Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Fluoxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), is renowned for its application in treating depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, and bulimia nervosa. First approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1987 under the trade name Prozac, fluoxetine has since become a cornerstone in psychopharmacology. Its market dynamics and financial trajectory are shaped by evolving clinical evidence, regulatory landscape, patent status, generics entry, and shifting healthcare paradigms.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Growth
The global antidepressant market, in which fluoxetine commands a significant share, was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3.5-4.0% through 2030, driven by increasing mental health awareness, demographic shifts, and expanding healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets. Fluoxetine remains a dominant product owing to its established efficacy and safety profile.
Prevalence of Depression and Related Disorders
Depression affects over 264 million people worldwide, according to WHO data, underpinning the sustained demand. The rise in mental health disorders, exacerbated by pandemic-related stress and social isolation, has reinforced the necessity for effective pharmacotherapy. Consequently, fluoxetine's long-standing usage position sustains its relevance.
Market Dynamics
Efficacy and Safety Profile
Fluoxetine's favorable safety profile, long-term data, and once-weekly dosing make it a preferred choice among clinicians. Its patent expiration in major markets led to widespread generic availability, influencing pricing and market share. The drug's patent expiry in the early 2000s precipitated a shift toward generics, sharply reducing medication costs and expanding accessibility.
Regulatory Environment and Patent Expiry Impact
The original patent for Prozac expired circa 2001 in the U.S., prompting multiple generic manufacturers to introduce bioequivalent versions. The resulting price competition significantly impacted the brand's revenue and shifted market dynamics toward generics. Nonetheless, specific formulations, patents on extended-release versions, and secondary patents temporarily buffered exclusivity for certain products.
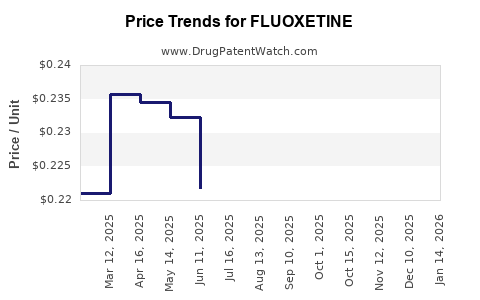
Generic Competition and Pricing Trends
The proliferation of generics has driven down prices substantially—by as much as 80-90% in some markets—altering the profit landscape for originators. Despite this, branded formulations have maintained niche markets, particularly where clinicians prefer specific formulations or proprietary delivery systems.
Emergence of Biosimilars and New Therapies
While biosimilars are prevalent in biological therapeutics, the psychotropic space remains dominated by small molecules like fluoxetine. Nevertheless, newer agents with faster onset, fewer side effects, or novel mechanisms have emerged, challenging fluoxetine’s dominance in specific indications.
Market Penetration in Developing Regions
Growing healthcare infrastructure and awareness present opportunities in emerging markets like India, China, and Latin America. As antidepressant awareness increases, trade channels expand, making generic fluoxetine increasingly accessible and boosting sales volume.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
Historical Revenue Trends
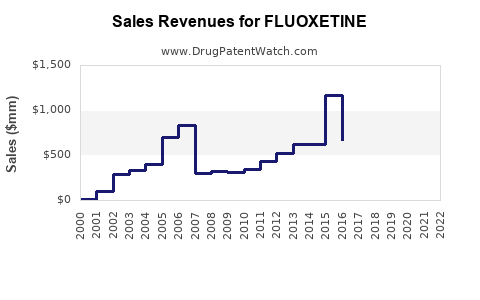
Initially, the branded fluoxetine sales peaked in the late 1990s, with Prozac generating over $1 billion annually at its height. Post patent expiry, revenue sharply declined due to generic competition, with recent estimates suggesting global sales of branded formulations have diminished to below $200 million annually.
Current Revenue Streams
Today, the bulk of fluoxetine revenue derives from generic sales, which are highly price-competitive. The primary revenue stems from established generic manufacturers; branded markets are limited mostly to niche therapeutic uses or formulations with secondary patents.
Profitability and Pricing
The profit margins on fluoxetine have compressed considerably due to generics’ entry. However, high-volume sales sustain overall revenue streams. The high degree of manufacturing standardization, coupled with minimal R&D costs post-original development, results in relatively low marginal costs.
Forecasting Future Trends
Market forecasts indicate steady demand in mental health markets with potential growth in regions with increasing mental health awareness. However, the influence of newer antidepressants, combination therapies, and possibly personalized medicine approaches could attenuate fluoxetine’s growth.
Influencing Factors on Market and Financial Trajectory
- Regulatory Approvals: Approval of formulations with improved safety profiles or delivery methods could renew interest.
- Patent Litigation and Legal Battles: Patent disputes over secondary patents can temporarily extend exclusivity.
- Healthcare Policy Changes: Initiatives promoting generic prescribing and price regulation impact revenue.
- Evolving Clinical Guidelines: Increased preference for psychotherapy or newer pharmacological agents may influence prescribing patterns.
Risks and Opportunities
Risks:
- Market saturation due to generic proliferation.
- Competition from newer antidepressants with novel mechanisms.
- Regulatory pressures limiting pricing flexibility.
Opportunities:
- Expansion into emerging markets.
- Development of new formulations, such as sustained-release versions.
- Potential repositioning for treatment of other indications, such as premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
Key Takeaways
- Dominance of fluoxetine has diminished post-patent expiry but remains significant due to established efficacy and cost advantages of generics.
- The global antidepressant market is projected to grow modestly, with fluoxetine positioned to benefit from expanding mental health needs, particularly in emerging regions.
- Price erosion from generics and competitive dynamics necessitate strategic focus on niche formulations, differentiated delivery, and emerging markets.
- Future revenue prospects hinge on regulatory developments, evolving prescribing trends, and potential indications expansion.
- Market players should monitor patent landscapes, formulary decisions, and clinical guideline shifts to navigate fluoxetine's financial trajectory effectively.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected fluoxetine's market share?
Patent expiry in the early 2000s led to a surge in generic versions, drastically reducing prices and shifting market share from branded to generic manufacturers. While the original brand's revenue declined, overall market growth persisted through increased accessibility and volume.
2. What are the primary driving forces behind fluoxetine's continued demand?
Persistent mental health issues globally and fluoxetine's proven efficacy, safety profile, and affordability sustain demand. Expansion in emerging markets further bolsters consumption.
3. Are there new formulations of fluoxetine entering the market?
Yes. Extended-release formulations and combination therapies are under development or approval, aiming to improve adherence and therapeutic outcomes.
4. How does competition from newer antidepressants impact fluoxetine’s market?
Newer agents with faster onset, fewer side effects, or broader indications may displace fluoxetine in certain clinical scenarios, though cost and familiarity support its continued use.
5. What strategic moves should pharmaceutical companies consider for fluoxetine's future?
Companies should explore niche markets, develop innovative formulations, seek new indications, and target emerging markets to sustain revenue streams amid competition.
References
[1] WHO. Depression. World Health Organization. 2022.
[2] MarketsandMarkets. Antidepressants Market by Type, Route of Administration, Distribution Channel, Region - Global Forecast to 2030. 2022.
[3] U.S. FDA. Approval history of Prozac (fluoxetine). 1987-2001.
[4] Datamonitor. Pharmacoeconomic assessments of antidepressants. 2021.
[5] IQVIA. Global Pharmaceutical Market Reports. 2022.