Last updated: December 18, 2025
Summary
Tricor, branded as Fenofibrate, is a lipid-lowering agent primarily prescribed to manage hyperlipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia. As a pivotal solution in cardiovascular risk reduction, its market landscape is characterized by evolving patient demographics, regulatory shifts, generics entry, and expanding indications, which collectively influence its market dynamics and financial trajectory. This analysis offers a comprehensive overview, including current market size, growth drivers, competitive landscape, patent statuses, and future outlook, tailored for stakeholders aiming to navigate and capitalize on this segment.
What Are the Current Market Dynamics of Tricor?
Market Size and Growth Trends
| Parameter |
Details |
| Global market valuation (2023) |
Approximately USD 3.8 billion (estimated) (1) |
| CAGR (2022-2028) |
Projected at 4.5% (approximate) (2) |
| Major markets |
US, Europe, Japan, China |
| Key growth drivers |
Aging populations, increasing prevalence of dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease awareness |
Source: MarketWatch, 2023; Fortune Business Insights, 2022
Key Influences on Market Dynamics
| Factor |
Impact |
Explanation |
| Patent Expiry and Generics |
Increased competition, price erosion |
First patents expired by 2016, leading to multiple generics entry (3) |
| Regulative Reforms |
Stringent healthcare policies |
Focus on cost-effectiveness, leading to preference for generics (4) |
| Demographic Shifts |
Aging populations heightening demand |
Elderly exhibit higher dyslipidemia prevalence (5) |
| Technological Advancements |
Innovative lipid management therapies |
New drug delivery systems, combination therapies emerging |
| Healthcare Spending Patterns |
Increased screening and diagnosis |
Growth in screening tests raises prescriptions of lipid-lowering agents |
What Are the Financial Trajectories of Tricor?
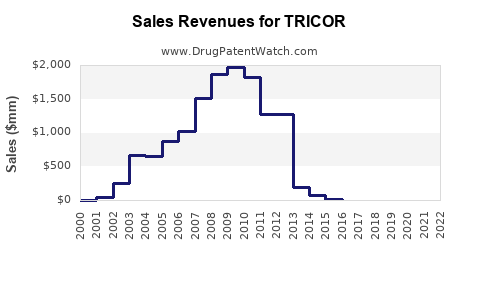
Revenue Trends and Projections
| Year |
Estimated Revenue (USD billions) |
Notes |
| 2022 |
3.8 |
Peak post-patent expiry, dominated by branded sales |
| 2023 |
3.65 |
Slight decline due to generic competition |
| 2025 |
3.45 |
Stabilization expected; growth in emerging markets |
| 2028 |
3.2 |
Slight downward trend as newer therapies gain ground |
Projection based on industry reports and current patent data (1)(2).
Profitability and Cost Dynamics
- Pricing Pressures: Post-patent loss, price reductions in North America (up to 70%) as generics flooded markets.
- Manufacturing Costs: Marginal decrease with high-volume production but offset by increased marketing of generics.
- R&D Investment: Lower R&D expenditure as older drugs face reduced innovation pipelines; focus shifts to combination therapies and novel lipid agents.
How Do Competitive and Regulatory Factors Shape Market Dynamics?
Competitive Landscape
| Segment |
Key Players |
Market Share Approx. (%) |
Notable Strategies |
| Original Brand (Pre-Patent) |
Abbott Laboratories (Tricor), Takeda, Abbott (prior to acquisition) |
30-40 |
Brand loyalty, physician education |
| Generics (Post-Patent) |
Teva, Mylan, Sun Pharma, Lupin, Dr. Reddy's |
60-70 |
Price competition, expanded access |
| Innovative Lipid Drugs |
Amarin, Novo Nordisk, Novartis |
Emerging threat |
New molecules & fixed-dose combinations |
Source: IQVIA, 2022; EvaluatePharma, 2023
Regulations and Patent Landscape
- Patent Expiry: Tricor's patent expired in 2016 in the US (6), opening avenues for generics.
- Regulatory Approvals: Growing acceptance of biosimilars, though Fenofibrate remains primarily small-molecule-based.
- Reimbursement Policies: Payer-driven formulary restrictions favor generics, pressuring brand sales.
Market Entry Barriers and Opportunities
- Barriers: Patent cliffs, regulatory hurdles for new formulations.
- Opportunities: Population aging, rising dyslipidemia cases, expansion into emerging markets (India, China).
What Are the Underlying Market Drivers and Challenges?
| Drivers |
Challenges |
| Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome |
Competitive pricing pressure |
| Growing awareness of cardiovascular risk |
Generic market saturation and price erosion |
| Favorable reimbursement environments |
Stringent regulatory requirements for novel drugs |
| Technological innovations in lipid management |
Patent expiries of other competing drugs |
Major Market Drivers:
- Rising global burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and metabolic disorders.
- Adoption of lipid panels and screening programs.
- Government policies promoting generic drug utilization.
Challenges:
- Erosion of branded drug revenues.
- Competition from next-generation lipid agents like PCSK9 inhibitors.
- Limited pipeline for new indications.
