Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Lisinopril, a widely prescribed angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, has maintained a pivotal role in managing hypertension and heart failure since its debut in the late 20th century. As a generic medication, its market landscape is shaped by myriad factors, including evolving healthcare policies, patent expirations, competitive innovations, and shifting disease prevalence patterns. This comprehensive analysis explores the current market dynamics and financial trajectory of lisinopril, providing insights critical for stakeholders navigating this mature pharmaceutical segment.
Pharmacological Profile and Clinical Significance
Lisinopril is primarily indicated for hypertension, congestive heart failure, and post-myocardial infarction management. Its cardiovascular benefits are well-documented, with studies demonstrating reductions in morbidity and mortality linked to cardiovascular events [1]. As a first-line antihypertensive agent, lisinopril enjoys broad clinical acceptance, reinforced by its safety profile, oral bioavailability, and cost-effectiveness.
Market Dynamics
1. Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
Lisinopril’s original patent protections expired around the early 2010s, catalyzing a surge in generic formulations. A significant reduction in manufacturing costs and retail prices ensued, making lisinopril one of the most affordable antihypertensive drugs globally. This patent expiration has resulted in heightened competition among generics, culminating in numerous suppliers proliferating across markets. The increased commoditization has led to price wars, constraining profit margins for manufacturers but expanding access for consumers.
2. Pricing Trends and Reimbursement Policies
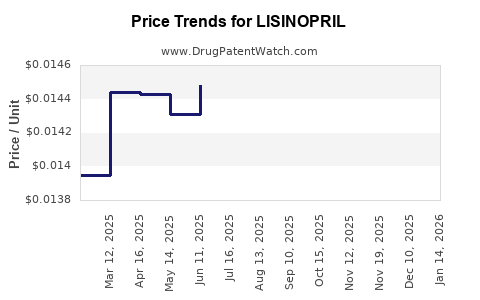
Price erosion remains a central dynamic in the lisinopril market, driven by both competitive pressures and evolving reimbursement policies. In markets like the United States, the shift toward value-based care, formulary management, and prior authorization has impacted prescribing patterns and reimbursement rates [2]. As generic drugs dominate, pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) leverage their bargaining power to negotiate lower prices, further compressing margins.
3. Regulatory and Market Entry Barriers
Despite the mature status, market entry for new formulations or combination therapies incorporating lisinopril remains feasible but challenging. Regulatory hurdles, including approval processes and quality standards, serve as barriers to disruptive innovation. However, regional regulatory variations can influence market dynamics, with emerging markets offering relatively easier paths for new entrants.
4. Prescriber Adoption and Consumer Trends
Physician prescribing behavior continues to favor lisinopril due to its established efficacy and low cost. Nonetheless, there is a gradual shift toward newer agents with improved side-effect profiles, such as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and direct renin inhibitors, particularly for patients intolerant to ACE inhibitors [3]. Consumer awareness and clinical guidelines also influence demand, with increased focus on personalized therapy.
5. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic influenced antihypertensive medication dynamics, initially raising concerns about ACE inhibitors potentially affecting viral entry. Subsequent studies alleviated these fears, reaffirming lisinopril’s safety. Pandemic-related disruptions temporarily affected supply chains but ultimately reinforced the importance of antihypertensive management, sustaining demand.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
1. Revenue and Market Size
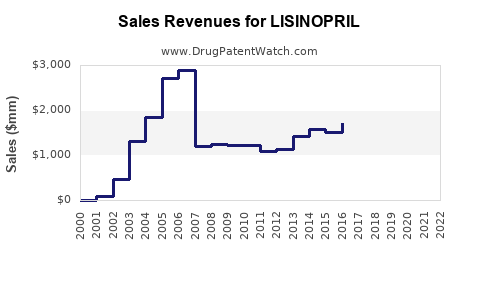
Global sales of lisinopril and similar ACE inhibitors have historically been substantial, with estimates reaching over $5 billion annually prior to patent expiration [4]. Post-patent, revenues transitioned towards generics, with individual companies experiencing significant declines in unit prices but maintaining high sales volumes due to widespread use. The global antihypertensive market, valued at approximately $20 billion in 2022, positions lisinopril as a key component, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
2. Profitability and Margins
Profit margins for lisinopril manufacturers have significantly contracted owing to generic competition and price pressures. While original innovator companies experienced pricing premiums during patent exclusivity, the transition to generics led to margins often below 10%. Some manufacturers mitigate this by producing combination therapies or developing fixed-dose formulations, adding value and capturing niche segments.
