Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Finasteride, a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor, has established itself as a cornerstone in managing benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness). Since its initial approval in the late 1990s, the drug’s market landscape has evolved amid shifting regulatory, demographic, and competitive factors. This analysis dissects finasteride’s current market dynamics, evaluates its financial trajectory, and discusses future growth prospects for stakeholders.
Market Overview
Finasteride’s approval for BPH (originally marketed as Proscar) occurred in 1992, followed by its indication for androgenetic alopecia in 1997 (marketed as Propecia). The drug's success stems from its dual indication profile, targeting widespread conditions affecting aging male populations.
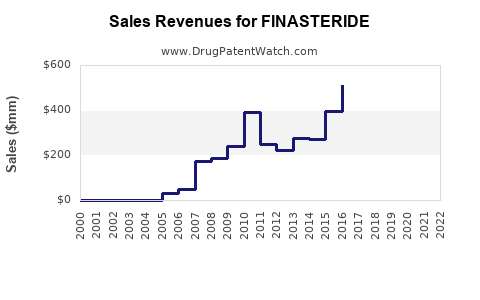
The global market for finasteride was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2022, with expectations of a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 4-5% over the subsequent five years. This growth is driven primarily by increasing prevalence rates, expanding indications, and evolving treatment paradigms.
Market Drivers
1. Demographic Shifts and Aging Population
The aging male demographic is expanding globally, especially in emerging economies. According to United Nations projections, the proportion of men aged over 60 will increase worldwide, amplifying demand for BPH and alopecia treatments. Finasteride remains a first-line therapy, bolstered by these demographic trends.
2. Rising Awareness and Diagnostic Rates
Improved awareness regarding androgenetic alopecia and BPH, coupled with increased healthcare access, contributes to higher diagnosis rates. This, coupled with clinician familiarity, sustains finasteride prescribing volumes.
3. Competitive Landscape and Patent Status
As no patents for finasteride for BPH or alopecia have been active since the early 2000s, generic versions dominate the market, intensifying price competition but expanding accessibility.
4. Regulatory Developments
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, have maintained finasteride’s approval for its licensed indications, but ongoing safety concerns influence prescriber patterns.
Market Challenges
1. Safety Concerns and Side Effect Profiles
Long-term safety concerns, including adverse effects such as sexual dysfunction, depression, and hormonal changes, have impacted patient adherence and prescriber confidence. The FDA issued warnings about persistent sexual dysfunction post-discontinuation (Post-Finasteride Syndrome), leading to cautious use.
2. Competition from Alternative Therapies
Emerging treatments, including minoxidil formulations, dutasteride (another 5-alpha reductase inhibitor with broader enzyme inhibition), and non-pharmacological interventions, challenge finasteride’s market share.
3. Generic Penetration and Price Erosion
The expiry of patents led to widespread generic availability, causing significant price erosion. Although this boosts access, it compresses profit margins for manufacturers.
4. Patent and Market Exclusivity Outlook
No major patent protections are in effect, and the landscape favors increased generic proliferation, limiting brand-specific revenues.
Financial Trajectory
1. Revenue Trends
Given market saturation for BPH and the mature status of alopecia indications, finasteride’s revenues are expected to stabilize or decline marginally over the coming years. However, geographic expansion, especially into emerging markets, and increased off-label use could mitigate declines.
2. Pricing Dynamics
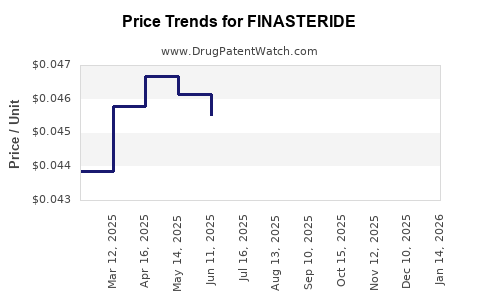
The widespread availability of generics has driven prices downward. In mature markets like the US and EU, average prices per unit have declined by approximately 30-50% since patent expiry.
3. Cost Structures and Profitability
Manufacturers experience reduced R&D outlays post-patent expiry, focusing instead on manufacturing efficiencies and marketing. Margins are expected to be compressed, though volume growth can offset pricing pressures.
4. Market Penetration in Emerging Economies
Rapid growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where healthcare expenditure increases, and awareness amplifies. Local regulations and reimbursement policies will influence these trajectories.
5. Future Revenue Opportunities
Potential revenue streams include combination therapies, new formulations (e.g., topical or sustained-release), and repurposing for other androgen-related conditions, although evidence and approval statuses remain variable.
Regulatory and Patent Outlook
Federal agencies are increasingly attentive to safety profiles, especially regarding long-term adverse effects. While no active patents hinder generic competition, innovative delivery methods or new indications could provide opportunities for patenting and premium pricing.
Competitive Landscape
Market leadership is fragmented among generic manufacturers, with dominant players including Teva, Mylan, and Sandoz. Brand loyalty has diminished due to patent expirations, though branded formulations retain niche markets driven by patient preference for specific formulations or perceived quality.
Dutasteride, marketed as Avodart, presents a significant competitor with broader enzyme inhibition (type 1 and 2 5-alpha reductase). Its indication for BPH and off-label use for alopecia sustains competitive dynamics.
Future Market and Financial Outlook
Considering demographic trends, increasing global healthcare access, and ongoing research, finasteride’s market will remain substantial, particularly in markets with aging populations. However, revenue growth opportunities are constrained by patent expiries and consumer safety concerns.
Forecasts suggest that in the next five years, the global finasteride market will experience a compound annual growth rate of approximately 2-3%, driven predominantly by emerging markets. Innovative formulations, combination therapies, and expanded indications may serve as growth inflections.
Key Takeaways
- Market stability for finasteride is primarily underpinned by demographic shifts and increasing awareness, though faces headwinds from safety concerns and competition.
- Generics dominate sales post-patent expiry, compressing profit margins but expanding accessibility.
- Emerging markets represent a critical growth frontier, with rising healthcare investments and shifting patient demographics.
- Future innovation—such as topical formulations or combination therapies—may provide selective growth avenues.
- Safety warnings remain a significant factor influencing prescriber and patient confidence, impacting long-term market penetration.
FAQs
1. What are the primary indications for finasteride?
Finasteride is approved for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness).
2. How has patent expiry impacted finasteride's market?
Patent expiration has led to the proliferation of generic versions, significantly reducing prices and compressing profit margins, but expanding access.
3. What safety concerns are associated with finasteride?
Long-term use has been linked to sexual dysfunction, depression, hormonal disturbances, and persistent post-discontinuation effects collectively termed Post-Finasteride Syndrome.
4. Which markets are expected to drive future growth?
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa, driven by demographic shifts and increased healthcare access, will contribute significantly.
5. Are there upcoming innovations or alternative therapies for finasteride’s indications?
Research into topical formulations and combination regimes is ongoing, offering potential for differentiation, though regulatory and safety considerations remain pivotal.
Sources
- [1] MarketResearch.com, “Global Finasteride Market Size & Trends,” 2022.
- [2] FDA Drug Database, “Finasteride (Proscar, Propecia),” 2023.
- [3] United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, “World Population Prospects,” 2022.
- [4] European Medicines Agency, “Safety Communications on Finasteride,” 2021.
- [5] PharmaIntelligence, “Post-Patent Generics Market Analysis,” 2023.