Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Furosemide, a potent loop diuretic, remains a cornerstone in managing edema and heart failure. Since its introduction in the 1960s, it has maintained relevance owing to its efficacy, affordability, and widespread clinical use. This comprehensive overview assesses the evolving market landscape and financial trajectory of furosemide, considering current trends, patent status, regulatory developments, manufacturing and supply chain dynamics, and competitive influences.
Market Overview and Demand Drivers
Furosemide's global adoption is driven primarily by its role in treating conditions such as congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal edema. The rising prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) boosts demand, particularly in aging populations across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions [1].
According to IQVIA data, diuretics constitute a significant segment within the cardiovascular drugs market, with furosemide accounting for a substantial share owing to its low cost and longstanding clinical utility. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates millions of patients rely on furosemide annually, ensuring steady baseline demand.
Market Dynamics
Patent Status and Generic Competition
Furosemide's patent lifecycle ended decades ago, allowing generic manufacturers worldwide to produce and market it broadly. The absence of patent protection has resulted in intense price competition, constraining revenue streams for original developers but facilitating widespread access.
Pricing Trends
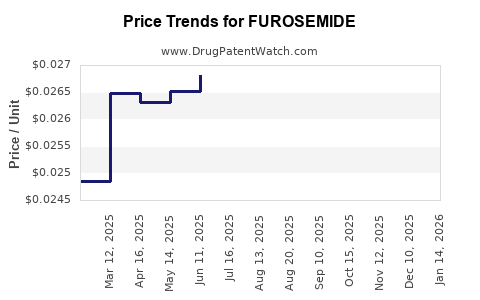
The drug’s pricing remains predominantly driven by generic competition. Analysts observe stable to declining unit prices in mature markets, though local regulatory and supply constraints can cause regional price variations. The minimal cost of production favors profit margins for manufacturers but limits significant revenue growth.
Regulatory Environment
While furosemide has transitioned to generic status, regulatory agencies continually monitor quality standards and manufacturing practices. Recent initiatives emphasize environmental impact mitigation, notably the reduction of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) waste and pharmaceutical residues in water systems, potentially influencing manufacturing costs.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Major manufacturing hubs include India, China, and Eastern Europe, offering cost-effective API production. Supply chain disruptions—accentuated by geopolitical tensions, COVID-19 pandemic effects, and raw material shortages—have intermittently affected global supplies. Companies investing in diversified supply chains and strategic stockpiles aim to mitigate these risks.
Market Penetration and Regional Variations
Demand remains robust in emerging markets due to increasing healthcare infrastructure and treatment access. However, the market faces challenges in regions where newer diuretics with better safety profiles and dosing convenience are gaining traction [2].
Financial Trajectory: Historical and Projected Trends
Historical Financial Performance
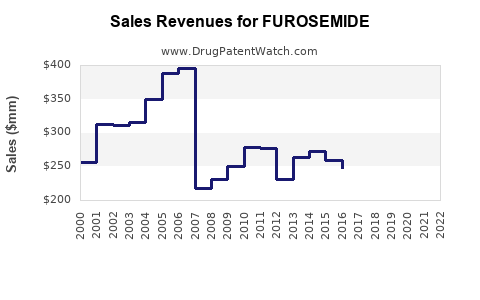
Given its patent expiry, furosemide's revenue in developed markets has plateaued or declined modestly, reflecting generic price erosion. Industry reports highlight that, in 2022, global furosemide sales are estimated to be approximately $600-700 million annually, with the majority emanating from North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific [3].
Forecasted Outlook
Analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1-2% over the next five years, primarily driven by growth in emerging markets and increasing prevalence of cardiovascular conditions. The introduction of biosimilar or derivative formulations might stimulate short-term innovation but is unlikely to dramatically alter revenue streams due to existing generic saturation.
Impact of Potential Regulatory Changes
Regulatory initiatives targeting environmental sustainability and drug residues could introduce costs, possibly marginally influencing profit margins. Conversely, streamlined approval pathways for established drugs might facilitate formulations’ minor modifications, opening secondary revenue avenues.
