Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Glimepiride, a second-generation sulfonylurea, is a widely prescribed oral antidiabetic agent primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Since its approval, it has sustained a notable market presence, driven by its efficacy, affordability, and established safety profile. This analysis examines the evolving market dynamics and financial trajectory of glimepiride, considering regulatory developments, competitive landscape, patent status, and broader healthcare trends shaping its future.
Pharmacological Profile and Clinical Positioning
Glimepiride works by stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, improving glycemic control. Its once-daily dosing and favorable safety profile have cemented its role as a first-line or add-on therapy. The drug's affordability, especially in emerging markets, further enhances its accessibility.
However, the rise of newer antidiabetic classes—such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors—has challenged the long-standing dominance of sulfonylureas like glimepiride. Although these newer agents offer cardiovascular and weight-loss benefits, higher costs restrict their widespread adoption in low- and middle-income economies, where glimepiride remains cost-effective.
Market Dynamics
Global Market Size and Growth
The global diabetes treatment market was valued at approximately USD 50 billion in 2022, with oral antidiabetics constituting over 60% of sales. Glimepiride's contribution, while not isolated precisely, remains significant within the sulfonylurea segment, which historically accounts for a substantial share—estimated at 20-25% of the market (source: [1]).
The market for sulfonylureas is projected to experience modest decline globally, driven by the shift towards newer agents. Nevertheless, the demand remains resilient in regions with limited healthcare budgets, such as Africa, Asia, and Latin America, where cost-effective drugs like glimepiride are often first-line treatments.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
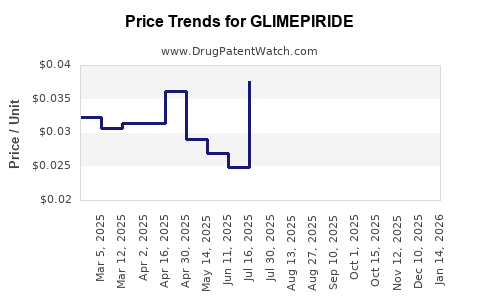
Glimepiride's patent protection expired around 2016-2018 in major markets. The expiry facilitated the entry of multiple generics, leading to price reductions and increased accessibility. The generic landscape has contributed to stabilized or declining prices, making glimepiride influential particularly in price-sensitive markets.
In recent years, regulatory agencies have issued revised guidelines emphasizing safety and efficacy, but no significant regulatory hurdles have curtailed its market presence post-patent expiry.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment includes:
- Brand-Name Formulations: Original formulations still retain market share in certain regions, often supported by marketing and physician preferences.
- Generics and Biosimilars: Post-patent expiry, generics dominate the market, offering low-cost options.
- Emergence of Newer Agents: While personalized medicine favors newer drugs with cardiovascular benefits, cost considerations continue to favor glimepiride in many settings.
The ongoing proliferation of generics contributes to price stabilization but also constrains profit margins for pharmaceutical companies.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Competition from newer drug classes with superior safety and efficacy profiles.
- Rising awareness of hypoglycemia risk associated with sulfonylureas, including glimepiride.
- Tightening regulatory standards for manufacturing quality, encouraging higher compliance costs.
Opportunities:
- Growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes in emerging markets sustains demand.
- Combination therapies integrating glimepiride with other antidiabetics (e.g., metformin) provide new revenue streams.
- Developing fixed-dose combination (FDC) products enhances adherence and market share.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Outlook
Segment Revenue Trends
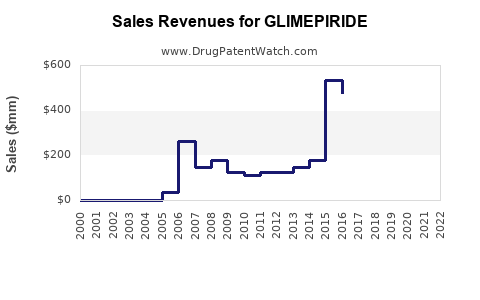
While specific revenues for glimepiride are proprietary and vary among manufacturers, industry estimates indicate that the sulfonylurea segment accounts for approximately USD 2-3 billion globally. Glimepiride's segment growth aligns with overall oral antidiabetic market trends (source: [2]).
