Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Efavirenz, marketed primarily under the brand name Sustiva, is an antiretroviral medication pivotal in the management of HIV/AIDS. Since its approval in the early 2000s, efavirenz has played a crucial role in fixed-dose combination therapies, transforming HIV treatment paradigms. This analysis explores the evolving market dynamics and projected financial trajectory for efavirenz, factoring in patent landscapes, manufacturing trends, competitive pressures, and emerging therapies.
Product Overview and Clinical Significance
Efavirenz is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) that blocks HIV replication. It is typically prescribed with other antiretrovirals as part of combination regimens. Its once-daily dosing and high efficacy have established it as a standard component of first-line regimens, especially in resource-constrained settings due to cost-effectiveness.
Market Landscape and Key Drivers
Global HIV/AIDS Burden and Therapeutic Demand
According to UNAIDS, approximately 38 million people worldwide live with HIV/AIDS, with an annual new infection rate of roughly 1.5 million [1]. The high prevalence sustains substantial demand for antiretroviral therapies (ART), including efavirenz-based regimens. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends efavirenz as part of first-line therapy in many settings, reinforcing its clinical significance.
Patent Status and Generic Competition
Initially patent-protected, efavirenz's patent expiration varied geographically. In the United States, the patent expired around 2018, facilitating the entry of generic manufacturers, notably Mylan and Aurobindo, which significantly reduced therapy costs. In emerging markets, patent protections lingered longer, maintaining higher prices and margins for originator products like Bristol-Myers Squibb's Sustiva.
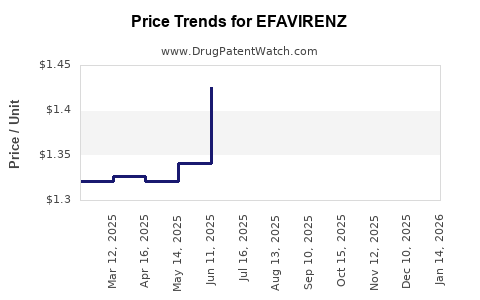
Pricing Trends and Cost Dynamics
Patent expiries ushered in aggressive price competition, dropping efavirenz's cost by up to 80% in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) [2]. This shift enhanced access but simultaneously compressed profit margins for original patent holders. High-volume sales in LMICs now dominate revenues, often subsidized by government procurement agencies and international donors.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Considerations
Manufacturers focus on cost-effective synthesis and scalable production, optimizing margins amid pricing pressures. Efforts include process innovations to reduce costs and ensure consistent supply, especially critical given the global HIV burden. Quality and biosafety standards drive manufacturing investments, with India and China emerging as key production hubs.
Regulatory and Policy Influences
Global policies increasingly favor efavirenz’s substitution with newer agents due to safety concerns associated with neuropsychiatric side effects and teratogenicity [3]. The WHO has also included alternatives like dolutegravir in first-line regimens, impacting efavirenz's market share over time.
Emerging Therapeutic Alternatives and Competitive Landscape
Shift Toward Integrase Inhibitors
Recent guidelines favor drugs such as dolutegravir and bictegravir, which demonstrate superior safety profiles, higher barriers to resistance, and fewer neuropsychiatric adverse effects. This trend constrains efavirenz's growth prospects, especially in high-income and some middle-income markets.
Development of Fixed-Dose Combinations
Advancements in fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) incorporating integrase inhibitors are gaining prominence, further diminishing efavirenz-containing regimens' share. Notably, Gilead's Biktarvy and ViiV’s Triumeq offer potent, once-daily FDCs with better tolerability.
Financial Trajectory and Forecasting
Revenue Outlook in Mature Markets
In high-income countries, efavirenz’s market share diminishes due to therapeutic shifts. Original patent holders face declining revenues, compounded by generic competition and regulatory challenges. Sales are projected to decline at a CAGR of approximately 7-10% over the next five years in these markets, barring new indications.