Pricing and Market Share Projections
Gains in market share are limited due to commoditization. Price reductions driven by intense generic competition are expected to persist, constraining profit margins. However, regional expansion into underserved markets and potential inclusion in combination therapies may offer incremental revenue opportunities.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
Global manufacturers include Teva Pharmaceuticals, Sandoz, Mylan (now part of Viatris), Sun Pharmaceutical, and local players in India and China. These companies benefit from established manufacturing infrastructure and extensive distribution channels.
Market Entry Barriers
High regulatory barriers in mature markets, coupled with competitive pricing, deter new entrants. However, regional manufacturers targeting emerging markets experience growth opportunities due to lower barriers to entry and local demand.
Innovation and Derivative Development
To extend lifecycle and enhance safety, companies explore formulations such as extended-release tablets, combination therapies, and alternative diuretics. Nonetheless, furosemide’s fundamental pharmacology limits the scope for transformational innovation.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Regulatory push toward reducing environmental footprints prompts manufacturers to adopt greener APIs and sustainable manufacturing practices. This transition may increase production costs but enhance compliance and brand reputation.
Digital and Digital-Enabled Supply Strategies
Manufacturers leverage digital tracking and supply chain analytics to enhance resilience. Digitization also allows better forecasting, preventing shortages and optimizing inventory management.
Personalized Medicine and Market Segments
While current usage relies on standardized dosing, future integration with personalized medicine remains limited, given the drug's well-established pharmacodynamics.
Key Challenges and Opportunities
- Challenges: Price erosion, patent expiration effects, regional demand disparities, regulatory compliance costs, environmental regulations, and competition from newer diuretics.
- Opportunities: Growing demand in emerging markets, increased global healthcare access, incremental formulations, and environmental compliance strategies.
Conclusion
Furosemide’s market remains stable, characterized by high generic competition and flat revenue streams. While growth prospects are modest, the drug persists as an essential, cost-effective therapy globally. Strategic focus on supply chain resilience, regional expansion, and environmental compliance will shape its financial trajectory’s future nuances.
Key Takeaways
- Furosemide's global demand sustains despite intense generic competition constraining revenue growth.
- Market growth is primarily driven by aging populations, rising cardiovascular disease prevalence, and emerging market penetration.
- Cost-driven manufacturing in Asia underpins supply chain stability, with environmental regulations posing future operational considerations.
- Competitive landscape dominated by established generic manufacturers, with limited scope for innovation but opportunities in formulation enhancements.
- Long-term financial prospects hinge on regional expansion, supply chain management, and adapting to regulatory and environmental trends.
FAQs
-
How does patent expiry influence furosemide's market?
Patent expiry in the 1970s facilitated the entry of generic manufacturers, resulting in a saturated market with price-driven competition and stabilized revenues for original companies.
-
Are there any recent regulatory concerns impacting furosemide?
Environmental regulations aiming to reduce pharmaceutical residues in water systems are expected to influence manufacturing practices and costs but have not directly restricted market access.
-
What regions exhibit the fastest growth in furosemide demand?
Emerging markets like India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa show the highest growth potential due to expanding healthcare access and increasing CVD prevalence.
-
Could innovative formulations revitalize the furosemide market?
While formulation improvements like extended-release versions can enhance safety and compliance, they are unlikely to generate significant revenue due to the drug’s widespread availability and low cost.
-
What impact has COVID-19 had on furosemide supply and sales?
The pandemic caused supply chain disruptions, affecting production and distribution; however, demand remained steady owing to the drug's essential status, prompting companies to enhance supply chain resilience.
References
[1] IQVIA. "Global Diuretics Market Analysis." 2022.
[2] World Health Organization. "Cardiovascular Disease and Diuretic Use." 2021.
[3] PharmaMarketWatch. "Furosemide: Market Trends and Forecast." 2023.