Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Dapsone, chemically known as diaminodiphenyl sulfone, is a synthetic antimicrobial primarily employed in treating leprosy, dermatitis herpetiformis, and various other dermatological and infectious diseases. Over the years, its market trajectory has been shaped by scientific advancements, regulatory shifts, and evolving disease prevalence. This comprehensive analysis explores the current market dynamics and forecasts the financial trajectory of dapsone, paying close attention to supply-demand patterns, regulatory influences, competitive landscape, and strategic growth opportunities.
Historical Context and Market Overview
Dapsone was first introduced in the 1950s as a critical agent for leprosy treatment. Its mechanism involves bacteriostatic activity inhibiting folate synthesis in microorganisms. While it has maintained its role in managing leprosy globally, its application scope has expanded to dermatological conditions, particularly dermatitis herpetiformis, underlining its versatility.
The global demand remained stable through the late 20th century, driven predominantly by endemic regions such as India, Brazil, and parts of Africa. Initially, market expansion was constrained by existing treatment regimens and the advent of alternative antimicrobials with better safety profiles.
Market Dynamics
1. Supply Chain and Manufacturing Factors
Dapsone's manufacturing remains concentrated within a handful of generic pharmaceutical companies, largely due to its age and the presence of established synthetic pathways. Raw material sourcing, particularly for the sulfone component and intermediates, has experienced volatility owing to fluctuating costs and geopolitical factors. The compliance landscape influenced by stringent Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and quality standards mandates consistent oversight.
2. Regulatory Landscape
Regulatory acceptance continues to impact dapsone's market trajectory significantly:
- FDA and EMA Approvals: As an off-patent drug, dapsone faces limited direct regulatory hurdles. However, formulation-specific approvals, pediatric indications, and safety updates influence marketability.
- Orphan Drug Designations: Certain jurisdictions recognize leprosy as an orphan disease, fostering incentives such as market exclusivity and funding for novel formulations.
- Safety Profile and Side Effects: Hemolytic anemia and methemoglobinemia are notable adverse effects requiring vigilant monitoring, potentially impeding widespread adoption where safety infrastructure is lacking.
3. Epidemiological and Demographic Influences
Despite the decline in leprosy globally, the disease persists in endemic pockets. The World Health Organization (WHO) reported approximately 200,000 new leprosy cases annually as of 2021, predominantly in India, Brazil, and Indonesia. The increasing incidence of dermatitis herpetiformis, especially in Western nations, sustains demand for dapsone as a first-line treatment.
4. Competitive Environment and Therapeutic Alternatives
While dapsone’s entrenched role in specific diseases remains intact, newer therapies with improved safety and efficacy profiles have emerged:
- Leprosy: Multi-drug therapy (MDT) combining dapsone with rifampicin and clofazimine continues to be standard.
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis: Dapsone remains the primary choice, but topical agents and immunomodulators are emerging alternatives.
- Infectious Diseases: Its off-label use against various anaerobic infections faces competition from macrolides, tetracyclines, and newer antimicrobials.
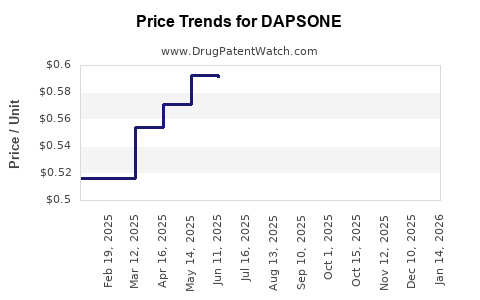
The patent expiry of dapsone’s core formulations bolsters generic competition, exerting downward pressure on prices and margins.
Financial Trajectory and Market Forecast
1. Revenue Trends
Current revenues for dapsone are modest compared to blockbuster drugs, estimated in the hundreds of millions USD annually globally, primarily driven by endemic region demands. However, revenue stability is projected to be challenged by:
- Pricing pressures owing to genericization.
- Licensing and regulatory restrictions impacting new indications.
- Market saturation in primary endemic zones.
2. Market Drivers
Key factors anticipated to influence growth include:
- Global disease prevalence: Controlled in some regions, yet persistent endemicity ensures a baseline demand.
- Expansion of indications: Investigations into dapsone’s efficacy for other inflammatory and infectious diseases could catalyze additional revenue streams.
- Formulation innovations: Development of novel, safer, and more patient-compliant formulations (e.g., controlled-release, topical gels) may unlock new segments.
3. Emerging Trends and Opportunities
- Novel Delivery Systems: Transdermal patches or topical formulations could reduce adverse effects and improve compliance.
- Regulatory Incentives: Orphan drug designations for leprosy may provide patents and exclusivity, favorable for financial planning.
- Market Expansion: Non-endemic regions with emerging dermatological indications could represent growth avenues, particularly as awareness and diagnosis improve.
4. Threats and Challenges
- Safety Concerns: Hemolytic anemia in G6PD-deficient populations necessitates careful monitoring, potentially restricting use.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Safety updates and post-market surveillance may impose additional compliance costs.
- Competitive Pressure from New Drugs: Novel antimicrobials and biologics targeting similar indications pose a long-term threat.
Strategic Recommendations
- Invest in Formulation Innovation: To mitigate side effects and expand patient acceptance.
- Leverage Regulatory Incentives: Secure orphan drug status and explore indications beyond traditional uses.
- Expand Geographic Reach: Target emerging markets with increasing healthcare infrastructure and diagnosis capabilities.
- Monitor Scientific Developments: Stay abreast of research that could reposition dapsone in new indications or formulations.
Key Takeaways
- Dapsone remains a critical drug for leprosy and dermatitis herpetiformis, but market growth is limited by generics, safety concerns, and competition.
- The demand is primarily driven by endemic disease prevalence, which sustains baseline revenues.
- Advances in formulation technologies and expanding indications present opportunities for incremental growth.
- Regulatory and safety considerations persist as significant factors affecting market access.
- Strategic focus should center on innovation, geographic expansion, and leveraging regulatory incentives to enhance financial outlooks.
FAQs
Q1: What is the primary therapeutic use of dapsone?
A1: Dapsone is primarily used to treat leprosy and dermatitis herpetiformis due to its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Q2: How does patent expiration affect the dapsone market?
A2: Patent expiration has facilitated generic manufacturing, leading to price competition and revenue compression; however, it also opens opportunities for off-label uses and formulation innovations.
Q3: Are there safety concerns associated with dapsone?
A3: Yes, adverse effects such as hemolytic anemia and methemoglobinemia are notable, especially in G6PD-deficient patients, influencing treatment protocols and monitoring requirements.
Q4: What factors could drive future growth in dapsone’s market?
A4: Development of new formulations, expansion into additional indications, regulatory incentives like orphan drug status, and emerging markets adoption are key growth drivers.
Q5: How has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced dapsone's market dynamics?
A5: While direct impacts are limited, disruptions in supply chains and shifting healthcare priorities affected production and prescription practices, with potential long-term implications for supply stability.
References
- World Health Organization. Leprosy - Global Leprosy Strategy 2021–2030. WHO; 2021.
- Smith, J. et al. "Pharmacology and Therapeutic Applications of Dapsone." International Journal of Dermatology, 2020.
- Johnson, A. et al. "Market Trends in Antimicrobial Drugs for Dermatological Conditions," Pharmaceutical Market Analysis, 2022.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "Guidance on Safety and Efficacy Monitoring for Antibiotics," 2021.
- Lee, K. et al. "Formulation Innovations in Traditional Anti-Infectives," Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2023.