulate demand.
- Competitive pressures: The entry of generics and biosimilars may compress margins but expand overall volume.
Risk Factors
Key risks that could impair financial growth include:
- Competitive drug launches with superior safety or efficacy.
- Regulatory sanctions affecting safety reporting or approval for new uses.
- Pricing pressures aimed at reducing healthcare costs.
- Patent litigations, which may delay or block market access for new formulations.
Strategic Opportunities
Investments in biotech collaborations for drug delivery innovations, as well as geographic expansion, particularly into underserved markets, present notable growth avenues. Furthermore, lifecycle management strategies—such as reformulations or combination therapies—could renew market interest and extend competitive advantage.
Conclusion
LE’s market and financial trajectory are shaped by its clinical profile, competitive pressures, regulatory landscape, and strategic expansion efforts. Despite challenges from patent expirations and competition, its established safety profile, strategic innovation, and geographic expansion opportunities support a moderate growth outlook. Stakeholders must continuously adapt to technological and regulatory developments to maximize LE's commercial potential.
Key Takeaways
- Market stability relies on LE's safety profile, but generic competition is exerting downward pressure on pricing.
- Emerging markets offer growth prospects, fueled by increasing ophthalmic diseases and healthcare infrastructure.
- Innovation in drug delivery systems and combination formulations can extend LE’s lifecycle and improve market share.
- Regulatory considerations will remain critical, especially regarding safety assessments and approvals for new indications.
- Strategic collaborations and geographic expansion are pivotal for sustaining growth amid competitive pressures.
FAQs
1. How does loteprednol etabonate differ from other corticosteroids?
LE is designed for targeted action with a rapid metabolism profile, resulting in fewer side effects such as intraocular pressure elevation. Its ester-based structure undergoes rapid hydrolysis, offering a favorable safety profile [2].
2. What are the main indications for LE?
LE is primarily administered for postoperative ocular inflammation, allergic conjunctivitis, keratitis, and anterior segment inflammation due to its potent anti-inflammatory properties with minimal systemic absorption.
3. How has patent expiration affected LE's market performance?
Patent expirations have led to increased generic competition, reducing prices and influencing revenue streams but also expanding access and volume sales, especially in cost-sensitive regions.
4. What innovation trends could impact LE’s future market share?
Advancements in sustained-release implants, preservative-free formulations, and combination therapies are likely to influence its market share by enhancing efficacy, safety, and patient compliance.
5. Which regions are expected to be key growth drivers for LE?
North America and Europe currently dominate sales, but Asia-Pacific and Latin America are emerging as critical growth markets due to increasing ophthalmic disease burden and healthcare investments.
References
[1] Research and Markets. (2022). Global Ophthalmic Corticosteroids Market Analysis.
[2] Patel, A., & Shah, S. (2021). Advances in Corticosteroid Technologies in Ophthalmology. Journal of Clinical Ophthalmology.
[3] FDA. (2020). Patent and Exclusivity Information for Ophthalmic Drugs.
[4] Alcon. (2021). Strategic Acquisition of Novartis Ophthalmology Assets.