Growth Potential in LMICs
Conversely, in LMICs where patent protections and affordability remain conducive, efavirenz continues to generate substantial revenues. Procurement volumes are driven by international agencies such as the Global Fund and PEPFAR. The market in these regions is expected to sustain a moderate CAGR of 3-5%, supported by government programs and evolving treatment guidelines.
Impact of Biosimilars and Patent Litigation
Patent expirations have catalyzed the introduction of biosimilar efavirenz formulations, further restricting revenues of originators, especially in LMICs. Patent litigations and regulatory delays could temporarily stabilize or boost revenues for patent-holders seeking market exclusivity extensions.
Future Revenue Streams and Licensing Agreements
Potential licensing deals with generic manufacturers and bulk procurement contracts will continue shaping revenues. There remains a niche for efavirenz in combination regimens for specific populations, such as breastfeeding women, providing marginal revenue streams amid declining overall sales.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Safety and Tolerability Concerns
Side effects linked to efavirenz pose ongoing challenges, prompting pharmacovigilance and product differentiation efforts. The potential for neuropsychiatric adverse effects hampers acceptance among specific patient groups, favoring newer alternatives.
Strategic Diversification and Lifecycle Management
Patent holders explore lifecycle management options, including developing fixed-dose combinations with newer agents or positioning efavirenz in niche markets. Investment in formulations with enhanced safety profiles could rejuvenate market interest.
Policy and Funding Landscape
Global health policies increasingly favor drug regimens with better safety profiles. Funding challenges and changing guidelines are potential headwinds but also opportunities to innovate in formulation and distribution strategies, especially in underserved markets.
Key Takeaways
-
Efavirenz remains integral to HIV treatment, particularly in resource-limited settings, driven by cost-effectiveness and existing procurement channels.
-
Patent expiries have led to increased generic competition, sharply reducing prices in LMICs and constraining revenues of originator companies.
-
The emergence of integrase inhibitors and favorable treatment guidelines are accelerating efavirenz’s market decline in high-income regions.
-
Future growth hinges on regional variables—ongoing demand in LMICs sustains modest revenues, while global policy shifts favor safer, more tolerable agents.
-
Manufacturers must explore lifecycle strategies, including formulation improvements and niche applications, to mitigate revenue erosion.
Conclusion
Efavirenz’s market dynamics are characterized by significant geographic diversity, with sustained demand in low-resource regions contrasted by declining relevance in high-income markets. The financial trajectory indicates a continuing downward trend globally but presents opportunities for adaptation, especially through developing combination therapies and engaging in strategic licensing.
FAQs
1. Will efavirenz be phased out entirely in all markets?
While high-income markets are shifting away, efavirenz remains essential in LMICs due to cost advantages and established supply chains. Its complete phase-out is unlikely in the near term but will diminish further in regions adopting newer therapies.
2. How do patent expirations influence efavirenz’s market share?
Patent expirations facilitate generic manufacturing, substantially lowering prices and increasing access. This boosts volumes in LMICs but reduces revenues for original patent-holders in those regions.
3. Are there ongoing efforts to develop safer formulations of efavirenz?
Yes. Research is underway to develop formulations with improved safety profiles and reduced neuropsychiatric adverse effects, aiming to extend efavirenz's clinical relevance.
4. What is the impact of new HIV treatment guidelines on efavirenz?
Guidelines favor integrase inhibitor-based regimens, which diminishes efavirenz’s role in many settings but does not eliminate its use in cost-sensitive environments.
5. Can efavirenz regain market share through new indications?
Limited indications beyond HIV treatment are being explored, but the primary driver remains its role in standard antiretroviral regimens. Regulatory and clinical barriers exist for expanding its use.
Sources
[1] UNAIDS. Global HIV & AIDS statistics — 2022 Fact Sheet.
[2] WHO. HIV/AIDS treatment prices 2020.
[3] CDC. Efavirenz side effects and safety profile.