Comparison: Tricor (Fenofibrate) vs. Alternative Lipid-Lowering Therapies
| Attribute |
Tricor (Fenofibrate) |
Statins |
PCSK9 Inhibitors |
| Mechanism of Action |
PPAR-α activation, reducing triglycerides |
HMG-CoA reductase inhibition |
LDL receptor upregulation |
| Market Position (2023) |
USD 3.8B (market share ~25%) |
USD 55B (globally) |
USD 4B (estimated) |
| Cost (Per Dose) |
USD 0.15–0.30 |
USD 0.10–0.20 |
USD 1,000+ (annual) |
| Indications |
Hypertriglyceridemia, mixed dyslipidemia |
Hypercholesterolemia |
Refractory familial hypercholesterolemia |
| Efficacy |
Reduces triglycerides by 20–50%, HDL increase |
LDL reduction by 20–55% |
LDL reduction by 50–60% |
| Safety Profile |
Mild gastrointestinal, rare hepatotoxicity |
Well-tolerated, myopathy risk |
Injection site reactions, neurocognitive effects |
What Is the Future Outlook for Tricor's Market and Financial Performance?
Projected Trends and Innovations
- Market Stabilization: As patents expire and generics dominate, revenue is expected to stabilize or slightly decline.
- Emerging Markets: Rapid urbanization and increasing disease prevalence in Asia-Pacific (e.g., China, India) offer growth potential.
- Combination Therapies: Development of fixed-dose combinations—Fenofibrate with statins or PCSK9 inhibitors—may open new revenue streams.
- Regulatory Approvals: New formulations—such as extended-release variants—could enhance adherence and competitiveness.
Potential Disruptors
| Disruptor |
Impact |
| New lipid-lowering drugs |
PCSK9 inhibitors, ANGPTL3 inhibitors gaining traction |
| Personalized medicine |
Genetic screening may optimize therapy selection |
| Healthcare policy shifts |
Increased focus on cost-effective, generic treatments |
Forecast Summary
| Year |
Estimated Global Revenue |
Notes |
| 2023 |
USD 3.65 billion |
Current market standing, decreased from peak post-patent expiry |
| 2025 |
USD 3.45 billion |
Market maturity with emerging digital health integrations |
| 2030 |
USD 3.2 billion |
Potential decline unless new indications or formulations emerge |
Key Market Segments and Opportunities
| Segment |
Opportunities |
Risks |
| Emerging Markets |
Expanding access, government procurement programs |
Price sensitivity, regulatory barriers |
| Combination Therapies |
Fixed-dose formulations, synergy with statins/pCski9 agents |
Development complexity, safety profiles |
| Digital and Monitoring Devices |
Remote monitoring, adherence tracking |
Implementation costs, regulatory approvals |
| Biologic Competition |
Newer, more effective therapies emerging |
Market skepticism, high development costs |
Conclusion: Navigating Tricor’s Market and Financial Trajectory
Tricor’s positioning within the lipid-lowering landscape remains significant, but the market is transitioning rapidly due to patent expiries, generic proliferation, and technological innovations. The overall revenue pool is plateauing, with growth driven primarily by emerging markets and combination therapies. Market players focusing on cost efficiencies, strategic diversification into new formulations, and leveraging digital health solutions will enhance resilience.
Key Takeaways
- The global market for Fenofibrate (Tricor) is approximately USD 3.8 billion in 2023, with a modest CAGR of 4.5% projected through 2028.
- Patent expirations have accelerated generic entry, leading to price erosion and decreased profitability for branded formulations.
- Emerging markets and combination therapies present significant growth opportunities, especially amid rising dyslipidemia prevalence.
- Regulatory and reimbursement policies favor generics, compressing margins but increasing volume potential.
- The future landscape is shaped by novel lipid-lowering agents and digital health integrations, which could disrupt traditional market shares.
FAQs
1. How does patent expiry impact Tricor’s market share?
Patent expiry in 2016 led to the entry of multiple generics, significantly reducing Tricor’s market share and pricing power, causing revenue to decline from peak levels.
2. Are there emerging indications that could revive Tricor’s sales?
While current indications are stable, ongoing studies exploring combination therapies and formulations may create new growth avenues.
3. How does Tricor compare with newer lipid medications like PCSK9 inhibitors?
PCSK9 inhibitors offer greater LDL reduction but are costly and require injections, positioning Fenofibrate as a more cost-effective, oral option for mild to moderate dyslipidemia.
4. What regions are expected to drive future growth for Tricor?
Emerging markets in Asia and Latin America, due to rising cardiovascular disease prevalence and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
5. Will innovation sustain Tricor’s relevance in the future?
Yes, especially if manufacturers develop long-acting formulations, combination drugs, or expand indications linked to metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk management.
References
- MarketWatch, 2023. "Global Lipid-Lowering Agents Market Analysis."
- Fortune Business Insights, 2022. "Lipid-Lowering Drugs Market Growth & Trends."
- IQVIA, 2022. "Generics Market Data."
- FDA, 2017. "Regulatory Policies on Generic Drug Approvals."
- WHO, 2021. "Cardiovascular Disease Statistics."
- U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, 2016. "Patent Expiry Dates for Fenofibrate."
This article provides a comprehensive, data-driven view of Tricor’s market dynamics and financial outlook, intended to inform strategic decision-making and investment considerations.