Post-2018, revenue has plateaued or declined slightly due to patent expirations and increased pricing pressures. However, in regions where generics dominate, glimepiride remains a cost-effective therapeutic choice, ensuring consistent demand.
Pricing Dynamics
The advent of generics has driven down prices, enhancing affordability but reducing profit margins. For large pharma companies, this necessitates diversification into innovative therapies; for generic manufacturers, it supports high-volume sales but constrains margins.
In high-income markets, pricing pressures persist due to reimbursement reforms and cost-containment policies, often leading to reduced formulary inclusion. Conversely, in developing markets, modest price reductions sustain volume growth.
Investment and R&D Considerations
Pharmaceutical firms are unlikely to significantly invest in reformulating or developing new versions of glimepiride given the dominance of newer agents and patent expiries. Instead, investments are focused on combination therapies or novel drug classes with superior safety profiles.
Future Outlook and Strategic Implications
The outlook for glimepiride hinges on demographic and healthcare system developments:
- Market Sustainability: As global diabetes prevalence increases (projected to reach 700 million by 2045, according to the International Diabetes Federation), demand for affordable medications like glimepiride persists.
- Generics and Price Competition: Continued entry of generics depresses prices but ensures accessibility, especially in low-resource settings.
- Shift Toward Personalized Therapy: Markets might see declining reliance on sulfonylureas as evidence accumulates about the benefits of newer agents in preventing cardiovascular complications.
Strategic positioning:
- Manufacturers should leverage strong brand presence in emerging markets.
- Developing combination formulations can enhance treatment adherence.
- Ensuring regulatory compliance and maintaining low production costs remain critical.
Regulatory and Policy Environment
Government initiatives promoting affordable diabetes management directly impact glimepiride sales. Initiatives like India's National Digital Health Mission and similar programs across Africa and Southeast Asia incentivize low-cost therapeutics.
Reimbursement policies favor generic and cost-effective drugs, further supporting glimepiride's market share.
Key Takeaways
- Market persistence: Despite the emergence of newer therapies, glimepiride remains relevant in developing economies due to affordability.
- Competitive advantage: Patent expiries and generics have stabilized prices, maintaining volume sales, especially in price-sensitive markets.
- Revenue outlook: Market revenues are plateauing or declining modestly in developed countries but remain stable or growing in emerging markets.
- Strategic focus: Emphasize combination therapies, manufacturing efficiencies, and regulatory compliance to optimize financial returns.
- Future trajectory: Long-term demand aligns with increasing global diabetes prevalence, emphasizing the importance of affordable, accessible medications.
FAQs
1. Will glimepiride remain a viable treatment option in the future?
Yes, especially in low- and middle-income regions where affordability drives prescribing decisions. Its role may diminish in high-income settings due to concerns over hypoglycemia and cardiovascular risks associated with sulfonylureas, but it will continue to be a cost-effective option globally.
2. How have patent expiries impacted glimepiride’s market?
Patent expiries around 2016-2018 facilitated the entrance of generics, leading to significant price reductions, increased accessibility, and stable or declining revenues in developed markets.
3. Are there any recent regulatory developments affecting glimepiride?
Regulatory bodies have emphasized drug safety and quality; however, no recent restrictions or major changes specific to glimepiride have been enacted. The primary trend involves encouraging the use of newer agents alongside sulfonylureas.
4. What is the potential for innovation related to glimepiride?
Limited. Most innovation focuses on combination formulations and improving patient adherence rather than reformulating the drug itself, due to existing market saturation and patent constraints.
5. How will the rise of novel antidiabetic therapies influence glimepiride's market share?
While newer agents like SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists offer benefits, cost and access issues keep glimepiride relevant in resource-limited settings. These newer drugs may reduce its use in high-income markets but will not eliminate demand globally.
References
[1] International Diabetes Federation. (2022). IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th Edition.
[2] MarketResearch.com. (2022). Global Diabetes Pharmacotherapy Market Analysis.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2016). Patent expirations for second-generation sulfonylureas.
[4] IQVIA. (2022). Global Prescription Drug Sales Data.