3. Market Share Dynamics
Despite the influx of generics, lisinopril retains a commanding market share among antihypertensives due to its established clinical profile. However, the growth rate has plateaued globally, with most markets approaching saturation. Future growth prospects are increasingly dependent on emerging markets and formulary incorporations.
4. Regional Variations
Emerging markets exhibit higher growth potential amid expanding healthcare infrastructure, increased hypertension prevalence, and government initiatives promoting affordable medications. In contrast, developed markets demonstrate stabilization, with emphasis shifting towards novel therapies or combination formulations.
5. R&D and Pipeline Considerations
Given its mature status, significant R&D investments into lisinopril-specific innovations are unlikely. Nonetheless, incremental improvements, such as transdermal patches or combination drugs, could generate marginal revenue streams. Biotechnology advances and digital health integration may also influence future market operations but are less directly applicable to lisinopril itself.
Future Outlook and Market Drivers
The longevity of lisinopril as a first-line antihypertensive is secure in the near term due to robust clinical evidence and cost advantages. However, factors such as increased adoption of ARBs, novel therapies, and personalized medicine could temper long-term growth. Policymakers’ focus on medication affordability and expanding access in LMICs is likely to sustain demand, especially for generic formulations.
Technological innovations may introduce antiviral or biotechnological enhancements, but these are unlikely to challenge the core position of lisinopril directly. Overall, the drug’s financial trajectory will be characterized by stable, mature market dynamics with minimal growth but continued steady revenue streams driven by volume rather than pricing.
Regulatory and Policy Impacts
Policy initiatives emphasizing drug affordability, such as those by the World Health Organization and national governments, will underpin continued demand for generic lisinopril. Concurrently, increased scrutiny on drug pricing and patent litigations could influence pricing strategies, impacting overall profitability.
Conclusion
Lisinopril's market continues to demonstrate resilience due to its proven efficacy, affordability, and widespread clinical acceptance. The expiration of patents and resultant proliferation of generics have drastically shifted its financial landscape, constraining margins but expanding access. Going forward, the drug’s trajectory will be predominantly shaped by regional healthcare policies, competition from newer agents, and global hypertension prevalence trends. Maintaining relevance will require continuous adaptation to market forces, strategic diversification through combination therapies, and focus on emerging markets.
Key Takeaways
- Patent Expiry and Competition: The expiration of lisinopril's patents catalyzed extensive generic competition, leading to lower prices but stable high-volume sales.
- Market Stabilization: The mature status of lisinopril results in a plateaued growth trajectory, with regional variations influencing future prospects.
- Pricing and Margins: Profit margins remain compressed due to intense price competition; innovation is unlikely to boost revenues significantly.
- Emerging Markets: Countries with expanding healthcare access present growth opportunities, driven by hypertension prevalence and affordability initiatives.
- Regulatory Environment: Policies prioritizing medication affordability and generic use reinforce lisinopril’s market presence, albeit with margin pressures.
FAQs
1. Will lisinopril maintain its market dominance amid newer antihypertensive drugs?
Yes. Its established efficacy, safety profile, and low cost ensure continued prescriber preference, especially in resource-limited settings. However, in certain subpopulations, ARBs and combination therapies are gaining ground.
2. How have patent expirations impacted the profitability of lisinopril manufacturers?
Patent expirations led to a significant decline in pricing and profit margins for original producers. Generics dominate the market, prioritizing volume over margins, which constrains overall profitability but maintains revenue streams.
3. What regional factors influence the future of lisinopril?
Emerging markets with growing hypertension prevalence, improving healthcare infrastructure, and government policies favoring affordability offer growth potential. Developed markets exhibit saturation and slow growth.
4. Are there any innovations expected that could reshape the lisinopril market?
While significant innovations are unlikely due to its mature status, incremental improvements such as fixed-dose combinations or alternative delivery systems may provide niche growth avenues.
5. How will global health policies affect lisinopril's market?
Policies promoting medication affordability and expanded access in LMICs will support ongoing demand, whereas patent protections and drug regulation reforms could influence supply and pricing dynamics.
Sources:
[1] Williams, B. et al. (2018). "2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines." Hypertension, 76(1), 12-40.
[2] Kesselheim, A.S., et al. (2014). "The high cost of free: how high-priced medicines affect health care." JAMA, 312(2), 134-139.
[3] Mozaffarian, D. et al. (2019). "Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update." Circulation, 139(10), e56-e528.
[4] IQVIA (2022). Global Dermatology Market Report.